Execute and troubleshoot certificate deployment in ISA Server 2006
Network Administration - In this series, we will introduce you to some basic knowledge about certificates and certificate authentication. How to use certificates in some reverse proxy scenarios and how to troubleshoot problems in using certificates as well as recovering.
Let's start with some basic knowledge about PKI, digital certificates, and certificate authorities.
PKI
In cryptographic terms, a public key infrastructure (PKI) is an architectural block built for a number of technologies for the purpose of issuing certificates to users, computers, and services. from a certificate authority (CA). The PKI role in issuing certificates is called the Registration Authority (RA).
Certificate
A public key certificate (or a certificate of identity) is an electronic document combined with a digital signature to bind a public key to identity information such as the name of a person or organization as well as their address, . The certificate can be used to verify a public key belonging to an individual or an organization. In a typical public key infrastructure (PKI) scheme, the signature will be verified by the certificate authority (CA).
CA certificate authentication
A CA certificate authority is a server or a set of servers in a CA organization whose systems issue digital certificates to users, computers, and services. Windows Server 2003 (and older versions) have their own CA implementation.
Certificate authorities can be a server or can be serialized into certificate chains, where architectures have special tasks like intermediate CA, issuing CA, etc. You can refer to an ant. CA structure in Figure 1 below.

Figure 1: CA architecture
Dynamic files are used in encryption
There are several extension files used when you work with ISA Server 2006 and certificates. Here are some examples:
lock upDescribe
CKS # 12
Private Information Exchange
.PFX
Private Information Exchange
.P12
Private Information Exchange
PCKS # 7
Cryptographic Message Syntax Standard
.P7B
PCKS # 7 certificate
.CER
DĐ-mã-mã X.509
Base-64-coded-X.509
.PFX
Private Information Exchange PCKS # 12
.CRL
Certification Revocation List
.P7C
Digital ID-file
.P7M
PCKS # 7 MIME-message
.P7R
PCKS # 7 certificate
.P7S
PCKS # 7 signature
Table 1: PKI extension files
Install CA
Installing and commissioning a CA is an easy process. What makes PKI designs so complex is that some applications use PKI for some purpose.
In this article we will not introduce you to the entire installation process, but just introduce some basic images.
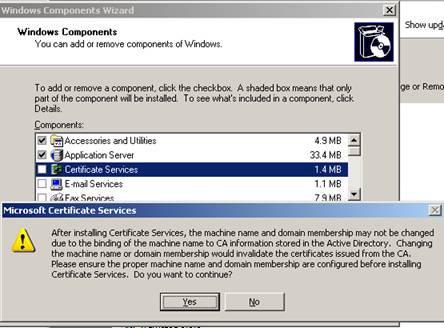
Figure 2: Installing a Windows CA
After installing a CA, do not change the Server name and domain member (If you feel this is required, please refer to some other articles to provide you with a way to switch CA).
There are several types of CA. For this example, we select a Enterprise Root CA that integrates into Active Directory.
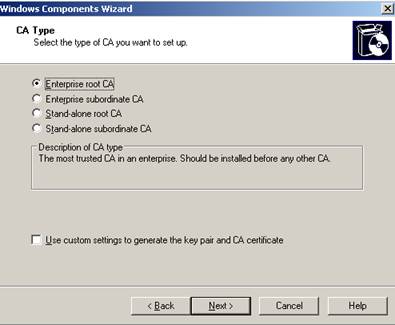
Figure 3: Select CA type
Name the CA and file name
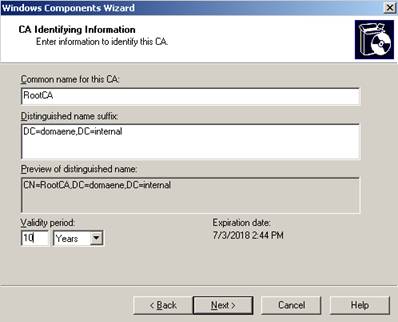
Figure 4: CA name
After installing CA, CA can be used for issuing certificates.
Snap-In for certificates
Modern Windows versions all have a certificate Snap-In used to manage locally installed certificates. If you are logged in as an administrator, you can manage certificates for your own user account, a service account, and a computer account.
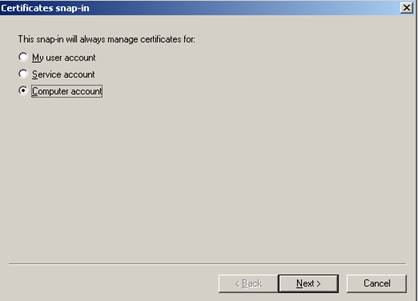
Figure 5: Managing certificates
A normal user account can only open its own certificate store.
Certificates can be managed in the console (Import, export, request new certificate and delete certificate).
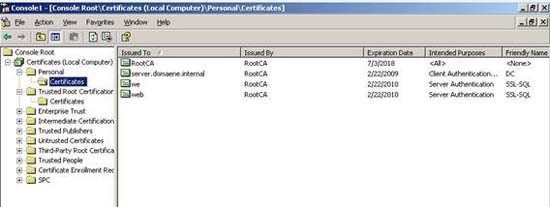
Figure 6: Managing certificates
There is a website that can be used to request new certificates or to download the original CA certificates.
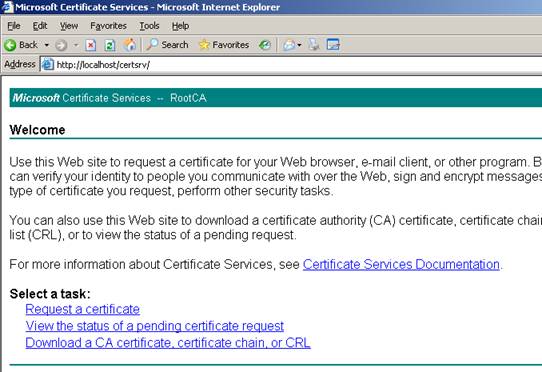
Figure 7: CA website
Settings in the reverse publish script
If you want to use ISA Server as a reverse publishing proxy to publish services such as Outlook Web Access (OWA) or Outlook Anywhere (OA), it is possible to enable SSL Bridging to enhance the security of ISA Server. . When SSL Bridging is enabled, ISA Server will stop connecting SSL from the server to the client; ISA will then check the traffic and encrypt HTTPS traffic. This is the safest scenario.
In this scenario, ISA server needs a Root CA certificate from the internal CA that issued certificates to the server to publish. ISA Server also needs a certificate for the ISA listener that Common Name (CN) has the same entry as the public name that clients enter when they want to establish a connection with the public server.
During the publish process, ISA Server 2006 has new certificate support to help you choose the correct certificate.
The certificate must be issued from a trusted CA, the certificate must be valid and closer to the Common Name of the certificate. CN must be valid with the public name that clients can use to connect to the server.
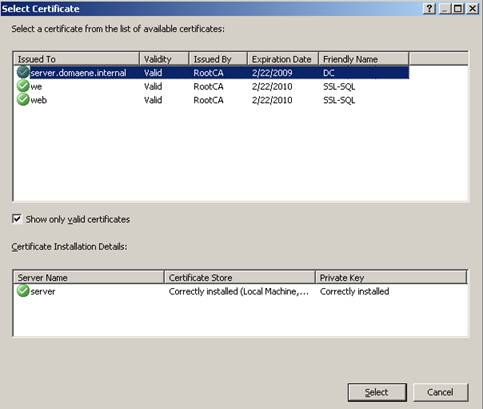
Figure 8: Certificate support
Bridging feature in ISA Server 2006
Have you ever tried to use the Bridging feature in publish rules? If you want to choose a certificate, ISA will often say no certificate?
To solve this problem, you must issue a user certificate for ordinary users. This issued certificate must be imported (with a private key) into the internal certificate store of the Microsoft ISA Server Firewall service. You can then use the certificate to direct the request to the internal server requesting certificate authentication.
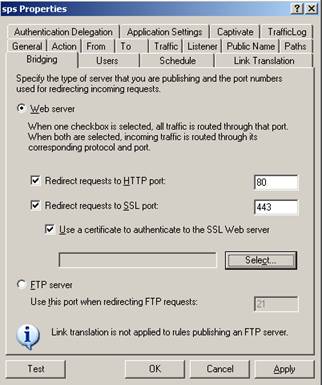
Figure 9: SSL Bridging
There is no certificate available because there is no certificate installed in the internal certificate store of the ISA Server Firewall service.
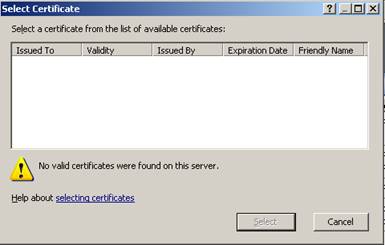
Figure 10: SSL Bridging - choose a certificate
Cancel the certificate
Certificate cancellation is a process in which the application requires a certificate chain management machine to evaluate the certificate, the revocation can be performed for all certificates in the chain. Include all certificates that are being issued from a CA to issued certificates. As a first step, the certificate chain will be evaluated. If the certificate chain is still unaffected, the process will check that:
- The certificate signature is valid
- Verify the current time from when the certificate has valid time.
- Verify each certificate is not error-free or not modified.
The certificate revocation list does not contain valid certificates. A process or software like ISA Server can check the required certificates using the certificate revocation list.
Users can configure ISA Server for a few legitimate requests. ISA Server can verify that incoming certificates are not in the certificate revocation list (CRL).
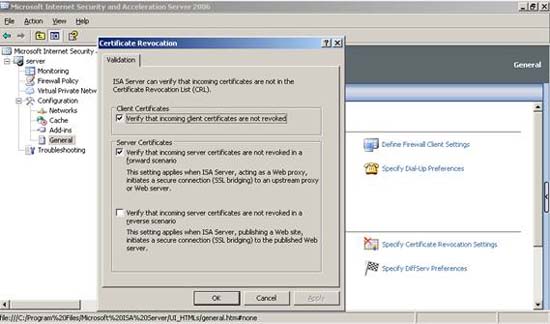
Figure 11: Cancel the certificate
Verify that incoming client certificates không phải đánh dấu
Verify that client certificates are not revoked
You must select this certificate if you want to allow ISA Server to perform the verification of the incoming certificate in the Certificate revocation List (CRL) list to see if the certificate has been revoked. If the certificate has been revoked, the client request will be rejected.
Đang xác định các máy phục vụ này không được xác định trước khi thực hiện một tiến trình Forward
Verify that the server certificates sent are not revoked in the forward scenario
This option is slightly different from the above scenario. In this scenario, ISA server checks to see if the incoming Server certificate in the SSL Bridging scenario is revoked. If the certificate is revoked, the request will be rejected.
Verify đó vào máy phục vụ các certificate không thể bỏ qua trong một reverse scenario
Verify that incoming server certificates are not revoked in the reverse scenario
Select this check box to specify whether ISA Server will automatically check for Certificate Revocation List (CRL) to see if the server certificates, in the Web publishing scenario are revoked. If the certificate is revoked, the request will be rejected.
Conclude
In this first part, I have shown you all aspects of using certificates in ISA Server 2006 for reverse publish scripts for Outlook Web Access (OWA), Outlook Anywhere (OA), and so on. There are some basic knowledge about certificates, certificate authorities, and certificate verification.