8 best Linux debugger tools for software engineers
In this article, TipsMake.com will send you a list of the 10 best Linux debugger tools. We invite you to consult.
1. GNU Debugger (GDB)
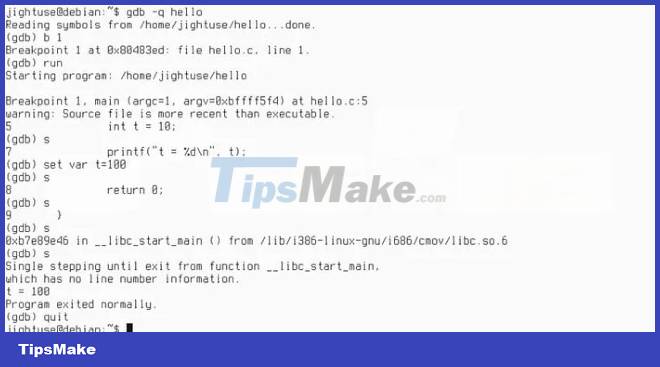
GNU Debugger (GDB) is one of the best Linux debugger available today. It is a powerful tool with a wide range of features. GDB supports many popular programming languages, including C, C++, Fortran and Java. It can also run on many CPU architectures such as x86, x86-64, ARM, PowerPC, SPARC and MIPS.
Install GDB using the following commands:
In Ubuntu/Debian-based distributions:
sudo apt install gdb
In Fedora/RHEL distributions:
sudo dnf install gdb
In Arch-based distributions:
sudo pacman -S gdb
As long as you compile with GCC with debug symbols, you can peek at the program's instructions at runtime by typing s. Typing r will run your program through the debugger. To start GDB once the program is loaded, simply type gdb into your terminal, followed by the program path.
Once you're logged in, typing help will give you a well-organized menu that explains everything you can do with this almighty debugger!
2. Data Display Debugger (DDD)
If you don't like using commands but still love the features that GDB offers, then DDD gives you a simple graphical user interface that provides all its features in a point-and-click interface. mouse. It's the quintessential Linux GUI debugger.

The user interface may look a bit simple but it is as powerful as any other debugger. The difference here is that you get GNU's signature debugger with a graphical interface!
To install Data Display Debugger (DDD), do the following:
In Ubuntu/Debian-based distributions:
sudo apt install ddd
In Fedora/RHEL distributions:
sudo dnf install ddd
In Arch-based distributions:
yay -S ddd
Anything based on Arch will have to use the AUR helper, as DDD doesn't exist in its official repositories. Alternatively, you can install DDD on an Arch-based system without the AUR helper:
sudo pacman -S --needed base-devel git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/ddd.git cd ddd makepkg -si
3. LLDB
LLDB is part of the LLVM project. This tool is becoming more and more popular thanks to its superior performance and efficient workflow. It also becomes the default debugger in macOS's Xcode and Android Studio. Some notable features of LLDB include support for multiple built-in editors, a language independent type system, and remote debugging.
For those familiar with basic GDB commands, LLDB will feel familiar. Typing run or r will run the program, and typing step or s will cycle through its subroutines.
To install LLDB:
In Ubuntu/Debian-based distributions:
sudo apt install lldb
In Fedora/RHEL distributions:
sudo dnf install lldb
In Arch-based distributions:
sudo pacman -S lldb
4. Delve
Delve is a simple yet feature-rich Linux debugger for Google's Go programming language. You can use it to interact with your programs at runtime and manipulate things like goroutines and stacks. Delve itself is also written in Go so it can provide high-speed runtime for programmers.
5. Xdebug
Xdebug is a powerful PHP debugger for Linux. It provides an easy-to-use debugger that can be used with many IDEs. Xdebug can be easily installed on Linux computers using the package manager.
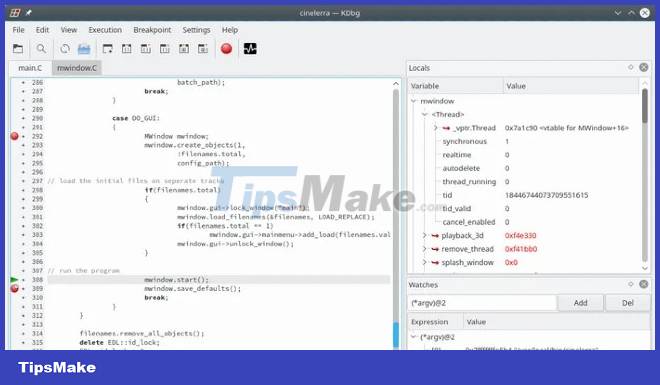
6. KDbg
KDbg is a graphical debugger for the KDE desktop environment. In fact, KDbg is just an interface to GNU Debugger. When using KDbg you will get all the features of GDB along with an intuitive user interface. Therefore, KDbg is suitable for beginners learning debugger.
7. Valgrind
Valgrind is a highly efficient debugger that provides a lot of additional tools for software analysis. It runs on all major platforms including Linux and Mac.
Furthermore, you can use it as a framework and create more flexible analysis tools. Overall, Valgrind is a perfect choice for professionals.
8. strace
strace is a usersapace utility for Unix. It allows users to monitor system commands and signals directly from the terminal. Programmers can use strace to dump stack traces, filter system commands, modify return codes, extract file descriptors, and more.
When you have powerful Linux debugger at hand, your programmer's job will be much easier. Almost any software engineer has had to install tools like GDB and LLDB. On the other hand, specialized debuggers like Delve and Xdebug will be intended for specific projects and ecosystems.