User administration in Exchange 2007 using Powershell
Markus Klein
Microsoft's Exchange Server 2007 owns an Exchange Powershell administration interface. Most administrative tasks can now be done using Powershell commands, even GUI can create Powershell commands from the GUI interface.
We will start with the article by introducing you to this useful tool and starting a series of closer considerations in some of the task implementations. We will look at how to administer Exchange Server 2007 from the command line utility. The first is to start the general administration tasks for an Exchange administrator who still performs during their daily work, through some examples of how they work.
Create new Mailboxes
Let's take a look at how to create new Mailboxes with Powershell CMDLet 'New-Mailbox'. The command syntax will be:
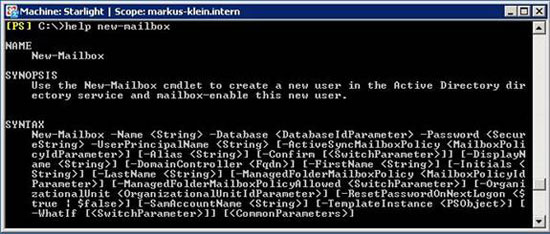
Figure 1: Syntax of the New-Mailbox command
As you can see in Figure 1 above, there are many properties that can be used here, but you do not need to use all of them, just some mandatory properties. This will help you simplify many problems.
The first example we will create an Active Directory User named 'John Doe' and the corresponding Mailbox for this user. The mailbox is located in First Storage Group, in the Mailbox Database database. The password is not specified so the Exchange Management Shell will ask for this issue. In addition, you also need to reboot when logging in the next time.

Figure 2: Create User with New-Mailbox Cmdlet
The next example will show how to create a user in Active Directory and resource Mailbox (Equipment Mailbox). The Mailbox resource is located in First Storage Group, in Mailbox Database. Password must be reset at the next login. Exchange Management Shell will remind you of the value of the original password because it was not specified.
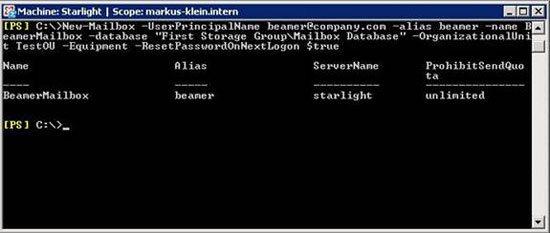
Figure 3: Creating an Equipment Mailbox using the New-Mailbox Cmdlet
Remove a Mailbox
Another interesting daily task is to remove a Mailbox. This operation is made easy and this is its syntax:
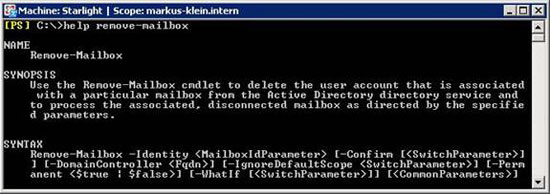
Figure 4: Syntax of the Remove-Mailbox Cmdlet
Let's take a look at how to disconnect a user's Mailbox from an account and remove it from Active Directory. Mailbox will remain in the Exchange database until the deleted Mailbox ownership cycle is configured for the Mailbox database.
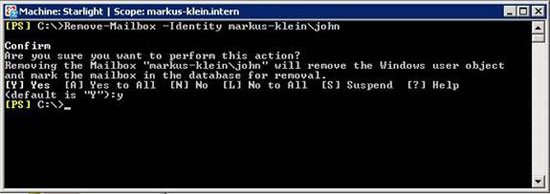
Figure 5: Disconnecting a Mailbox from a user account and removing it from Active Directory
Inside this example you will see that the problem is that there are some questions from the management utility in confirming the actions you are taking. Therefore, there is only a small risk in using this utility.
Change Mailbox settings
Let's consider a more complex CMDLet called 'Set-Mailbox'. This is the syntax of the command:
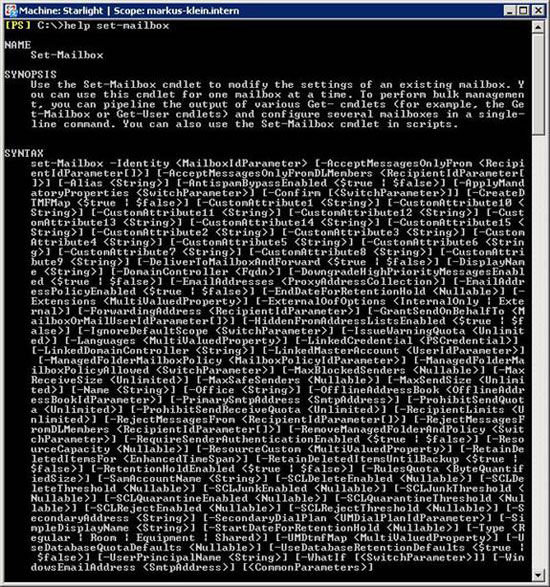
Figure 6: Syntax of the Set-Mailbox command
You may realize that this is a very powerful command and you can perform a lot of tasks through this syntax. It can be used for:
- Configure to accept mail only from a certain user.
- Configured to only send mails to certain recipients
- Link Mailboxes for each specific user
- Configure email addresses for users
- Set of ownership cycles
- And many other tasks
The first example we will look at how to forward John Does email messages to Mailbox by Jane Doe ( jane@markus-klein.intern ).
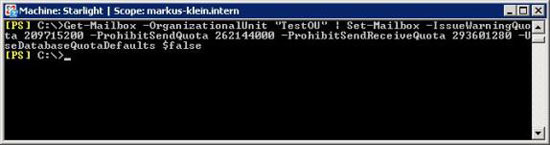
Figure 7: Forwarding configuration
Now we use the Get-Mailbox command to find Mailboxes in the TestOU, then use the Set-Mailbox command to configure these Mailboxes. Components like custom warning, prohibit send, prohibit send and receive limits are set to 200 MB, 250 MB, and 280 MB, respectively, respectively. The default limit of the Mailbox database is ignored. This command can be used to configure a set of Mailboxes with greater or smaller restrictions than the Mailboxes in the organization.
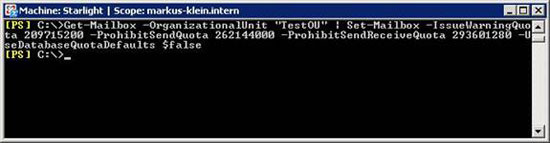
Figure 8: Configure Mailbox limits (1)
The third example uses the Get-User command to find all users in TestOU, then use the Set-Mailbox command to change the maximum size of outgoing messages up to 2MB.
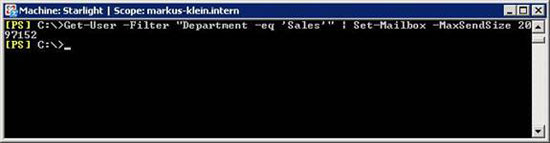
Figure 9: Configuring Mailbox limits (2)
Transfer Mailbox
Next we will look at how to transfer a Mailbox using the 'Move-Mailbox' command. The syntax of the command is:
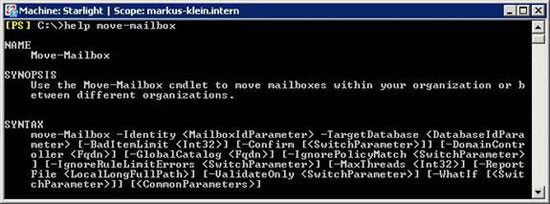
Figure 10: Syntax of the 'Move-Mailbox' command.
This is a very important command in the conversion process. You can configure the Mailbox transfer commands directly from the Powershell script. When you are migrating from Exchange Server 2000, there is no way to transfer Mailbox to Exchange Server 2007, because Exchange System Manager of Exchange Server 2000 does not support this operation as in Exchange Server 2003.
However, you will see in the following example the really interesting things for common administration tasks when moving Mailbox to another Mailbox database on the same server or other server simultaneously or in an Active Other forest directory.
We will use Move-Mailbox to move John Doe's Mailbox (john@markus-klein.intern) to a new Mailbox database called TestMBX, you will realize the difficulty of doing this task.
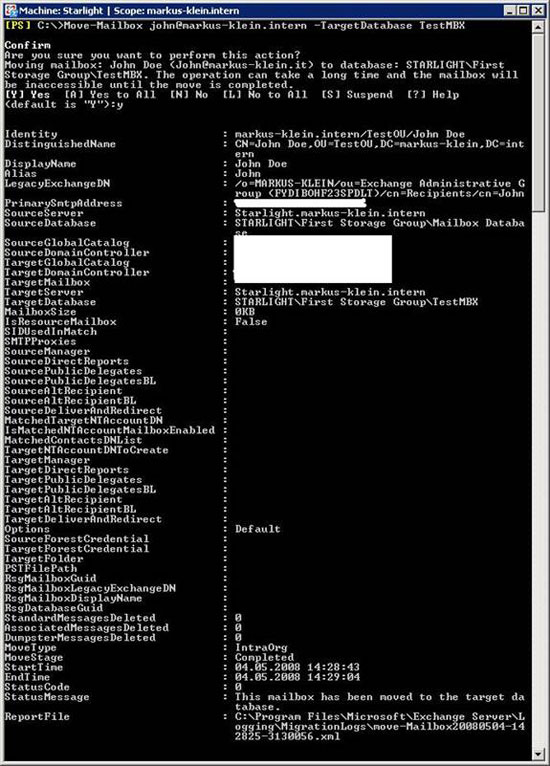
Figure 11: Transfer Mailbox to another Mailbox database
Displays the mailbox size of users
The final task of this article is to display the mailbox size of the user. The syntax is as follows:
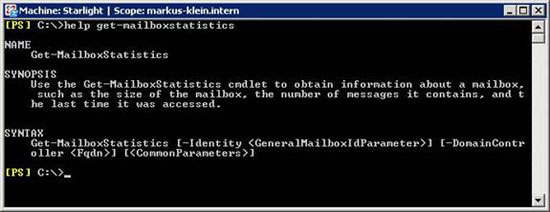
Figure 12: Syntax of the Get-MailboxStatistics command
First we will get Mailbox statistics for all Mailboxes on the internal server.
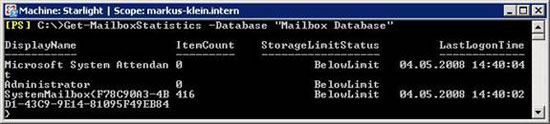
Figure 13: Retrieve all Mailbox information of a database
You can easily create statistics about Mailbox and save them as an Excel or HTML file. This approach makes it easy to distribute it to users by email or intranet
Conclude
As you can see from this article, administering Exchange Server 2007 is done quite easily using the Powershell CMDLet commands. They are quite simple and highly logical, so you will not have serious problems during use. If you don't know the syntax of each command (which is quite normal even for advisers or long-time admins), the help command will help you with how to use it.