Exchange 2007 Availability Services
When I think of the Client Access Server role in Exchange 2007 I immediately think of Outlook Web Access, Outlook Anywhere, ActiveSync and other non-MAPI forms in connection with mailbox servers. In addition, Client Access Server also contains other important services such as Autodiscover and Availability services. There are a number of critical services in the Exchange 2007 infrastructure and in this tutorial we will introduce you to more details about the Availability service and what the main role of this service is.
What is Availability service?
The availability service in Exchange 2007 relates in large part to how this user accesses busy / free information of other users. Before going into detailed instructions for this service, we need to review how these free / busy information is stored and accessed in Exchange 2000 and Exchange 2003, so that it can be compared. about the process of working with older versions with new improvements in Exchange 2007. In older versions of Exchange, a site directory exists by Schedule + Free / Busy names, the name used to store information. Busy / free schedule for each user. You can view this folder in Exchange System Manager by looking at the system directory instead of the public folders. Figure 1 shows an example of Schedule + Free / Busy system directories that are observed in Exchange System Manager.

Figure 1: Schedule + Free / Busy system folder
One thing to keep in mind is that there are two system folders, one of which is for the administrator group. By default, Outlook periodically publishes the free / busy schedule information in the system directory to allow other users' Outlook clients to query the data when they want to set the appointment time. On smaller systems this is a very good thing, although on large systems, the use of public folders such as a busy / free storage device can cause some problems. For example, there may always be a lack of free / busy information that should have been updated regularly, this problem is due to the slow retention of the public folder copy, in the worst case the copy failure. Public folders can cause serious problems. However, the main problem with this method is the future of public folders in Exchange. Over the past few years, you may have heard or read about Microsoft 's plans to' retire 'these public folders in the future version of Exchange, and so a new mechanism needs to be Yes to manage busy / free requests. That is why the Exchange Availability service is born.
Better method
The Availability service in Exchange 2007 is one of the new Web services. In short, Exchange 2007 Web services allow applications to access mailbox content via HTTP, so it is clear that application development is targeted at these services for production. 2007 product. We will discuss in more detail, busy / free information for each user configured on Exchange 2007 will now be stored directly in the mailbox, so access to this information can done through Web services, especially the Availability service. We will look at this new method through Outlook 2007 and Exchange 2007, so there will always be things that are not done through this new method if Outlook 2003 and Exchange 2003 are still mixed. Outlook 2007 places the Availability service through the Autodiscover service.
This article will not focus specifically on Autodiscover because this is a great topic. The Autodiscover service allows Outlook 2007 clients to access specific Exchange 2007 features like the Availability service we mentioned earlier, plus other general services such as the Offline Address Book (OAB) as well as services like Unified Messaging (UM). Essentially Outlook 2007 creates a request for a virtual directory called Autodiscover that is displayed on the Client Access Server. This Autodiscover service returns a lot of different information to the client, one of which is the URL for the service as Availability.
Version issues
Different access methods to get free / busy information are used in environments with Outlook 2003 and Outlook 2007 as well as Exchange 2003 and Exchange 2007. For example, when Outlook 2007 is used in conjunction with Exchange 2007 then This information can be obtained directly from the target mailbox of Exchange 2007 and not the Schedule + Free / Busy system directory. This is how free busy information can be upgraded better than the traditional traditional directory method. See Figure 2 below, an Outlook 2007 user with an Exchange 2007 mailbox requesting free / busy information for other Exchange 2007 users. In this case, the connection from Outlook is performed with the Availability service running on the Client Access Server, which will identify which mailbox server configures the target Exchange 2007 mailbox. A Remote Procedure Call (RPC) connection will be created for that mailbox server and the results will return to the Client Access Server before being transferred back to the user.
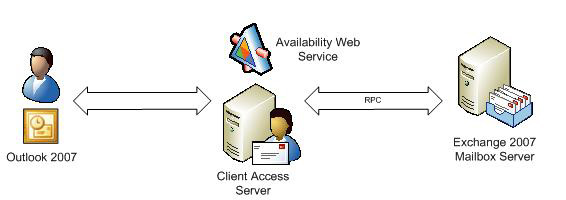
Figure 2: Outlook 2007 users are querying Exchange 2007 Free / Busy information
Figure 2 above assumes that the Client Access Server and mailbox server are all in the same Active Directory. So what happens if the free / busy request is made to the user whose mailbox resides on an Exchange 2007 mailbox server of another Active Directory? In this case, the Client Access Server in Active Directory of the user who initiated the request will authorize the request to a Client Access Server located in Active Directory of the target user. The results are returned to the original Client Access Server and then returned to the requested user.
There is another important scenario that we should consider here. What if the free / busy request was made to another mailbox at the same time, but that mailbox is still on an Exchange 2003 server? This situation will be very common during the transition from Exchange 2003 to Exchange 2007. In such a case, free / busy information for Exchange 2003 users is stored in the Schedule + Free / Busy system folder as what We already know in the first part of this article. Therefore, the Availability service must obtain the appropriate information from this directory and it does this by creating HTTP requests to the / Public virtual directory on the target Exchange 2003 mailbox server. This process is described in Figure 3. When this information has been called from Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2003 servers, the Availability service will combine these results and return them to Outlook 2007 users.
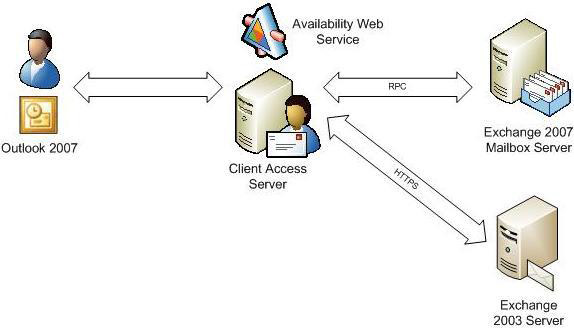
Figure 3: Outlook 2007 users are querying Free / Busy information on Exchange 2003 and Exchange 2007
Now that we have seen what happens when a user is using Outlook 2007. So when the user runs Outlook 2003 but has connected to an Exchange 2007 mailbox, what happens? In this case, you don't have to worry about the target mailbox located on Exchange 2003 or Exchange 2007 because the Outlook 2003 client will try to retrieve free / busy information from the Schedule + Free / Busy system folder. The reason for this is simply that Outlook 2003 always wants to publish this free / busy information here and therefore knows nothing about the Availability service. This is also a solution for earlier versions of Outlook, such as Outlook 2002 or Outlook 2000.
So far we've only listed Outlook as a client type in use. However, the principles are the same if you use Outlook Web Access. In other words, if your target mailbox is on Exchange 2007, the Availability service will create an RPC connection to that mailbox server. If the target mailbox is on Exchange 2003, the Availability service will create HTTP calls and retrieve information from the Schedule + Free / Busy system directory.
Conclude
The Availability service in Exchange 2007 is an important service in practice, it is responsible for collecting updates about the busy / free status of users, and allowing them to run over Outlook. 2007 and Exchange 2007. In this tutorial, I have introduced you to this service and how to use it to get this information.
 Additions for Exchange Server 2007 - Part 3: Email client access protection
Additions for Exchange Server 2007 - Part 3: Email client access protection Backup for Exchange Server with DPM 2007 (Part 1)
Backup for Exchange Server with DPM 2007 (Part 1) Statistics mailbox in Exchange 2007
Statistics mailbox in Exchange 2007 Installing, configuring and testing Exchange 2007 CCR on Mailbox Server (Part 1)
Installing, configuring and testing Exchange 2007 CCR on Mailbox Server (Part 1) Installing, configuring, and testing Exchange 2007 CCR on Mailbox Server (Part 2)
Installing, configuring, and testing Exchange 2007 CCR on Mailbox Server (Part 2) Transfer from Linux Mail Server to Exchange Server 2007 (Part 1)
Transfer from Linux Mail Server to Exchange Server 2007 (Part 1)