What is Spanning Tree? Benefits of Spanning Tree Protocol?

Spanning Tree is a very important concept in the field of computer networking, especially when it comes to ensuring that the network is not congested and that devices in the network can communicate with each other effectively. So what is Spanning Tree? Let's find out with TipsMake right through the article below.
What is Spanning Tree?
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a solution developed by Dr. Radia Perlman in 1985 to solve the problem of loops in networks. STP helps to create a spanning tree from a set of nodes in the network, where each node can only connect to a single path.

What is Spanning Tree?
The main goal of STP is to prevent loops in LANs, which is extremely important for maintaining network performance and stability.
Why Use Spanning Tree?
Using the Spanning Tree protocol brings many benefits to organizations and businesses, specifically:
Ensuring network reliability
When STP is active, it automatically detects and eliminates loops, which helps the network run more smoothly. It helps reduce the possibility of serious problems caused by loops, such as connection loss or congestion.
Enhance network performance
By eliminating redundant paths, STP optimizes network bandwidth and improves data transfer speeds. With no loops, packets have a better chance of reaching their destination, reducing response times and improving user experience.
Easy network expansion
Spanning Tree Protocol not only helps manage existing connections but also supports future network expansion. As new devices are added to the network, STP is able to automatically adjust the spanning tree structure, allowing new devices to be integrated without disrupting the operation of the existing network.
What are the benefits of using Spanning Tree protocol?
Spanning Tree protocols provide the following benefits:
- Provides link redundancy while preventing unwanted loops.
- Allows network administrators to manipulate network lines while preventing loops on switches.
- STP also allows for the creation of passive, redundant links in case an upstream switch fails or the network path cannot forward traffic.
- Minimizing operating costs By using STP, organizations can save on costs associated with troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Increases security by eliminating loops, which helps prevent unauthorized access to devices on the network.
States in an STP process
Below are the main states in the STP process:
Blocking
This is the initial state of a port when STP starts. In this state, the port only listens for BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units) and does not forward data. The goal is to define the network topology without creating loops.
Listening
After being in the blocking state, the port switches to the listening state. During this phase, the port still only listens for BPDUs to determine the network topology and does not forward any data.
Learning
The port enters the learning state, where it begins to learn the MAC addresses of the devices connected to it. During this phase, the switch builds a MAC address table but does not forward any data yet.
Forwarding
This is the final state, where the gateway has learned the information and can forward packets to other devices in the network.
Disabled
A port is in this state when it is disabled or configured to not participate in the STP process. This state does not allow the port to send or receive any data.
Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration Steps
To configure Spanning Tree protocol on switches, you need to follow these steps:
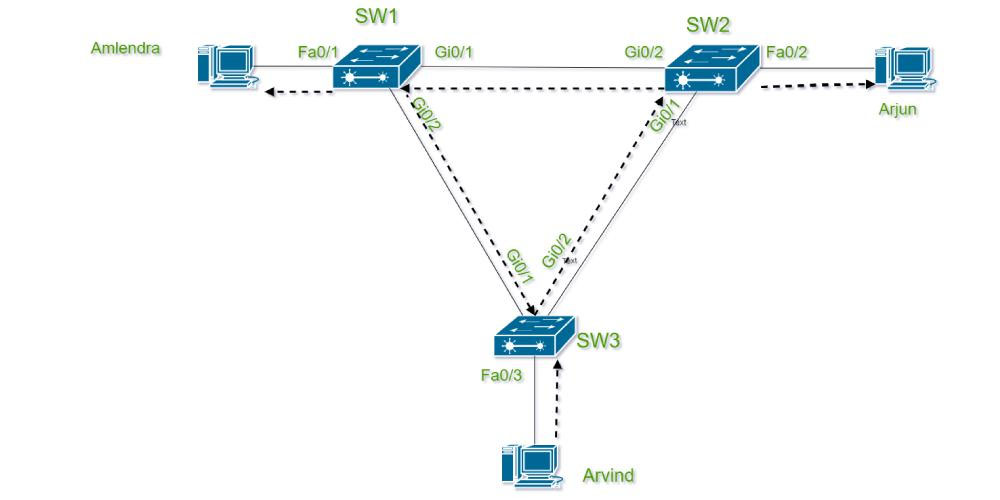
Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration Steps
Step 1: Determine network configuration
Before starting configuration, the administrator needs to clearly identify the devices in the network, the connections, and the specific requirements of the organization.
Step 2: Configure STP parameters
The administrator needs to configure parameters such as bridge priority, path cost, and port priority for each switch. These parameters will determine how STP operates and manages connections in the network.
Step 3: Check and maintain
Once the configuration is complete, the final step is to test and maintain the system. The administrator needs to regularly monitor the STP performance and make necessary adjustments to ensure that the network is always stable.
Conclude
Using the Spanning Tree protocol not only helps solve network loop problems but also brings many other practical benefits such as increasing reliability, improving network performance,.
It can be said that STP is an indispensable tool in modern network management. With the continuous development of technology, a deep understanding of STP will help organizations adapt and maximize the potential of their networks.
You should read it
- ★ The mystery of the 'ghost tree' poisoning itself in exchange for nutrients
- ★ Not only people but even animals do not dare to array to the unique tree species on this planet
- ★ 10 exotic tree species hold the world record
- ★ Feng shui tree behind the house brings luck and fortune
- ★ Binary Search Tree (Binary Search Tree)