The 5 best options to run Android on Raspberry Pi
Working on a Raspberry Pi project that needs more than a standard Linux desktop? Here are some ways you can use Android as your Raspberry Pi OS.
Why install Android on Raspberry Pi?
If you are using a touch screen setup then the default Raspberry Pi OS desktop (LXDE based PIXEL) is not suitable. Whether you're using a small touchscreen, a standard Raspberry Pi touchscreen, or some other display, Android is the ideal solution.
Even better, you have access to the largest software library possible. Productivity tools, streaming media applications, games are all available. (However, you will be limited by the hardware limitations of your Raspberry Pi model).
Meanwhile, if you don't use a touchscreen, you can connect a mouse and keyboard, just like you would with any other Android device.
Note: Use the normal method of installing Raspberry Pi OS to try these Android builds unless otherwise stated.
5 Android Raspberry Pi builds you can try
The following Android versions for Raspberry Pi 3 are available for download:
- LineageOS
- AOSP
- OmniROM
- EmteriaOS
- Android TV is based on LineageOS
With one of these services installed, you can have access to regular Google services or keep things more private.
Note: Installing apps on a Raspberry Pi running Android requires installing GApps or relying on a third-party store like F-Droid.
All this makes Android the perfect solution for many Raspberry Pi projects. Here are the options to consider when installing Android on Raspberry Pi.
1. LineageOS
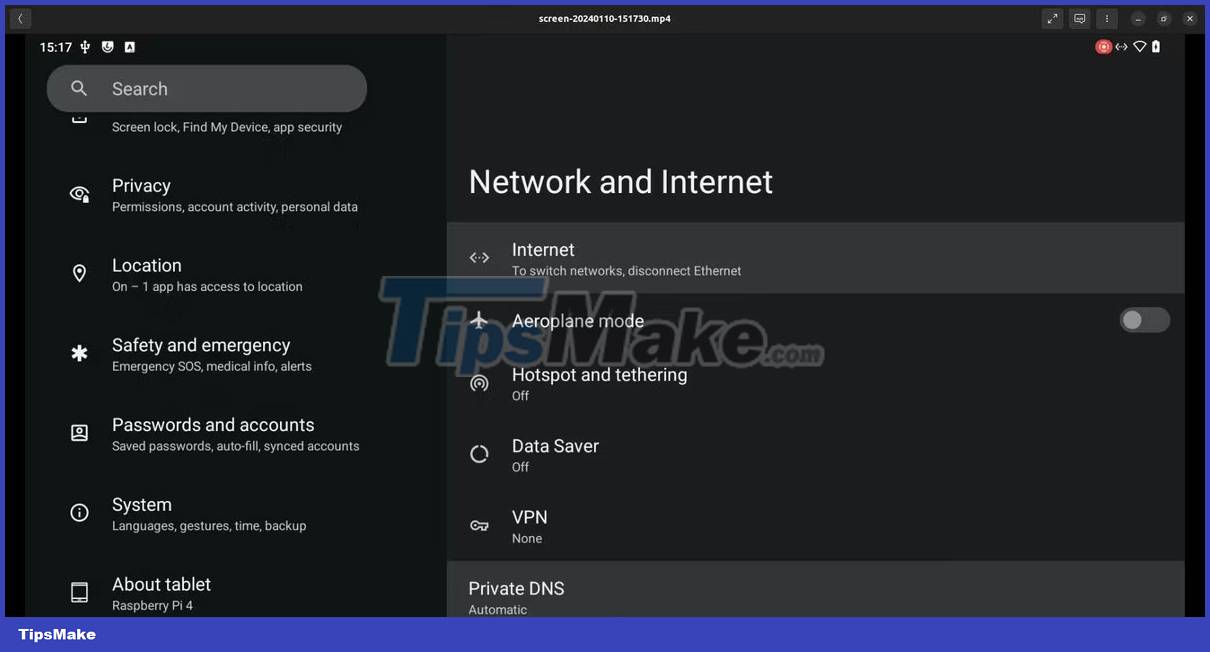
Perhaps the most famous custom build of Android is LineageOS, available for a number of handsets. Thanks to a developer named KonstaKANG, LineageOS is available in various builds for several Raspberry Pi models.
It is available for Raspberry Pi 3 (LineageOS 17) and Raspberry Pi 4 (as LineageOS 20), with Android 14 available for the latter version. (LineageOS 20 will also run on Raspberry Pi 400 and CM4 models).
- Download |
Standard Raspberry Pi SD flashing steps are required to install LineageOS. However, if you need Google Apps, the GApps package will also need to be flashed. Each build of KonstaKANG has slightly different steps, so check these out before continuing.
2. AOSP
Android Open Source Project (AOSP) is the source of Android. As the name suggests, this is an open source project built by Google, Samsung, Huawei, etc. for you to find on your phone, tablet or TV.
Because it is open source, AOSP can be adapted by any developer. KonstaKANG's efforts have resulted in an AOSP-based Android build for the Raspberry Pi 5 (a build for the Pi 4 is also available).
- Download |
You can install AOSP using any of the usual methods. Like LineageOS, you'll need the GApps package if you want a 'Google-like' Android experience.
3. OmniROM

For a long time, the development team behind OmniROM has been providing alternative Android builds for specific phones. As of 2022, the project has expanded to include the Raspberry Pi 4.
Based on AOSP, OmniROM has a native Pixel UI and is installed in two parts. For best results, you will need a standard microSD card for the Raspberry Pi (to install the TWRP recovery software) and the appropriate OmniROM build. At the time of writing, the latest build was released in March 2023 for Raspberry Pi 4.
- Load
Installing OmniROM is arguably the most difficult process on this list. It requires you to download and flash the master recovery image to a microSD card, then flash the build you want to run from the USB stick. This is a bit complicated but the result is that Android on Raspberry Pi 4 works fine.
4. Emteria
As an alternative to OmniROM, Emteria is a specialized Android build for a narrow group of devices. This list includes Raspberry Pi CM 3 and CM 4 models, as well as Raspberry Pi 3, 4, and 5 boards.
Installing Emteria is very simple as you can find it in the Raspberry Pi Imager tool.
- Load
With the tool installed and the microSD card inserted into your PC:
- Click Choose Device to select your Raspberry Pi model.
- Click Choose OS.
- Access Freemium and paid-for OS.
- Click Android by emteria.
- Choose Android 13 or Android 14 for Raspberry Pi 4 or Android 14 for Raspberry Pi 5.
- Click Choose Storage to select the microSD memory card
- Click Next to proceed with the installation
Note: You can configure additional settings post-installation by accessing Raspberry Pi Imager's advanced options with Ctrl + Shift + X.
Emteria offers a variety of subscription options, but the basic Starter plan is free and offers over-the-air system updates.
5. Android TV
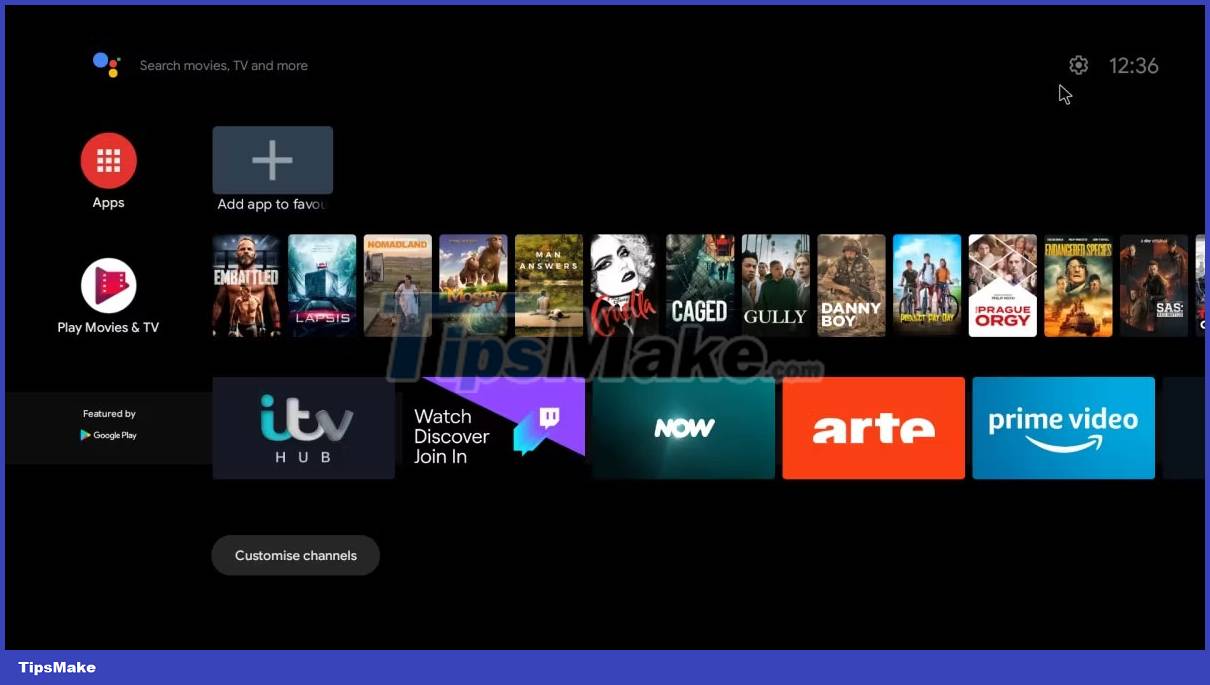
What's amazing is that KonstaKANG also produces an Android TV build (using LineageOS 20) specifically for Raspberry Pi 4.
- Load
This is designed for use with media center projects and includes everything you need to get started right away. No need to install additional software; you don't need to install GApps for this, just install your favorite streaming apps.
With the Raspberry Pi 4 and Raspberry Pi 400 models, this Android TV works surprisingly well.
You should read it
- ★ Comparing Odroid-N2+ and Raspberry Pi 4: Which option offers better value?
- ★ How to use the advanced options of Raspberry Pi Imager
- ★ How to add an ADC to Raspberry Pi: What you need to know
- ★ Troubleshooting Raspberry Pi not reading SD card
- ★ Raspberry Pi Zero vs Model A and B, how are they different?