The WORKDAY.INTL function - The function returns a date before or after the date starting with a custom weekend in Excel
The following article introduces you to the WORKDAY.INTL function - one of the functions in the date and time group function is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function returns a date before or after the start of a specified number of working days with a custom weekend. The weekend parameter indicates which day and how many days.
Syntax: WORKDAY (start_date, days, [weekend], [holidays])
Inside:
- start_date: The start date, is a required parameter.
- days: A day not in the weekend and holidays before or after start_date, is a required parameter.
+ days> 0 -> number of days generated in the future.
+ days <0 -> number of days created in the past.
- weekend: Indicates which days are weekends not included in the working day, are optional parameters with the following values:
+ weekend = 1 -> The weekend is Saturday and Sunday.
+ weekend = 2 -> The weekend is Sunday, Monday.
+ weekend = 3 -> Weekends are Monday and Tuesday.
+ weekend = 4 -> Weekends are Tuesday and Wednesday.
+ weekend = 5 -> Weekends are Wednesdays and Thursdays.
+ weekend = 6 -> Weekends are Thursday and Friday.
+ weekend = 7 -> Weekends are Friday and Saturday.
+ weekend = 11 -> Weekends are only Sunday.
+ weekend = 12 -> Weekends are only Monday.
+ weekend = 13 -> Weekends are only Tuesday.
+ weekend = 14 -> Weekends are only Wednesday.
+ weekend = 15 -> Weekends are only Thursday.
+ weekend = 16 -> Weekends are only Friday.
+ weekend = 17 -> Weekends only Saturday.
- holidays: Days to be excluded from working days which are not on public holidays.
Attention:
- Excel stores dates as sequential serial numbers to facilitate the calculation process.
- Any one of the arguments is invalid -> the function returns the #VALUE! Error value
- If start_date + days value creates an invalid date -> the function returns the #NUM! Error value
- If days is a decimal, it is truncated to an integer.
For example:
Calculate the day after the working day a certain number of days, weekends are defined by the values in the weekend column of the following jobs:
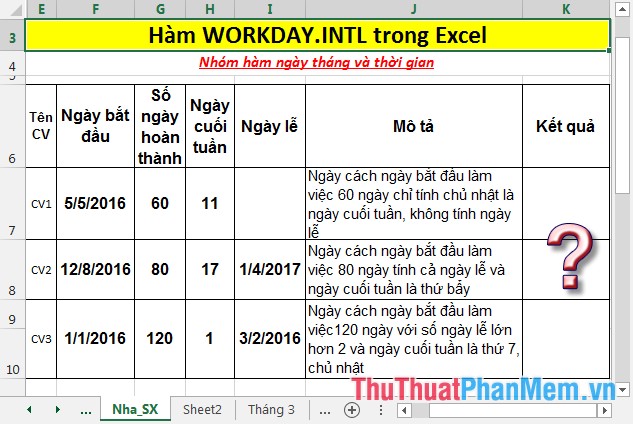
- In the cell to calculate, enter the formula: = WORKDAY.INTL (F7, G7, H7, I7).
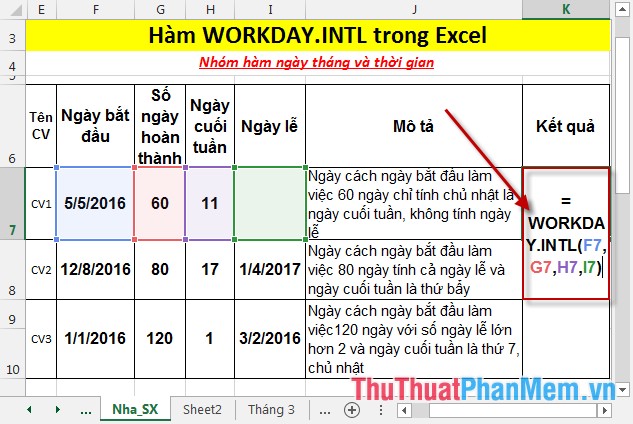
- Press Enter -> return value is:
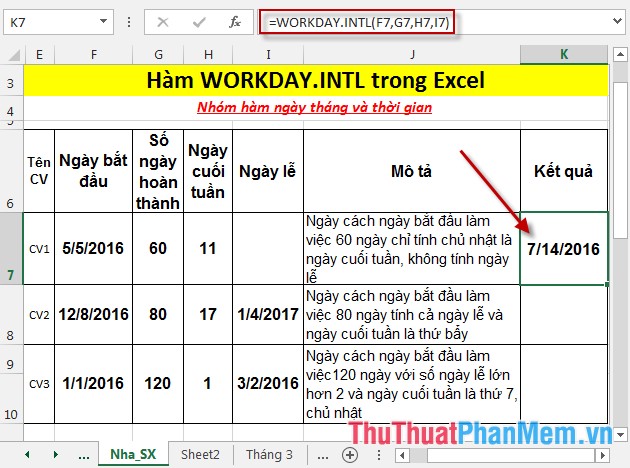
- Similarly copying the formula for the remaining value results:
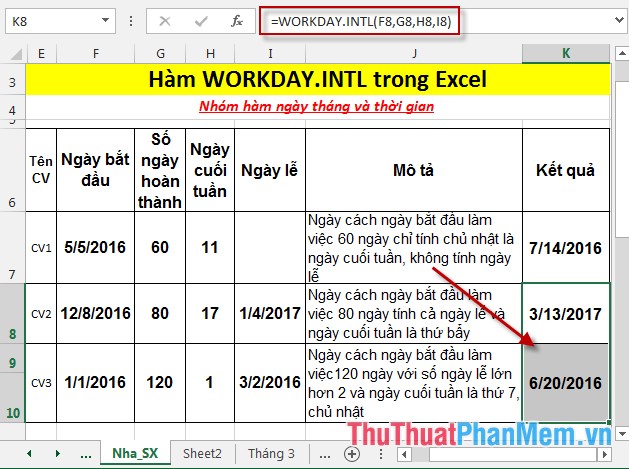
Above are instructions and some specific examples when using the WORKDAY.INTL function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ DATE function - The date function in Excel
- ★ DAY function - The function returns the date value of a specific date in Excel
- ★ NOW function - The function returns the current date and time in Excel
- ★ NETWORKDAYS.INTL function - The function returns the number of whole working days between 2 dates, specifying weekends in Excel
- ★ COUPNCD - The function returns the next coupon date in Excel