What are TIFF files?
What is the TIFF file format?
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is an old image file format developed by Aldus and Microsoft Corp, first released in 1986. It was later merged with Adobe Systems. The TIFF format is one of the highest quality, stable, document-rich, feature-rich uncompressed formats for saving raster images, so it is commonly used in photography and desktop publishing. , scanners, faxes, word processing, optical character recognition, geographic information systems such as GeoTiff.
For many years, TIFF has been the standard file format for many scanners and digital imaging software. As scanners became more powerful and desktop memory became larger, TIFF evolved to be able to capture both grayscale and color images. TIFF, along with JPEG and PNG, is the most popular format for color photos today.
TIFF is a flexible and customizable file format that stores all image data in one file, including headers, tags, size parameters, data layout, compression level, and geometric characteristics. belong to image.
In fact, images are edited by creating different tags, layers and transparency levels. If you save those images in a TIFF file, when you open it later, you can edit each layer of the image, which is not possible with JPEG, BMP and PNG images.
Raster images use a grid of pixels (small, colored rectangles), to form an image.
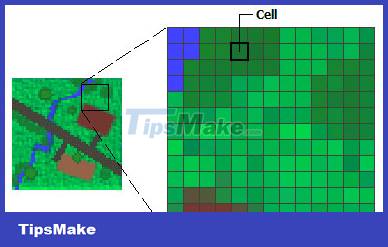
If you zoom in on the image, you will see a colored grid as shown above.
Characteristics of TIFF image format:
- Supports compression without affecting data quality (lossless)
- Device and processor independent file format
How do TIFF files work?
TIFF are important file formats that professionals use to ensure that they can continue working on their projects using any image editor on any computer at any time.
Unlike JPEG where all the edits and adjustments you make are permanently applied to the image, TIFF allows you to continuously make adjustments by allowing separation between images, layers, channels , transparency, color configuration and metadata.
- Layer: Refers to individual elements in an image that can be edited individually. These layers can be stacked to create the final image. For example, in photo editing software, you might have one layer for the background, another for text, and a third for an image overlay. This allows for precise adjustment of different parts of the image without affecting the whole.
- Channels: A way to separate and process color information in an image. In most images, you have red, green, and blue (RGB) color channels. By working with channels, you can adjust the intensity of each color, which is useful in tasks such as color correction or creating special effects.
- Transparency: The part of an image that is see-through or allows what is behind it to show through. In images, this is often represented by an alpha channel or transparency mask. This is especially important when you want to make an image background transparent while still maintaining parts that can be seen through, such as a logo, watermark, or creating a collage.
- Color profiles: TIFF files can store color profiles, ensuring that your colors look consistent across different devices or software. This is important for maintaining the desired look of your photo.
- Metadata: Like digital tags, TIFF files can store all types of metadata, including EXIF data containing information about camera settings, dates, etc.
With all of these properties adjustable in one combined file, editors can continue working on TIFF projects without permanently changing the image they are working with.
Besides non-destructive editing, TIFF also ensures that the original image file remains intact through lossless file compression algorithms such as LZW and ZIP. Color depth is also not an issue as TIFF can support both 8-bit and 16-bit color depth, allowing you to store very high quality images from high-end professional cameras.
Now you know why professionals use TIFF. Next, let's discuss how you can use TIFF on your computer.
How to create TIFF files
Because TIFF is a popular file format, almost any image viewing and image processing software can create TIFF files.
To create a TIFF file in Adobe Photoshop, click File > Save As. A save menu will appear. All you need to do is click the Save as type drop-down menu, select TIFF and press Save.
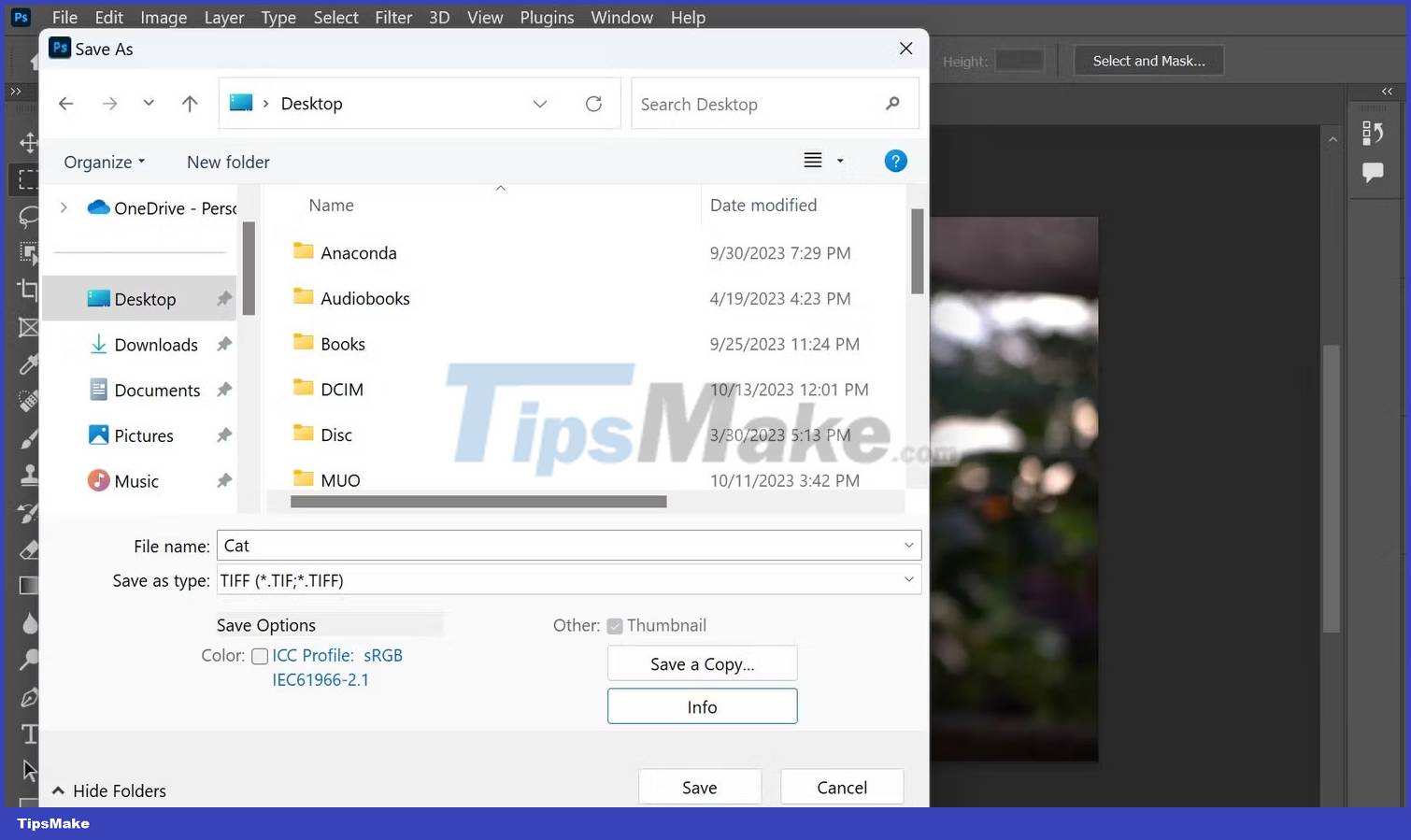
You can then choose the compression level you want to apply to the image. You should default to None, but if you need to save space then using LZW and ZIP will be fine without affecting your images.
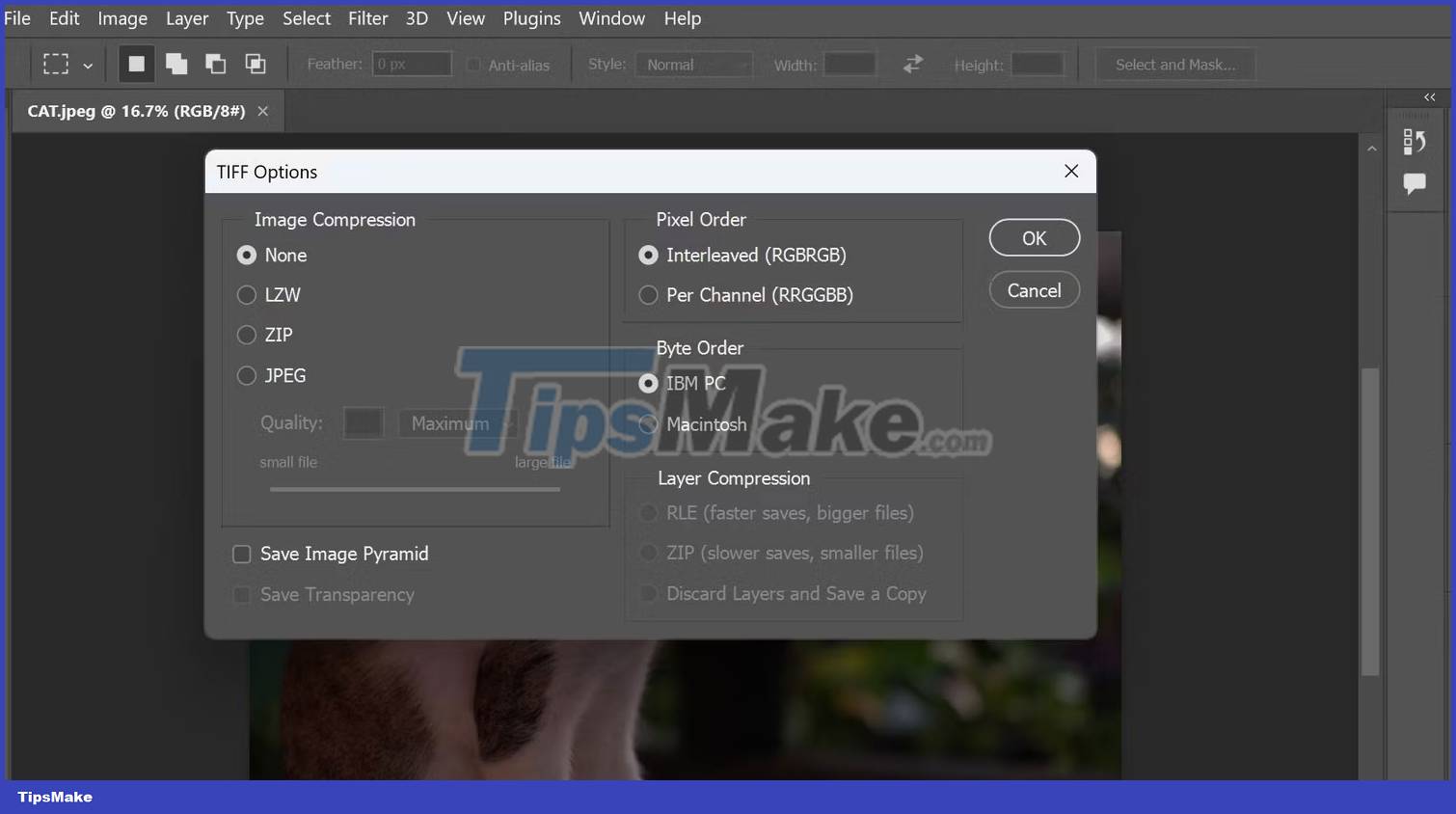
As for Pixel Order, Interleaved is sufficient for most projects, while Per Channel allows you to individually manipulate specific color channels, which is great for color grading applications. After setting your preferred options, press OK and the project will be saved as TIFF.
For those working on multiple images, you can also do batch conversions in Photoshop. To do so, put all your images in one folder. Then open Photoshop and click File > Scripts > Image Processor.
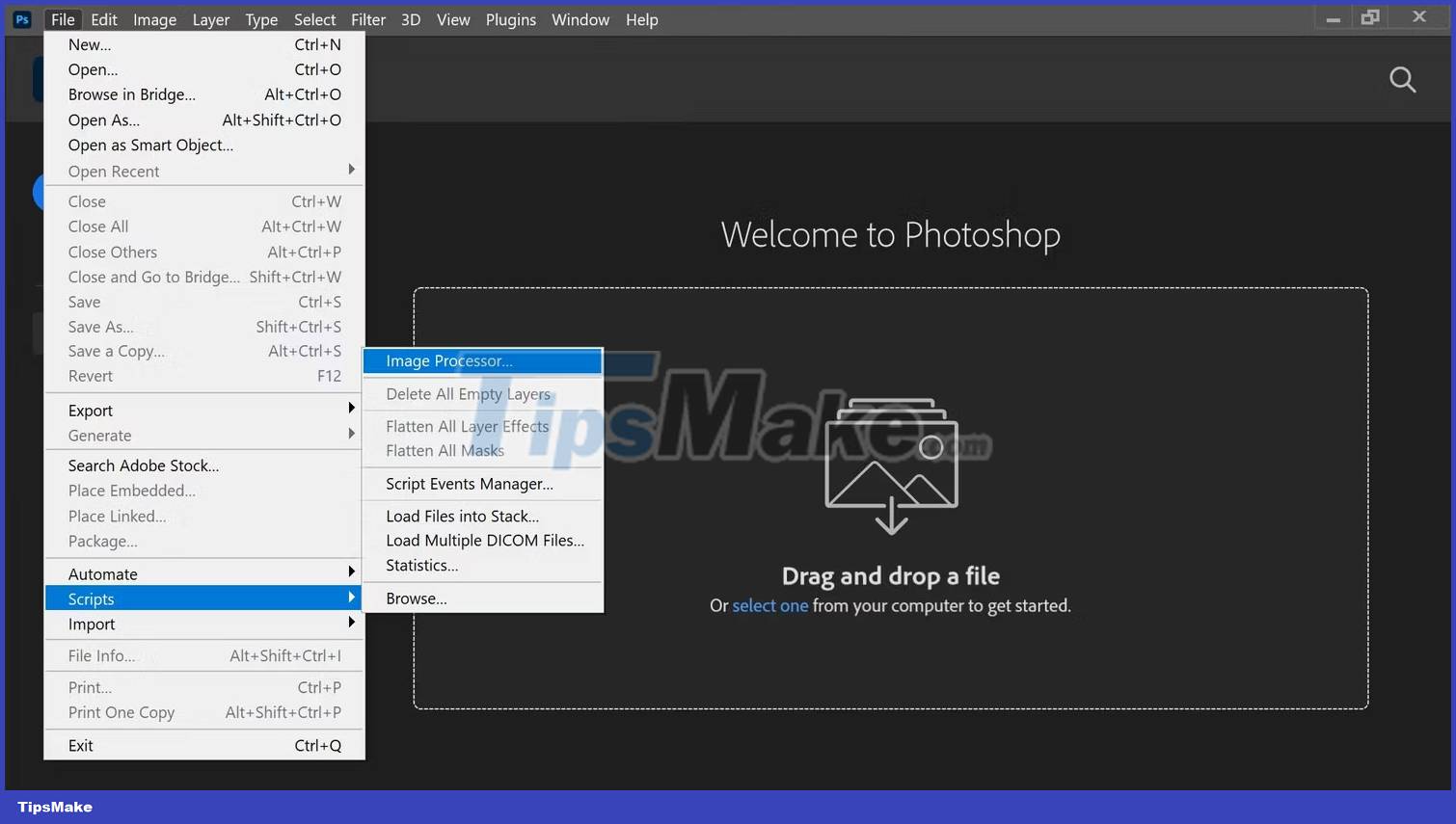
You will be prompted with the file installation menu. The menu will be numbered into 3 parts: Select folder, select image location, select file type and additional options. Go ahead and select the folder where you placed your images, then the location where you want to save the TIFF file, and finally check the Save as TIFF box in the File Type area.
If you want to make TIFF files use less memory, you can also check the LZW Compression option. After all that, double check your settings, then hit Run.
As you can see, TIFF files will take up more space than the original files. Make sure you always have enough storage space before creating TIFF files because they take up a lot of space.
If you're in a hurry, you can also convert images to TIFF using your operating system's default image viewer. This is possible for Windows, macOS, and most Linux distributions.
Just open your image in an image viewer, then right-click on the image or press Ctrl + S on your keyboard to bring up the Save as option. Click Save as, give it a name, select TIFF from the drop-down menu, then click Save. It is done! You have created a TIFF file using your built-in image viewer.
How to open TIFF files
You will have no problem opening TIFF files on your computer. The good thing about TIFF is that you can view TIFF files like any other file. Just double-click the TIFF and it will load into your default image viewing software.
You can also open TIFF files directly in your favorite image processing software the same way you usually do with regular images. In the case of Photoshop, click File > Open then select the TIFF file.
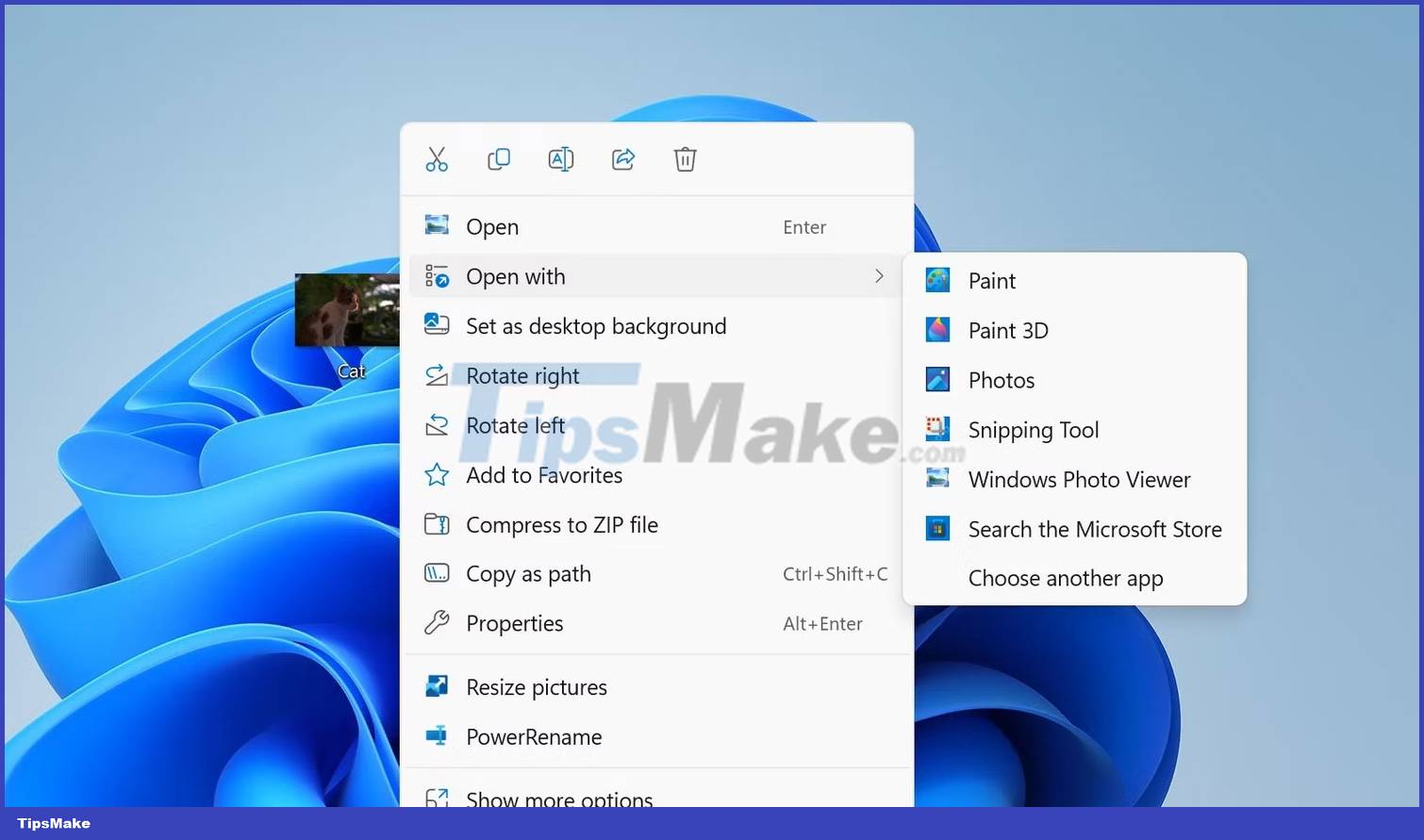
But what happens if you're deep in a folder and find a TIFF file that you want to open in your editing software? To open the file in your editor, right-click the TIFF file, select Open with, then choose your image editor.
If your preferred image editor isn't in the selection, click Choose another app, then scroll down and click Choose an app on your PC. This will open the file manager. Now, find your application in the program files on your computer, then click Open.

This will load the TIFF files directly into your editing software, and add the program to the selection the next time you open the TIFF file.
What are TIFF files used for?
In fact, beginners and common people don't even know about TIFF files. If you see this file in the system, many people will be worried when opening the file and think it is a virus. In fact, many people never use TIFF files. People usually only work with JPG, PNG, GIF, BMP images. This format is often popular among artistic people such as photographers, graphic designers, geographers, medical professionals, scientists, etc.
Newspapers or magazines need to print accurate and high-quality news in large format, without losing image quality, so the TIFF format is quite popular.
Photographers take landscape photos of city hills and valleys, then store them as TIFF files or RAW files.
Scientists have used TIFF to save scientific images, helping all the data to be perfectly preserved. This file is also used as a primary format in digital image processing.
In the medical industry, X-ray images are often saved as .tiffs or DICONDE when performing a CT study.
Advantages of TIFF files
Some advantages of TIFF files are as follows:
1. TIFF supports lossless compression.
2. TIFF format preserves image quality.
3. Major operating systems support the TIFF format and have software available to open it.
4. TIFF files allow saving multi-page documents to help complex documents be saved into a single .tiff file.
5. TIFF files are device and processor independent file formats that can be moved between devices.
6. TIFF supports images with many resolutions. These images have different resolutions for each part of the image.
7. TIFF is extensible, so new improved specifications can potentially be added without affecting download compatibility.
8. TIFF uses tags to make finding text inside TIFF images easier. This facility is not provided by JPG and PNG image formats.
9. TIFF files can store many different image types such as Bilevel (B/W), Grayscale, Palette-Color, RGB full color
Disadvantages of TIFF files
1. TIFF file capacity is larger than JPEG, PNG and WEBP images.

2. It takes a long time to transfer TIFF files over a slow Internet connection because the file size is very large.
3. The TIFF file handler must read all tags to interpret and gather image data processing information. Therefore, if a large number of tags are used, reading may take time.
4. Additionally, TIFF files are not used in web and web pages. Firefox and Chrome cannot open these files correctly, or even at all.