What is BIOS? What is its function in computer system?
What is BIOS?
BIOS stands for "Basic Input/Output System". In essence, BIOS is a set of instructions stored on a firmware chip located on the computer's motherboard.
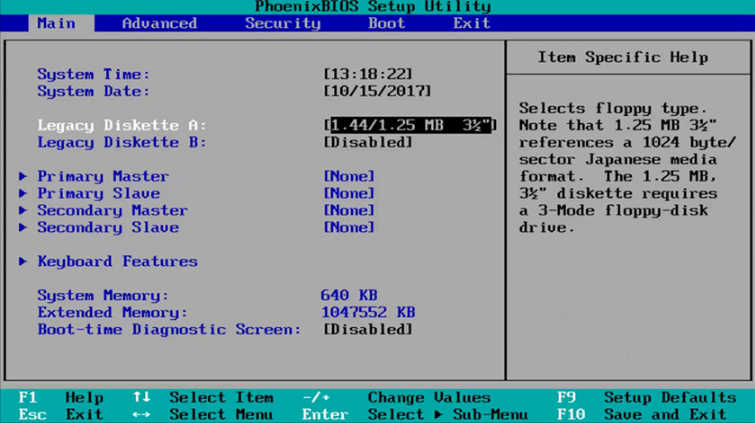
True to its name, BIOS controls the basic functions of the computer that we rarely pay attention to: Connecting and running drivers for peripheral devices (mouse, keyboard, USB, etc.), reading the hard drive order to start the operating system, displaying signals on the screen, etc. In short, when the computer starts up, the BIOS's task is to "wake up" each component and check whether this component is working or not. Then, BIOS will transfer the control task back to the operating system.
How does BIOS work?
When you turn on your computer's power button, the CPU first accesses the BIOS even before the operating system loads. The BIOS then checks all your hardware connections and locates all your devices. If everything is okay, the BIOS loads the operating system into the computer's memory and completes the boot process.

The BIOS is also used after the computer boots. It acts as an intermediary between the CPU and the I/O (input/output) devices. Because of the BIOS, your programs and operating system do not need to know the exact details (such as hardware addresses) of the I/O devices attached to your PC. When device details change, the BIOS simply needs to be updated. You can make these changes by entering the BIOS when your system boots.
What is BIOS used for?
If you are the only "techie" in your family or at your office, you will definitely have to use BIOS at least once. Although BIOS features may be very simple, most of them cannot be performed inside the operating system (Windows, Linux, etc.). In case your computer has problems, understanding the capabilities of BIOS will help you a lot. Below are some basic BIOS features:
Change drive read order at startup
When you turn on your computer, you can enter the BIOS or press another shortcut key to display a list of drives that are read when you boot the computer.
If you install multiple operating systems on multiple hard drives, you can change the order in which the hard drives are read, to (for example) boot from the Ubuntu 10 hard drive before booting from the Windows 8 hard drive.
If Windows is corrupted, you will also need to set the CD/DVD drive to the first place in the list of boot drives to use the repair features from the Windows installation disc or reinstall Windows.
Monitor temperature, fan speed
If you can't boot into the operating system, you can open the BIOS to check the temperature of the components to see if any fans are stopped and the machine is overheating, and you can even monitor (and control) the voltage level to devices like RAM and CPU, especially if you are the type of tech-savvy person who "bloodthirstyly" overclocks.
When running Windows, you can also use software like HWMonitor to monitor your computer's temperature.
Overclocking
You will need to open the BIOS to change the CPU's clock speed and/or voltage to overclock. Overclocking increases the processing speed of your computer, but it also comes with certain risks, the most dangerous of which is the risk of overheating and freezing if not cooled down further (with a dedicated fan or water cooling).
Lock the machine
In BIOS, you can set a password to lock the entire computer, not allowing the use of any operating system.
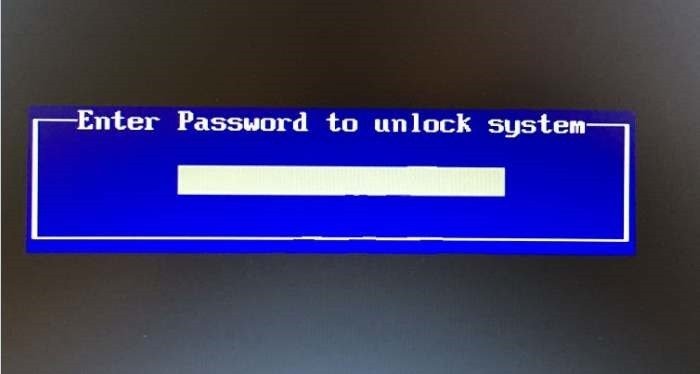
UEFI also supports Secure Boot, which prevents unauthorized operating systems from booting onto your computer via external devices or over the network. Most regular users will ignore this feature, but for top-secret systems, setting a password in the BIOS can be an effective security solution.
Other features
In BIOS, you can choose to customize many other settings, such as choosing the amount of memory allocated to the integrated graphics card, the RAM clock speed, choosing the operating mode of the computer (power saving or increasing processing performance), choosing whether to allow USB components to start the computer from sleep state or not. Each BIOS will have different features, so learn and try to customize the settings in BIOS. Once you understand BIOS, you will be able to easily handle computer problems in the future.
You should read it
- BIOS - Basic information for beginners
- 5 tips for using the BIOS to help you master your computer
- How to Check BIOS Version
- Set BIOS and UEFI password to protect data on your Windows 10 computer safely
- Display BIOS information on Windows 10 using Command Prompt
- Understanding BIOS: An Indispensable Component of a Computer
 How to turn on virtual keyboard on computer, laptop in a snap
How to turn on virtual keyboard on computer, laptop in a snap TOP Best Livestream Webcams, Easy to Use
TOP Best Livestream Webcams, Easy to Use Summary of useful computer shortcuts that you need to know
Summary of useful computer shortcuts that you need to know Instructions for installing Ubuntu parallel to Windows 10 easily
Instructions for installing Ubuntu parallel to Windows 10 easily What is a portable hard drive? Which portable hard drive is the best today?
What is a portable hard drive? Which portable hard drive is the best today? How to copy photos from computer to iPhone simply and quickly
How to copy photos from computer to iPhone simply and quickly