Compare the most popular Linux distributions today
It can be said that Linux is not a complete operating system, it is just a kernel operating system, which is the foundation for developing other operating systems.Operating systems based on Linux kernel are called Linux distributions.Developers will combine Linux kernel and other free software to create complete operating systems.There are many different Linux distributions that are widely used in the world.
If you want to "install Linux", you will need to choose a distribution.You can also use Linux From Scratch to compile and build your own Linux system from the beginning, but it's a complicated and time-consuming task.
Ubuntu
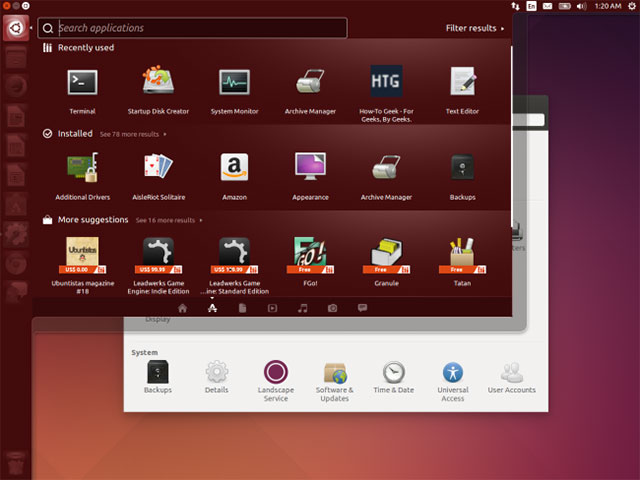
Ubuntu is probably the most famous Linux distribution.Ubuntu is based on Debian, but it has its own software repository.Most software in these repositories is synchronized from the Debian archive.
The Ubuntu project focuses on providing users with a desktop experience (and server).Ubuntu is not afraid to build its own custom technologies to realize that goal.Ubuntu was originally developed for the GNOME 2 desktop environment, but now it uses its own Unity desktop environment.Ubuntu even builds its own Mir graphics server while other distributions are only active on Wayland.
Ubuntu is a modern distribution, constantly improving but still retaining its own identities.Ubuntu releases updates every six months, along with major updates, more stable and long-term support delivered to users every two years.Ubuntu is currently working hard to expand its influence on smartphones and tablets.
Linux Mint
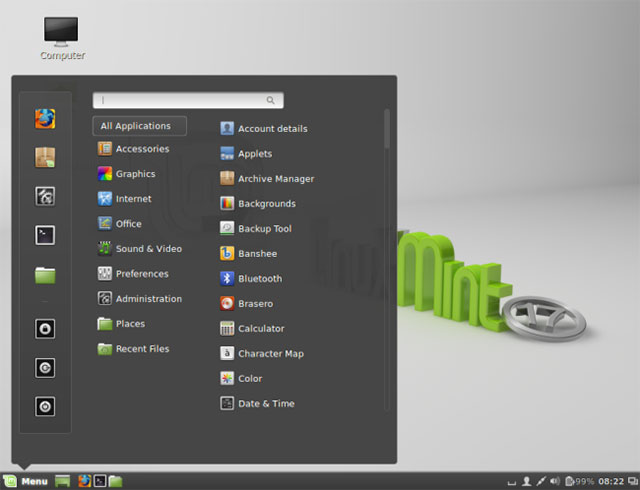
Mint is a Linux distribution built on Ubuntu.It uses Ubuntu's repositories, so similar software will be available and available on both distributions.Initially, Mint was a favorite alternative distribution mainly because it included media codecs (media codecs) and proprietary software that Ubuntu did not provide by default.
This distribution currently also has its own identity.You won't find Ubuntu's Unity desktop anymore, instead, you'll get a more traditional Cinnamon or MATE screen.Mint takes a more relaxed approach to releasing software updates and will not automatically install important software updates.However, this is also a controversial issue, making some Ubuntu developers think it is not safe.
- Distinguish Ubuntu and Linux Mint
Debian
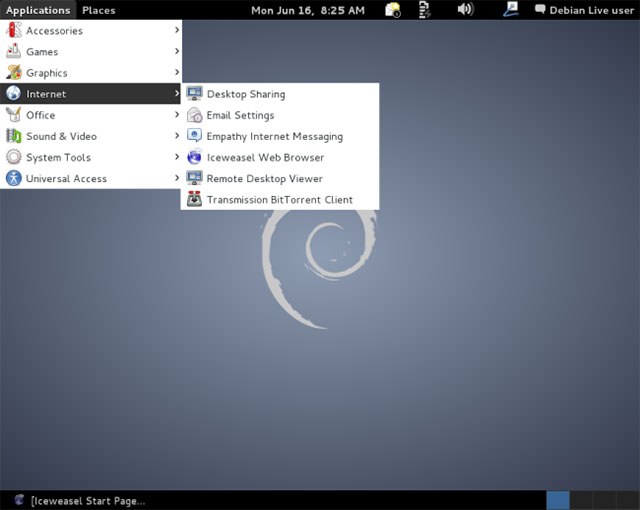
Debian is an operating system that only includes free open source software.The Debian project has been operating since 1993, ie about 25 years ago!This project has been highly respected in the community of developers since its inception.So far, Debian has been releasing new versions regularly, but unfortunately, these new versions are updated by Debian much slower than distributions like Ubuntu or Linux Mint.This can make it more stable and conservative and contains ideal elements for some systems.
Ubuntu was originally set up to take Debian's stable core bits and make them faster, optimizing the software together into a user-friendly and updated system more often.
Fedora
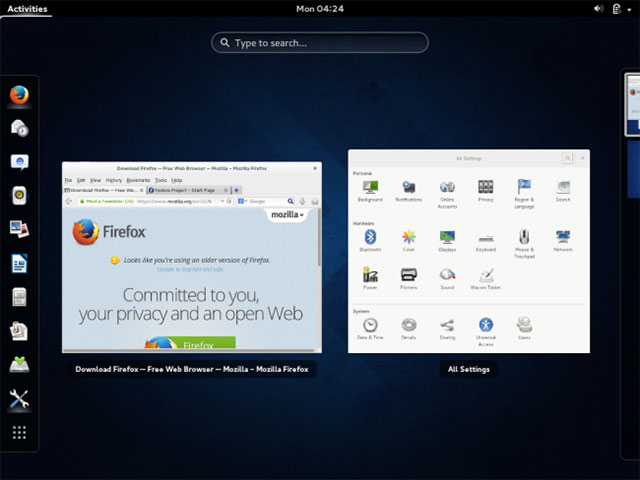
Fedora is a project that focuses primarily on free software.You will be hard pressed to find an easy way to install proprietary graphics drivers on Fedora, although third-party repositories are always available.Fedora is still being developed and optimized.
Unlike Ubuntu, Fedora does not create its own working environment or other software.Instead, the Fedora project uses 'upstream' software, which provides a platform that integrates all of these software without adding custom tools.Fedora also comes with the GNOME 3 desktop environment by default, and you can also use Fedora with other desktop environments.
Fedora is sponsored by Red Hat and is the foundation for the commercial Red Hat Enterprise Linux project.Unlike RHEL, Fedora is capable of not being supported for a long time.If you want a more stable release that is supported longer, Red Hat recommends that you use their Enterprise product.
CentOS / Red Hat Enterprise Linux
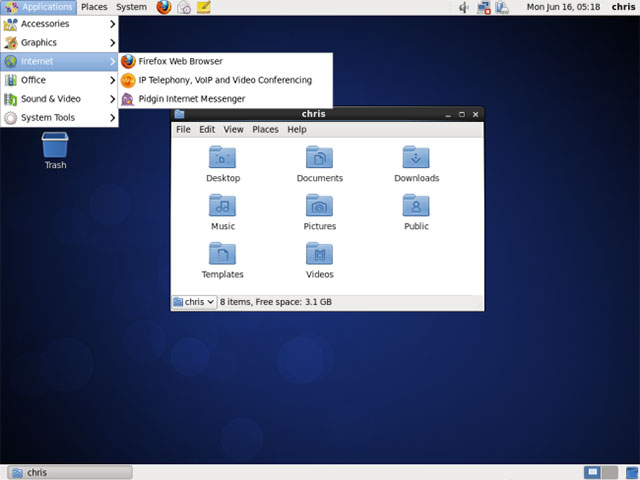
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is a commercial Linux distribution for servers and workstations.It was developed based on the Fedora open source project, but was designed to be a stable platform with longer-term support.
Red Hat uses trademark protection laws to prevent their official Red Hat Enterprise Linux software from being redistributed illegally.However, the core software is free and open source, and CentOS appears.CentOS is a community project that takes the code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, deleting all Red Hat brands and is provided as well as distributed for free.In other words, this is a free version of RHEL, so it would be appropriate if you want a stable platform to be supported for a long time.CentOS and Red Hat recently announced they are collaborating, so CentOS is now part of Red Hat.
openSUSE / SUSE Linux Enterprise
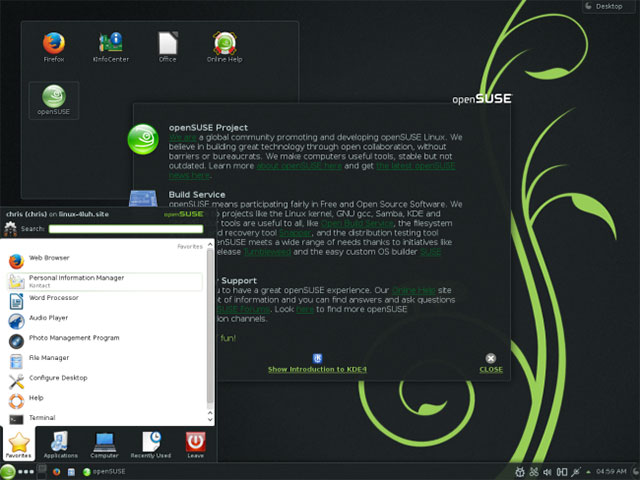
openSUSE is a community-developed Linux distribution and is sponsored by Novell.Novell bought SuSE Linux in 2003 and they still create an enterprise Linux project called SUSE Linux Enterprise.While Red Hat has a Fedora project provided for Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Novell has the openSUSE project provided to SUSE Linux Enterprise.
Like Fedora, openSUSE is a more powerful version of Linux.SUSE was once one of the most user-friendly Linux distributions for users, but in the end, Ubuntu compared it.
Mageia / Mandriva
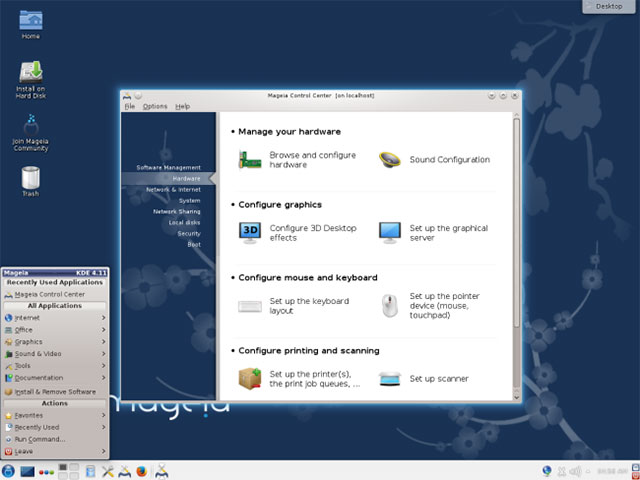
Mageia is a branch of Mandriva Linux created in 2011. Mandriva is known as the previous Mandrake name.It has also been one of the most user-friendly Linux distributions.
Like Fedora and openSUSE, this is a community-developed project to create an open-source Linux distribution.Mandriva SA no longer supports desktop Linux distributions, but their enterprise Linux server projects are still based on Mageia code (like Fedora and openSUSE provide code for businesses of they).
Arch Linux
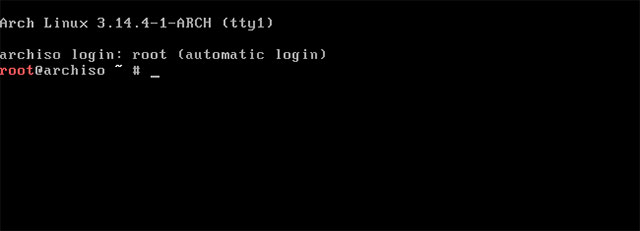
Arch Linux can be considered the 'senior' of other Linux distributions on this list.It is designed to be flexible, compact, as simple as possible.Keeping it simple doesn't mean that Arch provides many graphic utilities and automated configuration scripts to help you set up your system.Instead, it means that Arch gives you the tools for you to 'treat yourself'.
You will be responsible for configuring your system properly and freely installing the software you like.Arch does not provide a formal graphical interface for package managers or complex graphical configuration tools.Instead, it provides clean configuration files designed to be easily editable.When installing, you will need to enter the appropriate commands in the terminal to manually configure the system, partition and install the operating system.
Arch uses a model called "rolling release", which means that any installed image is just a snapshot of the current software.Each bit of the software will be updated from time to time, you do not need to upgrade to the new release of Arch.
This distribution has one thing in common with Gentoo.These are two capital distributions that are popular at the same time.Both Linux distributions are designed for users who know how their systems work or at least they are willing to learn new things.However, Arch uses binary packages while Gentoo focuses on compiling each software from the source.This means that installing the software on Arch will be faster because you don't have to spend a lot of time waiting for the software to be translated again.
Slackware Linux
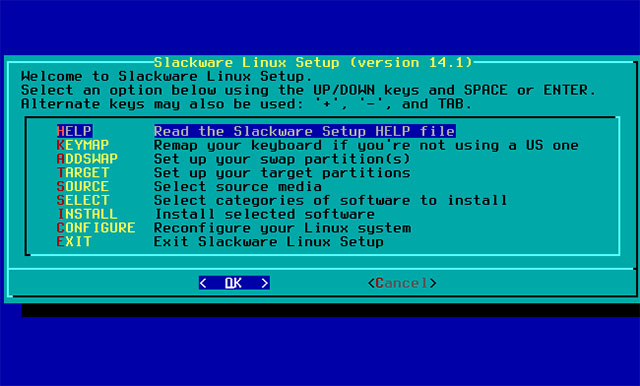
Slackware was launched in 1993 and the oldest Linux distribution is still maintained and offers regular new releases.
Like Arch, Slackware distributes all unnecessary graphic tools and automated configuration scripts.Without the graphical installation process you will have to partition the disk manually and then run the installation program.Slackware starts the command line environment by default.This is a very conservative Linux distribution.
Puppy Linux
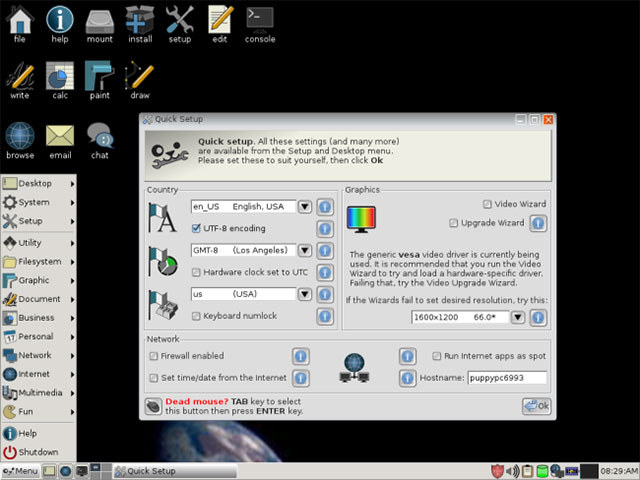
Puppy Linux is a quite famous Linux distribution.Previous versions of Puppy Linux were built on Ubuntu, but the latest version was developed from Slackware.Puppy Linux is designed to be a small, lightweight operating system that can run well on very old computers.Puppy Linux's ISO file is 161 MB in size.Puppy Linux can run on computers with only 256 MB of RAM, although it is recommended to use it on computers with at least 512 MB of RAM for the best experience.
Puppy is not the most modern distribution and does not have all the features of 'big bang' but it can help you revive an old PC system.
See more:
- 7 commands to manipulate the most basic files and folders everyone must know
- Basic Linux commands everyone needs to know
- How to install and use Kali Linux on VmWare virtual machine
- Basic Shell commands in Linux