Managing certificates in Exchange - Part 2
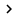 Managing certificates in Exchange - Part 1
Managing certificates in Exchange - Part 1
Network Administration - In this section we will introduce the requirements that need to be considered when working with certificates.
Introduce
Certificates can be used to encrypt communication data streams between two end points, which can be clients and servers. They are also used by endpoints to authenticate themselves. There are several components in Exchange 2007 that rely on certificates for encryption and authentication. In the first part of this article series, I talked about an overview of Exchange components that use their certificates and their uses. In addition, the first part also introduces some features of the default self-signed certificate. In Part 2 of this series, we will introduce the requirements of a certificate you need to know when working with them. To conclude, in part three of this article series, I will give you a closer look at the Exchange Management Shell commands used to create, manage, and delete Exchange certificates.
How to trust the self-signed certificate?
As introduced in part 1 of this series, it is possible to configure Exchange to use a self-signed certificate for internal scenarios. To ensure that your clients do not encounter any security warning messages when connecting to the Exchange 2007 Client Access server, you need to make the user trust the self-signed certificate. Remember, it is not an absolute perfect idea to educate users to remove security warnings! Figure 1 shows that the Self-Signed certificate is not trusted when using Outlook Web Access.
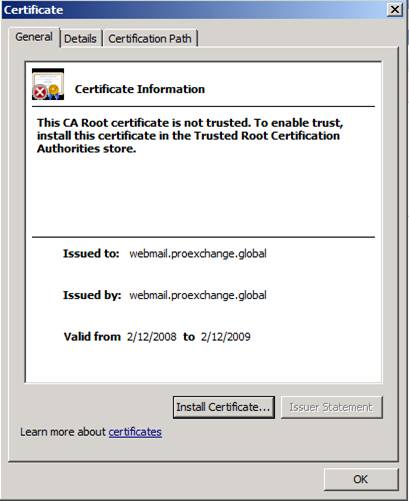
Figure 1: Self-signed certificate is not trusted
There are several methods to ensure that a user who recognizes a self-signed certificate is a trusted certificate. However, we will only introduce one method, which is the method that does not require any action from the user itself and this method publishes a self-signed certificate using Group Policies. Note, however, that you still need to repeat this action every time you renew the self-signed certificate!
Export self-signed certificate
To export a self-signed certificate, you can use the Export-ExchangeCertificate command. Since this command will group the private key automatically, you need to define the password, you can see the example we did in Figure 2. Note that you can only export the self-signed certificate if marked a certificate to obtain a private key with export capability (see introduction in section 1).
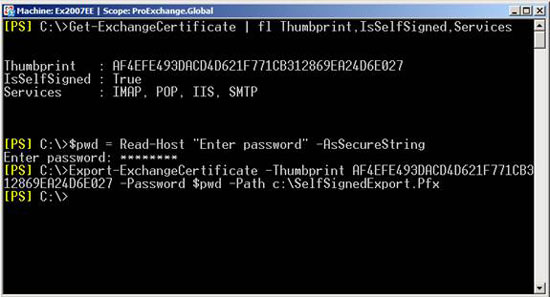
Figure 2: Export certificate
Publish the certificate as a trusted certificate through Group Policy
You can publish an exported certificate in the user's personal repository using Group Policy. In the example below, we used the Group Policy Management interface to create a new policy and apply it to the domain (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Creating and linking a new GPO to the domain
We call the new GPO Trust Self Signed Certificate and do not use any Source Starter GPO (Figure 4).
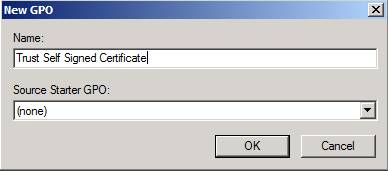
Figure 4: Name of the new GPO
Because we want to import an exported self-signed certificate, go to User Configuration, Policies, Windows Settings, Public Key Policies, and right-click Trusted People to launch the Certificate Import Wizard (see Figure 5).
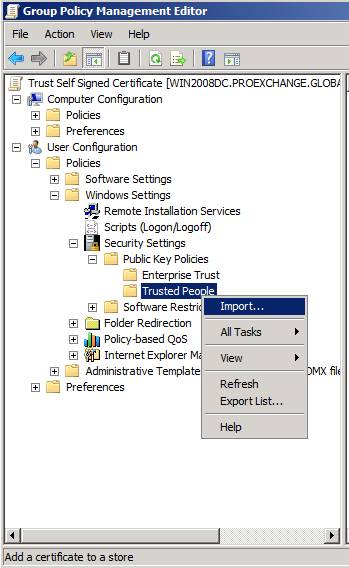
Figure 5: Launch the Certificate Import Wizard
Specify the previously created file by running Export-ExchangeCertificate, and click Next (Figure 6).
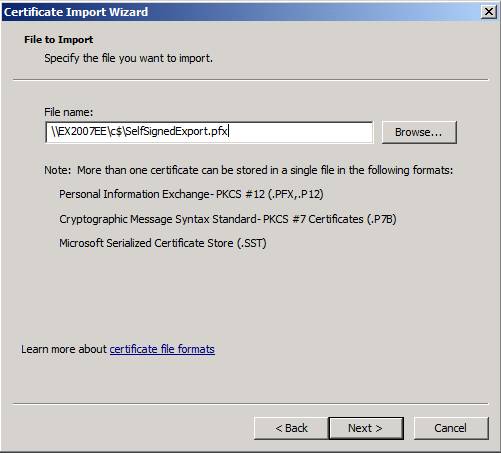
Figure 6: Select File to Import
Next, enter the password that was used to export the private key, then click Next to continue (Figure 7).
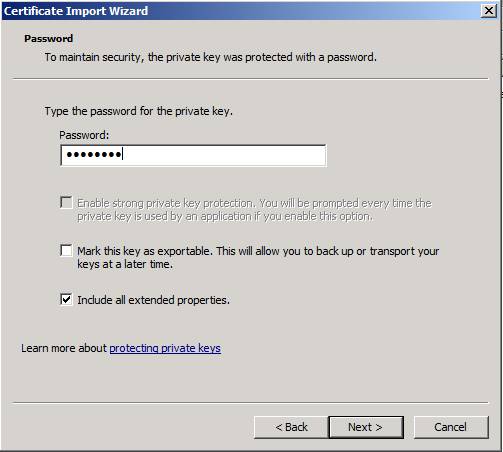
Figure 7: Typing the password used to protect the private key
The certificate store will be set to Personal Store, click Next to continue (Figure 8).
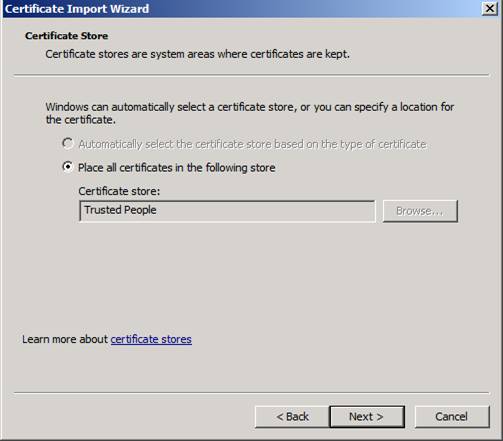
Figure 8: Select where to store the certificate
To finish, click Finish after reviewing the settings (Figure 9).
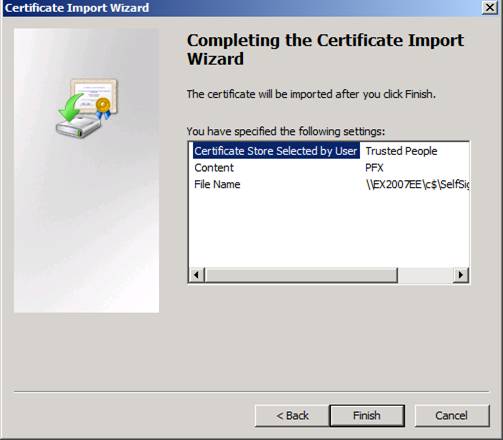
Figure 9: Complete the Certificate Import Wizard
The Certificate Import Wizard will tell you that the import process has been successfully performed. When you click OK and import is done, Group Policy is now ready for you to use (Figure 10).
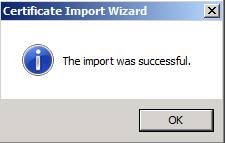
Figure 10: The import process is successful
The next time the user logs in to the domain, or refreshes the group policy, then the self-signed certificate will be trusted. You can see when increasing access to Outlook Web Access (Figure 11).
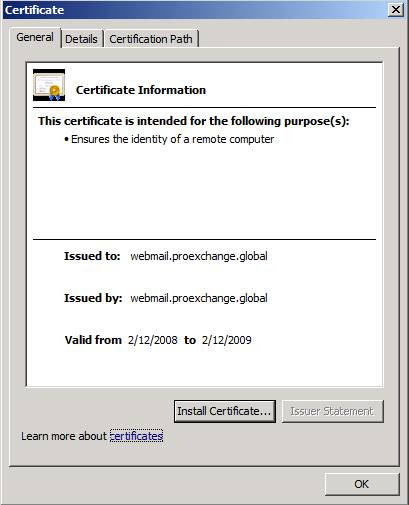
Figure 11: Self-signed certificate has been trusted
Get a certificate from a public assessor
Although Exchange 2007 has the ability to create a self-signed certificate during the installation process, you can enable clients to trust it, but keep in mind what was introduced in part one:
- Self-signed certificates are only valid for one year
- The self-signed certificate is only trusted by its issuer
- Self-signed certificates are not supported for Outlook Anywhere without Exchange ActiveSync
So you need to get a certificate from the appraiser. You can deploy your own certification authority or get a certificate from a public assessor. The second way is advised by Microsoft in the following situations:
- Access external clients to Exchange (POP, IMAP, Outlook Web Access, Outlook Anywhere, Exchange ActiveSync, Autodiscover)
- If you want to install Domain security with partner organizations
If you get a certificate from a public certificate authority, you will take a lot of hassle in letting the certificate authority recognize a certificate trusted by clients that have not yet entered the domain, and the The partner organization wants to configure domain security for the Exchange environment.
Microsoft has published an article titled Unified Communications Certificate Partners for Exchange 2007 and for Communications Server 2007, which provides a list of Unified Communications Certificates issued certificates for Microsoft Exchange and for Communications Server 2007. , can be used to deploy Domain Security features.
What is a public certification examiner?
A public certificate authority is a certificate issuer trusted by all mainstream browsers and applications. When deciding to get a certificate from an appraiser, you need to consider whether the public certification authority is trusted by all the applications you will use and see if it can allow you to get a certificate. only you need (mention name, valid date and, .)
Name in a certificate
Observe a certificate and why a certificate is not acceptable to be used for encryption and authentication by Exchange, it is encapsulated into one of the following reasons:
- The security certificate must be issued by a trusted certificate authority;
- The security certificate must not be revoked by the reviewer who issued it;
- The security certificate must not expire;
- The security certificate comes with a name that does not match the expected name.
Although some applications such as Outlook Web Access allow you to use a certificate that is not even issued by a trusted appraiser or a security certificate that has been issued to a different website address, the user remains Don't ignore these warnings because it's almost like someone or some process wants to attack you or block your data (Figure 12).
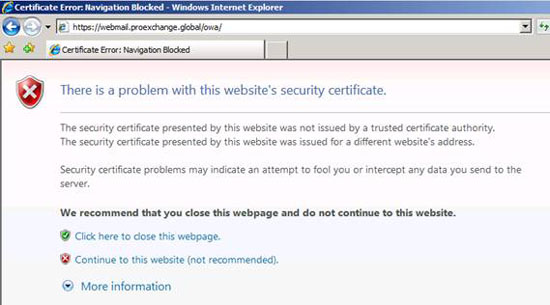
Figure 12: Security certificate warning
Outlook Anywhere and Exchange ActiveSync will not work if there is a problem with the certificate (Figure 13).
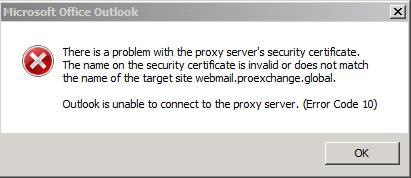
Figure 13: Outlook Anywhere fails when connecting because the name of the security certificate does not correspond to the name of the target site.
We have to consider the names you need for a security certificate for your Client Access server:
- NetBIOS name of Client Access server;
- Full Qualified Domain Name of Client Access server
- Autodiscover domain of Exchange organization
- The name is used to publish Outlook Web Access, Outlook Anywhere, Exchange ActiveSync, Pop, or IMAP to other external computers.
The names you need for a security certificate for the Hub / Edge Transport server:
- Fully Qualified Domain Name
- All domains are accepted in the Exchange organization.
And with the Unified Messaging server, you only need Fully Qualified Domain Name of the Unified Messaging server role.
Example situation
Imagine you have an environment as shown in Figure 14 below.
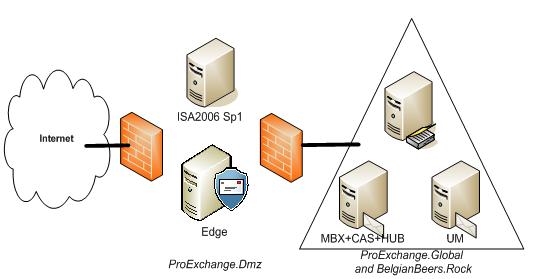
Figure 14: An example Exchange organization
In this Exchange environment, you will publish both Outlook Web Access and Outlook Anywhere using the ISA server located at the DMZ. Mails sent to and from the organization will go through the Exchange Edge server role, also placed in the DMZ. Your Exchange organization has two domains that are responsible for it: ProExchange.Global and BelgianBeers.Rock. You have agreed to configure Domain Security between your Exchange organization and one of your partner organizations Sunshine.Edu. EdgeSync is configured to create a copy of your configuration and recipient information into the Edge server. You will obtain two certificates from a public CA, one to publish Outlook Web Access and Outlook Anywhere and one to establish domain security between the Exchange organization and Sunhine.Edu.
Table 1 lists the Exchange servers that exist in this Exchange environment and their roles.
FQDN Exchange ServerThe role has been installed
Edge.ProExchange.dmz
Edge Server role
Ex2007EE.ProExchange.Global
Mailbox + Client Access + Hub Transport server role
Ex2007SE.ProExchange.Global
Unified Messaging role server
Table 1
Look closely at your Exchange organization showing the URLs listed in Table 2 that have been used externally and internally by users who connect to their mailbox.
Connecting toConnect using HTTP (s)
Connect with RPC
Outlook Web Access
https://webmail.proexchange.global
https://webmail.belgianbeers.rock
https://Ex2007EE.proexchange.global
Outlook Anywhere
https://webmail.proexchange.global
https://Ex2007EE.proexchange.global
Free and Busy information
https://webmail.proexchange.global/EWS/Exchange.asmx
https://Ex2007EE.proexchange.global/EWS/Exchange.asmx
Download OAB
http://webmail.proexchange.global/OAB
http://Ex2007EE.proexchange.global/OAB
Change Unified Messaging settings
https://webmail.proexchange.global/UnifiedMessaging/Service.asmx
https://Ex2007EE.proexchange.global UnifiedMessaging / Service.asmx
Autodiscover
https://autodiscover.proexchange.global/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
https: //autodiscover.belgianbeers.rock/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
https://Ex2007EE.proexchange.global/Autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
Table 2: URLs
These URLs are also retrieved and changed using the Exchange Management Shell. Figure 15 shows the command to retrieve the URLs provided by Exchange Web service Autodiscover for Microsoft Office Outlook 2007 clients.
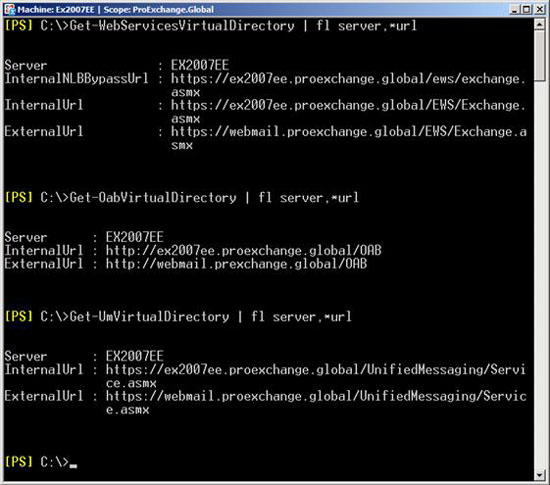
Figure 15: Configuration settings for InteralUrl and ExternalUrl
Table 3 lists the records that are registered in DNS
NameType
Data
Autodiscover.ProExchange.Global
Alias (CNAME)
Webmail.ProExchange.Global
Autodiscover.BelgianBeers.Rock
Alias (CNAME)
Webmail.BelgianBeers.Rock
Webmail.ProExchange.Global
Host (A)
External IP ISA Server
Webmail.BelgianBeers.Rock
Host (A)
External IP ISA Server
ProExchange.Global
Mail Exchanger (MX)
[10] Edge.ProExchange.Dmz
BelgianBeers.Rock
Mail Exchanger (MX)
[10] Edge.ProExchange.Dmz
Edge.ProExchange.Dmz
Host (A)
External IP Edge Server
Ex2007SE.ProExchange.Global
Host (A)
10.10.10.102
Ex2007EE.ProExchange.Global
Host (A)
10.10.10.101
Table 3: Logs registered in DNS
To enable secure access to Outlook Web Access and publish Outlook Anywhere, the following names must be present on the certificate that you will enable for the IIS service on the Client Access Server inside and export to the ISA 2006 server. Sp1:
- Common Name = Webmail.ProExchange.Global, Outlook Anywhere requires generic name to match the external host name used to activate Outlook Anywhere
- Subject Alternative Names:
Webmail.ProExchange.Global
Webmail.BelgianBeers.Rock
Autodiscover.ProExchange.Global
Autodiscover.BelgianBeers.Rock
Ex2007EE.ProExchange.Global
Ex2007EE
Ex2007SE.ProExchange.Global
Ex2007SE
To enable EdgeSync, provide TLS and configure domain security with partner organization Sunshine.Edu, you need a certificate for the Microsoft Exchange Edge server role with the following names:
- Common Name = Edge.ProExchange.Dmz
- Subject Alternative Names:
ProExchange.Global
BelgianBeers.Rock
Conclude
This is all introduced in part two. In Part 3 of this series, we will give you detailed steps on how to create a certificate request with Subject Alternative Names and how to import and activate the certificate obtained for translations. Exchange service.
You should read it
- ★ Apache 2 supports SSL / TLS: Step-by-step instructions (continued Part II)
- ★ What kind of SSL certificate does your website need?
- ★ What's new in SQL Server Management Studio 18.7?
- ★ Execute and troubleshoot certificate deployment issues in ISA Server 2006 - Part 2
- ★ Secure the installation of ISPConfig 3 with Certificate Class1 SSL of StartSSL