How to configure VMware High Availability (VMHA)
David Davis
In this article, I will show you what VMware's High Availability solution is and how to configure it.
Introduce
We are not inclined to a virtualization solution or a solution but just introduce a product with great features when we have reviewed them. VMware ESX Server product suite and VMware Infrastructure have a lot of interesting features for other virtualization products. One of those features is VMware's High Availability feature, abbreviated as VMHA.
When a physical server encounters or loses all network connections it is also when VMHA plays an important role and can migrate virtual clients from the server that is 'off' to one another server is active. That way, virtual machines can be set up and run in a timely manner.
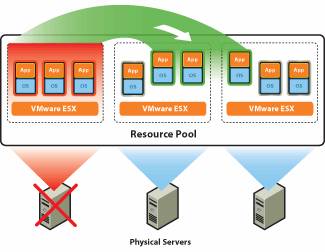
Figure 1: VMware High Availability (VMHA) - Image Courtesy of VMware.com
This is a very powerful feature because it means that any operating system or device is highly usable by using a combination within the VMware Infrastructure infrastructure.
However there are some requirements to do that and there are both good and bad qualities for VMHA. In this article we will cover all of those issues and show you how to configure VMHA.
What requirements make VMHA work?
There are several conditions to make VMHA work. those conditions are:
- VMware Infrastructure Suite Standard or Enterprise (can't be done with the free ESXi version or done with the VMware Foundations Suite).
- At least two ESX host systems must be present.
- A shared SAN or a NAS between ESX Servers servers, where virtual machines will be stored. Note that with VMHA, virtual disks for virtual machines (VMs) are implemented by VMHA. What happens when a host system encounters an error is that the ownership of the virtual machines will be transferred from an error host to a new host.
- CPU compatibility between hosts. The easiest way to test this compatibility issue is to use VMotion of a virtual machine from one server to another and see what happens. This is what shows incompatibility:
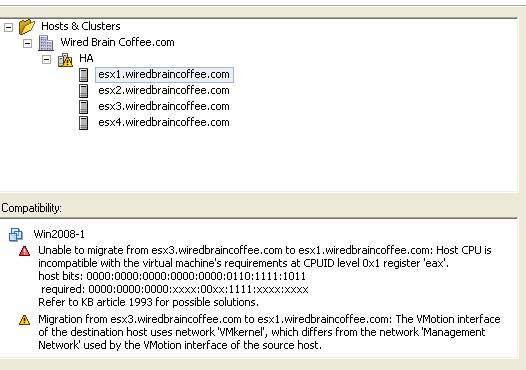
Figure 2: CPU incompatibility
If you cannot complete CPU compatibility between hosts in the HA resource system, you need to configure CPU Masking.
- Highly Recommended - to have VMware management network redundancy (at least two NICs related to VMware port used for VMotion and iSCSI). If you don't have this backup, you'll see:
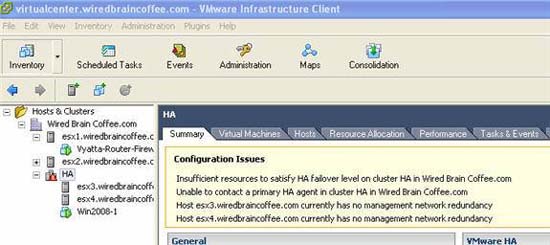
Figure 3: Configuration problems because there is no network management VMware redundancy
What's great about VMHA?
Here are some great features of VMHA:
- Provides high availability for all virtual machines at the lowest cost (compared to buying a HA solution).
- Jobs for any operating system running inside VMware ESX.
- VMHA is easy to configure. If you have the right device, registration and VMware Infrastructure already set up, you can configure VMHA quickly.
- Jobs with DRS (resource distribution kit) so that when virtual machines will be brought to other hosts in the resource system due to a host error, DRS will be used to determine where the download will be and that load balancing.
What still exists with VMHA?
As with any solution, there are a number of VMHA features that still exist. The remaining features of those issues are:
- CPUs on each host must be compatible or you must configure CPU masking on each virtual machine.
- Virtual machines located on a malfunctioning host system need to be rebooted.
- VMHA does not know about applications located below those virtual machines. That means that if the underlying application data is modified from an application error and server reboot, whether or not the virtual machine is migrating and restarting from an application error machine may not useful.
How to configure VMHA?
VMHA configuration is quite simple, just follow the steps below:
Note : Recognizing that you have two ESX Server host systems, the VMware Infrastructure Suite (VI Suits), CPUs on compatible host systems, a shared storage system and all associated registrations VMHA and VMHA are all relevant.
- In the VI Client, Inventory View, right-click the datacenter and select New Cluster.
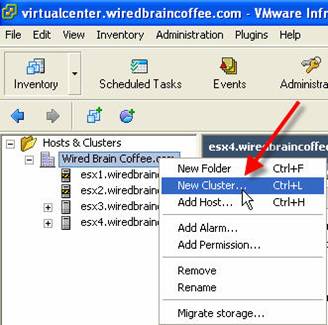
Figure 4: Adding a New HA Cluster
- This will bring up the New Cluster Wizard. Give your Cluster a name and (acknowledge that you only created one HA cluster), check the VMware HA feature.
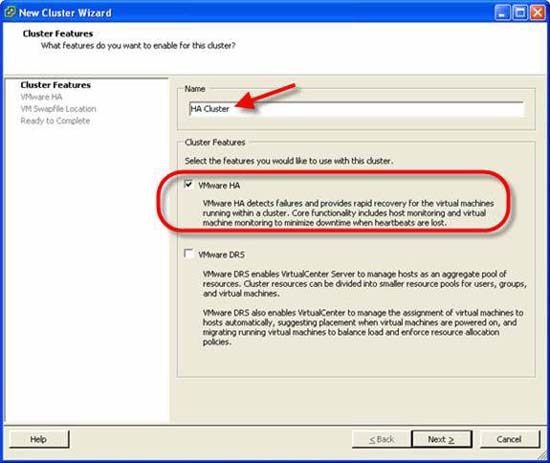
Figure 5: Name the HA Cluster
- Next, we will configure the HA options for this group of machines. There are many issues to consider here, you should consult the documentation on VMware 3.5.
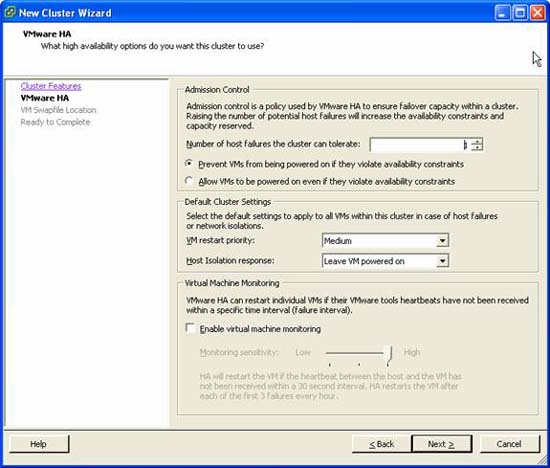
Figure 6: Configuring HA options
- Select a swapfile location - with the virtual machine on the shared storage or on the host. We recommend that you keep swapfile for virtual machines on shared storage.
- Finally you will see the 'ready to complete' screen, this is the screen you can review what you have done, then click Finish.
- When the HA cluster is created, you need to migrate ESX host systems into the cluster by clicking on them and dragging them into the cluster. You can also transfer virtual machines to the cluster in the same way. Here are the results we received after the implementation:
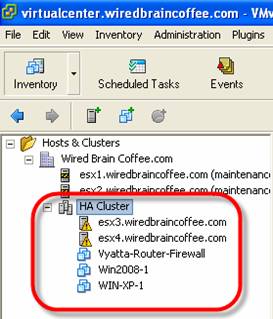
Figure 7: HA Cluster created with ESX Server hosts and internal virtual machines
- Here, you need to click on the cluster to see if there are any configuration issues (as you see in Figure 3). You should also note tabs like Summary, Virtual Machines, Hosts, Resource Allocation, Performance, Tasks & Events, Alarms and Permissions.
- Although you have configuration problems (without a backup management network), the VMHA cluster still functions properly. To resolve the error message 'insufficient resources to satisfy configured failover level for HA' temporarily translated as 'lack of resources for pre-configured failover for HA' when opening a virtual machine , we need to change the HA configuration to 'Allow VMs to be powered on even if they violate availability constraints'.
How do I know if VMHA works?
To check if VMHA is working, we do the experiment with two Dell servers in our group. A Windows Server 2008 system is running on ESX host 'esx4'. To perform a simple HA test, restart the host 'esx4' without going into maintenance mode. This will cause Windows 2008 Server to switch from 'esx4' to 'esx3' and be restarted. This is what before and after implementation.
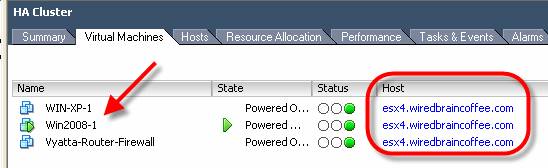
Figure 8: Before causing an error for server ESX4
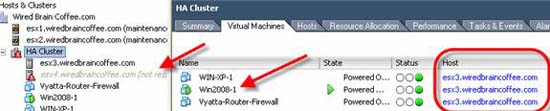
Figure 9: After server error ESX4 - providing VMHA was successful
In this test, we see that the Windows 2008 virtual machine is switched from 'esx4' to 'esx3' when 'esx4' is restarted.
Conclude
In this article, I have talked about VMware's High Availability solution and how to configure it. In the article we began by introducing the necessary conditions for using VMHA. We then introduced what is good and bad about VMHA. After showing you how to configure VMHA, we went on to demonstrate exactly how it works in a real server error. VMHA is truly a leading solution when it comes to high availability problems in virtualization.