Instructions for upgrading BIOS
Network administration - Upgrading the BIOS for a computer can help your system to boot faster, overcome some compatibility issues and improve performance.
A tiny BIOS chip hidden deep inside each computer, it not only supports computers but also helps protect. The BIOS stands for basic input and output system and the BIOS is the first software that the computer will load on startup, before all other devices in the computer such as CPU, GPU and motherboard chipset. But a few years ago, motherboard manufacturers partnered with Microsoft and Intel introduced an alternative system for the traditional BIOS chips called UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, extended firmware interface). Best).
Most motherboard products now have UEFI chips, not BIOS chips, but both have the same purpose: to prepare the system to boot into the operating system. That said, most people still call UEFI "BIOS" because of the familiarity of the term.

How to upgrade the BIOS
- Why should you (or should not) upgrade the BIOS
- How to upgrade the BIOS
- Step 1: Determine your current BIOS version
- Step 2: Check the motherboard manufacturer's website
- Step 3: Read the accompanying documentation
- Step 4: Upgrade the BIOS
Why should you (or should not) upgrade the BIOS
Understanding UEFI is important to understand how to take advantage of feature updates and fixes that come with BIOS updates provided by motherboard manufacturers.

The motherboard can use any firmware revision that the motherboard manufacturer has built. During the time of using the motherboard, manufacturers will release a firmware package or update the new BIOS, allowing new processor and memory support or common errors to be resolved. For years, the only real reason to update for the new firmware version is to solve some bugs in UEFI or change a newer CPU for the motherboard.
However, Duo's report indicates that UEFI firmware attack is a dangerous attack. Anti-virus software may not be detected. Some people want to regularly check and update UEFI firmware package. However, this may damage the motherboard. It is best not to update the UEFI firmware unless the firmware updates the content you need. However, it is possible to update BIOS updates if you have a new chip or motherboard platform.
How to upgrade the BIOS
When you start your computer, you will see a message text indicating the button to press to enter UEFI BIOS. Press it! (Need to have the correct button because the UEFI control panel design of all motherboards is different).
- Instructions for entering BIOS on different computers
Although not all motherboards provide this feature, but with certain types, you can boot into the UEFI control panel and use an integrated utility to connect to Internet and latest firmware from the manufacturer's server.
If your computer does not have this live support utility, follow the steps below.
Step 1: Determine your current BIOS version
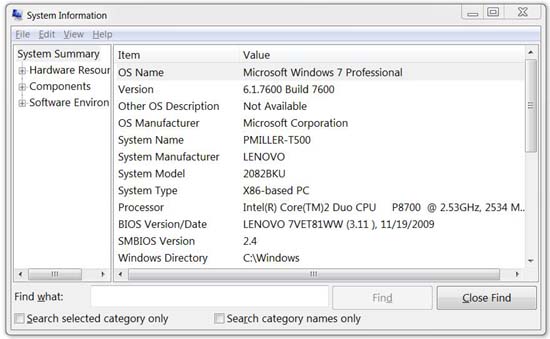
The BIOS version of the computer is displayed in the BIOS setup menu, but you do not have to restart the computer to check this version number. There are several ways to view the BIOS version from within Windows and they work similarly to the traditional BIOS or newer UEFI firmware.
Check the BIOS version using System Information
The easiest way to find the BIOS version is to open the System Information application in Windows - just type msinfo32 in the search bar (Windows 7 / Vista) or the Run box (XP) and click System Summary; Your BIOS version will now be displayed on the right, under the speed display section of the processor. Write down your version number (and the date that appears after that version number, if any).
Check the BIOS version at Command Prompt
To check your BIOS version from Command Prompt, click the Start menu, enter 'cmd' in the search box, then click on the 'Command Prompt' result. Note there is no need to run with admin rights.

At the prompt, enter (or copy and paste) the following command, then press Enter:
wmic bios get smbiosbiosversion You will see the version number of the firmware BIOS or UEFI in the current PC.

For Windows 10 version, readers refer to the article: Display BIOS information on Windows 10 with Command Prompt to know how to implement details.
Step 2: Check the motherboard manufacturer's website
Most computer manufacturers proceed to upgrade the BIOS based on a certain line or model, so visit your BIOS manufacturer's support page and check in its list. If you download and install a BIOS software for another model, your computer will definitely not work (but most BIOS upgrade kits have the smart ability to tell you that you are install it on incorrect hardware. If there is an upgrade file for your BIOS in the list, download the upgrade file to your computer, along with any accompanying documentation, because of the specific warnings and instructions that will be placed inside the documents. Read Me data.
In the process of searching for BIOS updates from the motherboard manufacturer's website. If you can't remember the manufacturer's model number, then you can search it without opening the case by downloading and running CPU-Z, then clicking on the Mainboard tab .
Different motherboards use different utilities and processes, so no tutorials are suitable for all motherboards. However, the basic implementation process is the same on all motherboards.
If you have purchased a built-in computer, visit the computer manufacturer's website, search for a computer model and see the manufacturer's download page. You will find any BIOS updates available there.

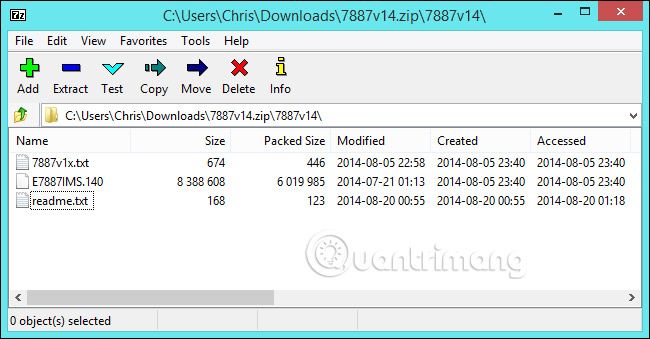
BIOS updates are usually downloaded in ZIP file format. Extract the contents of that file. Inside the extracted folder, you will find some BIOS file types. In the screenshot below, it is the E7887IMS.140 file .
You need to choose one of the many different BIOS flash tools, depending on the motherboard you are using and what it supports. The BIOS update comes with a README file that will suggest the ideal hardware option.
Step 3: Read the accompanying documentation
The BIOS upgrade file may include a list of patches and new functions, often to support new hardware. For example, when upgrading BIOS for Lenovo Thinkpad T500 computer, software upgrade support for new AC adapter and screen resolution of 1600x900-pixel on external monitor; This upgrade also fixes fan speed and Webcam issues, which are problems that cannot be solved by upgrading Windows.
However, more important are the notes in the Read Me file: If you are using Vista on a T500 computer as our test, you need to make sure you have installed a patch; and if the T500 has another graphics card, you will need to upgrade the driver for it on this version before upgrading the BIOS. Please read the documentation carefully or you will probably make your computer unable to boot without knowing why.
Step 4: Upgrade the BIOS
Most new computers have a procedure to upgrade the BIOS easily: Just download the .exe file from the manufacturer's website, exit all programs, run the .exe, and it will do the work itself. work for you; then restart. If your computer suddenly turns off during the BIOS upgrade, you won't be able to boot, so make sure you don't run out of laptop battery power.
However, older computers may require you to set up a boot disk to upgrade the BIOS. You can download an application used to configure USB, blank CD / DVD, even a floppy disk to do this, or an ISO image file used in the application to burn the disc to create a BIOS upgrade CD. . Other systems will prompt you to copy some files to the boot disk, restart and open the BIOS during startup (usually press a key for installation options) and change the boot order to find the system. The device starts up before loading the operating system from the hard drive.
Some manufacturers offer the option to flash BIOS directly in their BIOS or as an option to press a special key when you boot the computer. You copy the BIOS file to the USB drive, restart the computer, then go to the BIOS or UEFI screen. From there, select the BIOS update option, select the copied BIOS file to the USB drive and update the BIOS to the new version.
Often users can access the BIOS screen by pressing the appropriate key while the computer is booting. It is usually displayed on the screen during the boot process and will be noted in the motherboard or PC manual. The keys to access common BIOS are usually Delete and F2. Access to the UEFI setup screen may vary slightly on each computer.
There are also more traditional DOS-based BIOS flash tools. When using those tools, you create a USB live DOS drive, then copy the BIOS flash utility and BIOS file to that USB drive. After that, restart your computer and choose to boot from the USB drive. In a minimal DOS environment that appears after rebooting, you run the appropriate command, usually a command similar to flash.bat BIOS3245.bin, and the tool will put the new BIOS version into the firmware.
DOS-based flash tools are usually provided in BIOS archives (download from the manufacturer's website). If desired, users can download this section separately. Look for a file with an extension of .bat or .exe.
Previously, this process was done with floppy disks and bootable CDs. But on modern hardware, using USB is the most convenient way.

Some manufacturers offer Windows-based flash tools. Users can run them on Windows desktop to flash the BIOS and then reboot. Using these things is not recommended and even if the manufacturer provides these tools, you should be cautious when using them. For example, MSI recommends that users use the BIOS-based menu option instead of their Windows-based utility in the README file in the BIOS update as an example in this article.
Flashing the BIOS from within Windows can lead to more problems. All software running in the background, including security programs, can interfere with the process of recording the BIOS in the computer, causing the process to crash and damage the BIOS. Any system that has a problem or is 'frozen' may result in a BIOS failure. Safety is first, so you should use a BIOS-based flash tool or boot into a minimal DOS environment to flash the BIOS.

After running the BIOS flash utility, restart the computer and download the new BIOS or UEFI firmware version. If there is a problem with the new BIOS version, you can downgrade by downloading the old version from the manufacturer's website and repeat the flash process.
Once again, updating the BIOS on your computer can be beneficial, but it's important to understand the risks. Do not touch it if there is no clear, convincing reason to update UEFI firmware.
See more:
- Update motherboard BIOS
- How to enter BIOS (UEFI) on Windows 10
- 5 tips for using the BIOS to help you master your computer