What is RARP and how is it different from ARP and ICMP?
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol is a protocol developed to solve the need for mapping IP addresses from MAC addresses. In this article, TipsMake will explore RARP in depth, learn how it works, and compare it to other protocols such as ARP and ICMP.
What is Reverse Address Resolution Protocol?
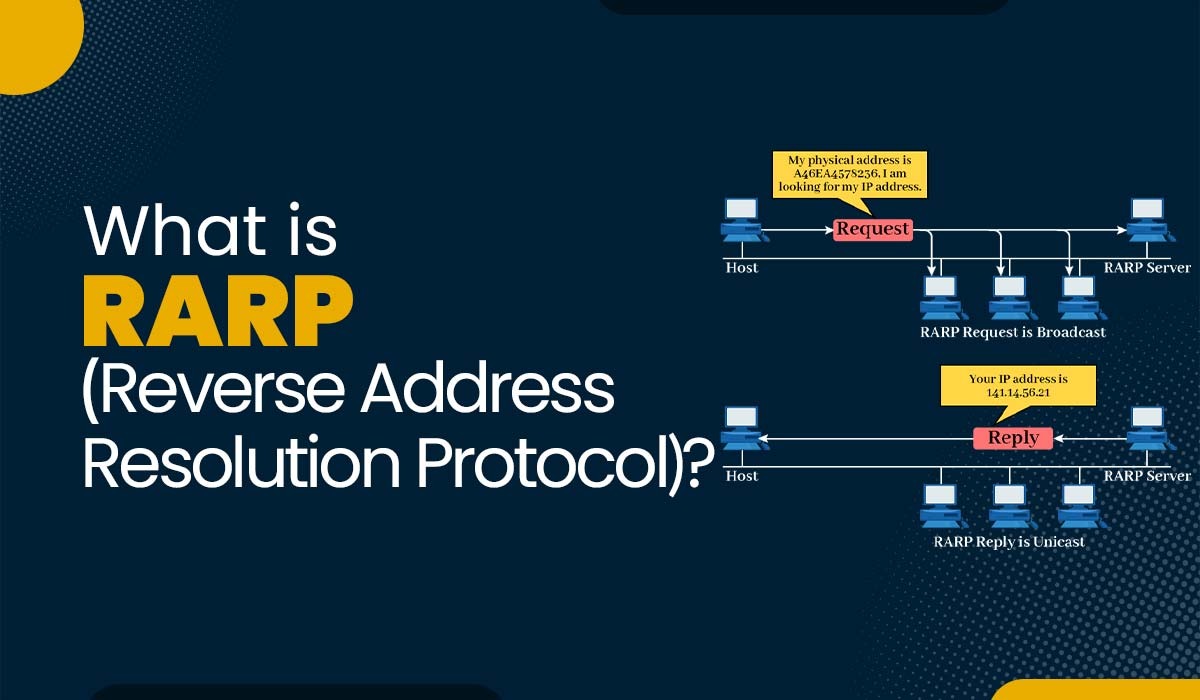
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is a network protocol used to map a device's Media Access Control (MAC) address to its corresponding Internet Protocol (IP) address. It works in reverse of Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which maps IP addresses to MAC addresses.
What is Reverse Address Resolution Protocol?
RARP was developed in the 1980s in a time when IP address management was still relatively new. Before RARP, devices typically had to know their IP addresses in advance, which made network management and configuration difficult. The development of RARP eliminated these obstacles by providing an automated mechanism for IP address discovery.
With the advent of Ethernet networks, where each device is assigned a unique MAC address, RARP quickly became popular. This protocol allows devices to send requests to a server to obtain the appropriate IP address without the need for manual configuration.
How does RARP work?
RARP request startup:
When a diskless system boots, it sends out a RARP Broadcast request packet with its MAC address. This packet is sent to all devices on the network.
Receive and process requests:
RARP request packets are received by all devices on the network, but only the RARP Server processes this request. The RARP Server is a server that stores the mapping between MAC and IP addresses in its configuration file.
Address search and mapping:
The RARP Server looks up the MAC address in the configuration file and maps it to the corresponding IP address. If no mapping is found, the request packet is discarded.
Reply RARP:
If a mapping is found, the RARP Server creates a RARP Reply packet containing the corresponding IP address and sends it back to the source machine as a Unicast.
Complete the startup process:
The source machine receives the RARP Reply packet and receives its own IP address. This IP address is used to communicate with other machines on the network until the source machine reboots.
Is RARP obsolete? If so, what alternatives exist?
With the development and advancement in network technology, the question is: Is RARP still relevant and necessary today?
RARP has undergone significant changes over the past few decades. Newer protocols such as DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) have been developed to address the problems that RARP encountered.
RARP is no longer widely used in many organizations and businesses today. However, RARP still retains its role as a historical protocol, but its lack of flexibility and extensibility makes it gradually obsolete.
Alternatives
-
DHCP : DHCP is the most popular protocol today that allows automatic provision of IP addresses and many other configuration information to devices on the network.
-
BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) : This protocol also aims to automatically provide IP addresses, but is capable of providing more information than RARP.
-
IPv6 autoconfiguration : With the advent of IPv6, devices can automatically configure their IP addresses through the autoconfiguration mechanism, thanks to the MAC address.
How is RARP different from ARP and ICMP?
To better understand RARP, we also need to compare it with two other important protocols in computer networking: ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) and ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol). Each protocol has its own functions and different ways of working.
How is RARP different from ARP and ICMP?
Conclude
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) is an important protocol in the history of computer networking, helping devices determine the IP address corresponding to their MAC address. Although RARP was once very useful, with the development of technology and the emergence of new protocols today, RARP has gradually become obsolete.
Comparing RARP with other protocols such as ARP and ICMP also clearly shows the differences and unique functions of each protocol. Hopefully, this article has helped you better understand RARP, how it works, and its importance in modern networking environments.
 How to reset IP address using Ipconfig command
How to reset IP address using Ipconfig command What is CSMA/CA? Difference between CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD
What is CSMA/CA? Difference between CSMA/CA and CSMA/CD What is DNS 8.8.8.8? How to change DNS 8.8 8.8 on Windows, MacOS and Android
What is DNS 8.8.8.8? How to change DNS 8.8 8.8 on Windows, MacOS and Android What is Spanning Tree? Benefits of Spanning Tree Protocol?
What is Spanning Tree? Benefits of Spanning Tree Protocol? What is PSTN? Comparison between PSTN and VoIP
What is PSTN? Comparison between PSTN and VoIP What is SRV Record? Structure and how to create SRV Record
What is SRV Record? Structure and how to create SRV Record