CONFIDENCE.NORM function - The function returns the confidence interval of the population by using a normalized distribution in Excel
The following article introduces you to CONFIDENCE.NORM - one of the functions in the group of statistical functions that is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function returns the confidence interval for the population by using normalized distributions. Support functions from Excel 2010 onwards.
Syntax: CONFIDENCE.NORM (alpha, standard_dev, size)
Inside:
- alpha: The critical level to calculate the confidence level, with confidence level = 100 * (1- alpha) , is the required parameter .
- standard_dev: The overall standard deviation for the data range, and considered to have been determined, is the required parameter.
- size: Sample size , is a required parameter.
Attention:
- If any of the parameters' values are not numeric -> the function returns the #VALUE! Error value .
- If alpha ≤ 0 or alpha ≥ 1 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- If standard_dev ≤ 0 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- If size is not an integer -> it is truncated to an integer.
- If size ≤ 1 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- If deg_freedom <1 or deg_freedom> 10 ^ 10 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- Assuming alpha = 0.5 -> confidence interval is:
[overline chi pm 1.96left ({frac {sigma} {{sqrt n}}} right)]
For example:
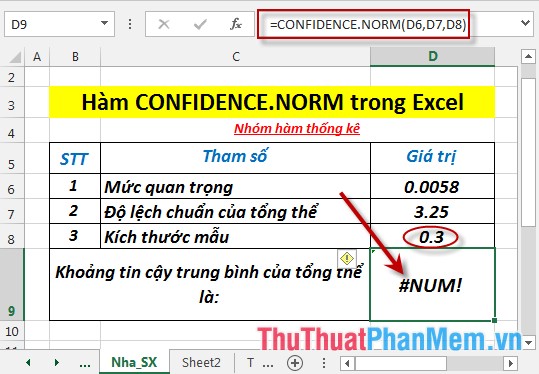
Calculate the average overall confidence interval with the data in the table below:
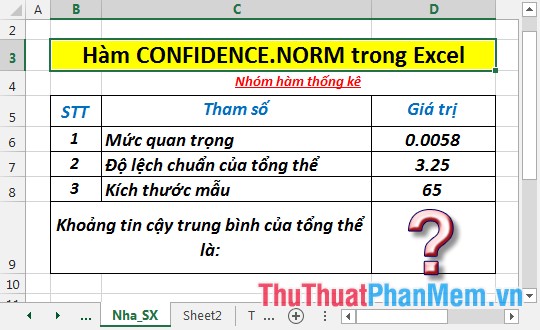
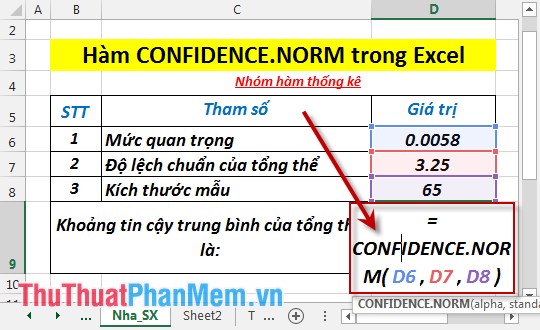
- In the cell to calculate, enter the formula: = CONFIDENCE.NORM (D6, D7, D8)
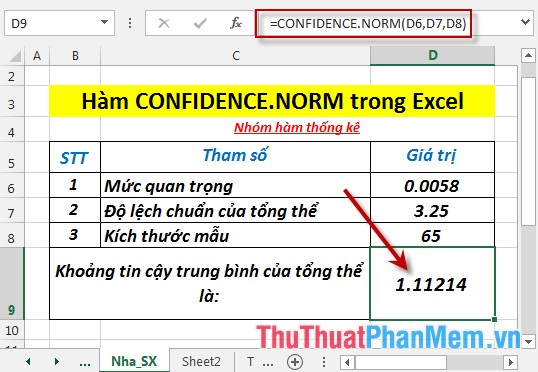
- Press Enter -> the overall confidence interval for the population is:
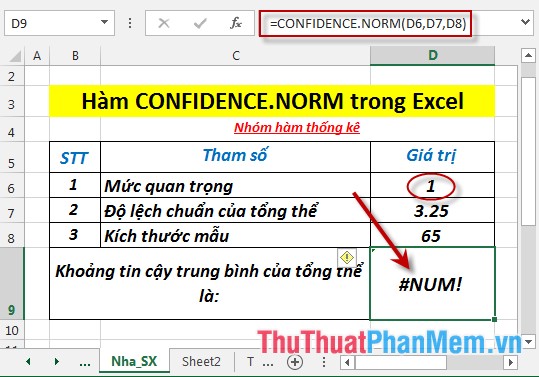
- Where alpha ≤ 0 or alpha ≥ 1 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- Where size ≤ 1 -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
Above are instructions and some specific examples when using the CONFIDENCE.NORM function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ NORM.S.INV function - The function returns the inverse of the normalized distribution with an average value of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 in Excel
- ★ GUSSE function - The function returns the probability that an element of the population is normalized in Excel
- ★ NORM.INV function - The function returns the inverse of the standard cumulative distribution in Excel
- ★ NORM.DIST function - The function returns the normal distribution with the standard deviation and the mean value specified in Excel
- ★ STANDARDIZE function - The function returns the normalized value from a specific distribution in Excel