Analysis of disaster recovery perspective and high availability of Exchange Server
Dr. Vas Srinivasan and Bilal Ahmed
Email today is very popular and has become a standard tool for communication in many businesses, large and small. Microsoft is a software company that has a dominant role in the mail market through its Exchange Server products. Businesses choose Exchange's reliability, scalability, performance, and the combination of rich client features such as Microsoft Outlook, Outlook Web Access, and associated collaboration services. for workflows as well as other applications.
Email is becoming an increasingly important application in most businesses and always faces challenges in recovering and backing up information in it. If a problem occurs and if the data is not restored, it can have serious consequences for businesses. Therefore, backing up and restoring data efficiently for companies is an important issue as well as protecting them from major losses in production as well as downtime for troubleshooting.
High availability solutions for Exchange Server
Failover group (Failover Clustering)
Microsoft Clustering allows users to avoid hardware failures by adding redundant hardware, called nodes, through a central cluster manager to share the load and manipulate data. Typically, these nodes can share common storage space and are capable of separating the load from components that have hardware or software malfunctions. There are two types of cluster environments - active / active and active / passive. Previously each node in the environment was in an active state and capable of handling requests. When a node has problems, other nodes will handle additional requests to carry the load for this node. Later, there's an active button to handle all incoming requests. When the hardware or software in this active node has a problem, the passive button will automatically be included to take over the processing of the ongoing data requests. In this way, the hardware shortage in failover is mitigated through redundant hardware.
Microsoft Exchange Server supports both active-active and active-passive cluster environments. Exchange Server Clustering provides high availability by overcoming node errors. However, it does not prevent storage errors. With typical cluster environments, many hard drives are used to build a large storage array. In Network and System Administration, with a large number of devices being used, an incident is evident. When a hard drive fails, the application failure is unavoidable, because all the nodes in the cluster may be using a certain drive that allows sharing all the files in that has Exchange Server database files. Typically RAID configurations protect this case, but in many cases, with a high performance perspective, this will significantly reduce I / O in small systems due to data logging. on multiple disks at the same time. Administrators must balance that performance and understand that this implementation has many limitations. Here RAID's solution is to protect against hard disk errors but not to prevent site disasters.
In contrast to the dependence on this storage, the use of other replication methods can overcome the storage and hardware failures and software. Failover servers are located in a single physical location, Exchange Servers are used as a shield for any type of error that occurs.
Exchange Server Clustering environments are almost costly compared to Standby. The main reason for this high cost is its hardware and software requirements. Clustering requires Windows NT Enterprise Edition, Windows 2000 Advanced Server or Windows 2003 Enterprise Edition and Exchange Server Enterprise Edition. In addition, it only supports hardware listed in the list of appropriate Microsoft hardware. In other words, Standby or Failover servers do not have special hardware requirements and simplify software solutions for disaster recovery needs. As an additional cost, LAN connectivity is required between Exchange Server cluster nodes to send and receive synchronization signals and other communication types. This signal is used by nodes to determine if other nodes are available. In case a node is not available, the remaining nodes will take over. With Standby, a LAN or WAN connection will work to replicate Exchange Server mailboxes. The speed of this process is directly related to the size of the mailbox and the bandwidth of the network.
Copy of file level or block level (Block)
Different types of replication techniques can be used to create copies of data between two servers both locally and remotely. With block level, replication is done by storage controllers or by mirroring the software. With the file system level (copy of file system changes), the host software performs replication. In both replication levels, any type of application is performed. They are completely impossible for the application, but some firms have solutions for a number of specific application types. Some disadvantages are:
Typically, the same software / hardware is required in both production and replication of servers
Ability to spread viruses and errors from production servers to replica servers.
High availability features of Exchange 2007
Exchange Server 2007 includes four features that provide high availability for that Mailbox server: Local Continuous Replication (LCR), Cluster Continuous Replication (CCR), Single Copy Clusters (SCC) and Standby Continuous Replication (SCR).
• Local Continuous Replication (LCR) : LCR is a single server solution that uses asynchronous log transfer technology for the purpose of creating and maintaining copies, or copies of data groups on a set of secondary disks connect to the server with the production storage group. LCR allows the transfer of logs, relay logs and quick manual conversion to secondary data copy.
• Cluster Continuous Replication (CCR) : CCR is a group solution that uses asynchronous log transfer technology to create and maintain a group copy stored on a secondary server. CCR is designed to choose one of two data center solutions, providing both availability and site resilience.
• Single Copy Clusters (SCC) : SCC is a group solution that uses one copy of a storage group shared among nodes in a cluster. SCC is very similar to grouping in previous versions of Exchange Server, but there are significant changes and improvements.
• Standby Continuous Replication (SCR) : SCR is designed for scenarios that use or activate using standby recovery servers. SCR allows separation of high availability and site resilience. It can be combined with CCR to replicate internal storage groups (using CCR for high availability) and remote in secondary sites (using CCR for site resilience).
These highly available features provide good functionality but require users to master the knowledge of using Exchange Server. Here are some of the constraints that users will encounter when executing a high availability of Exchange 2007 features.
- Exchange Server 2007 runs the 64-bit computer name and therefore costs more
- For best performance, you should run Active Directory Domain Controllers on 64-bit computers, but it's not mandatory.
- Not supported for Exchange 2000 and Exchange 2003.
- The replica server is in passive and inaccessible mode for reporting, checking and storage purposes.
- Cannot create copies for all storage groups at the same time
- You must store the mailbox in the Storage Group, otherwise Exchange 2007 Replication will not work.
Method of creating a mailbox copy
In this method, replication is done at the mailbox level and it is very special. You can pick and choose the mailboxes that need to be replicated. You can also set up an administrative, sales and IT user plan, in which case the copy appears more often to store Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO ) necessary. For others in the company, you can set up other plans that do not need regular time to create copies.
The advantage of this method is that the replication and failover servers are in active mode (Active). Failover server can be accessed for reporting and inspection purposes. With other replication methods, the failover server is in passive mode and cannot be used for maintenance, inspection, and reporting purposes.
Backup and make copies
Some solutions provide both backup and replication issues as part of a solution. In this case, the backup is integrated with replication and the user gets a 2-in-1 solution. Considering the two-layer architecture, these solutions include an application and an agent environment. The application server also allows network sharing to store all backup files. Files are stored on the shared network and not on any target server to avoid the loss of backup files. If the target server has a problem, users will continue to access their backup files to rebuild the target server with as little downtime as possible.
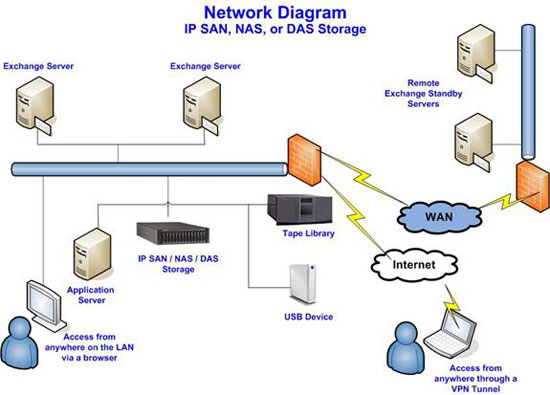
Figure 1
The mailboxes will be returned to the backup server and then replicated to the remote failover server. Full backup and backup is done first, then changes will be applied. With the recovery of emails and mailboxes, internal backup data can be used while disaster recovery will be a failover server.
Failover / Failback (failover capability)
When a disaster strikes the main site, all users will not be able to use the site remotely. When the main problem is rebuilding, you must perform the failback process. There is only one way to make sure it is tested periodically. However, to do that, you need to failover the entire Exchange server. With the mailbox replication method, it is possible to create a test mailbox and use it for failover / failback periodic testing.
Conclude
Companies will be adversely affected if significant loss of productivity and profitability is experienced if the Exchange server crashes. By increasing the reliability of the business to the Exchange server, customers will need instantaneous failover capabilities to local or remote servers. This concept means the survival of the business in case of trouble. Therefore, the high availability and disaster recovery of Exchange Server needs to be properly considered for companies to implement appropriate solutions to protect them.
You should read it
- ★ Installing, configuring and testing Exchange 2007 CCR on Mailbox Server (Part 1)
- ★ Introducing Exchange Server 2019, how to install Exchange Server 2019
- ★ Transfer from Linux Mail Server to Exchange Server 2007 (Part 1)
- ★ Backup for Exchange Server with DPM 2007 - Part 3: Backup process
- ★ Discover EMC in Exchange Server 2010 (Part 2)