Learn about Micro applications in Linux
For Linux users, Vi - text editing application is one of the indispensable support tools . Unlike Nano - a text editing application in Terminal format, Vi has a variety of useful and functional shortcut keys, with 2 main modes of operation: Insert and Command.
Micro editor in Linux
- Open Micro on Linux
- Command mode
- Insert mode
- Saving and Quiting
- Write a very small C program using Vi
- Common options for opening files in Vi
- Move between characters
- Common commands in Vi
- Copy and paste command in Vi (Practice!)
- Advanced micro command
- Work with two or more files (Practice!)
Open Micro on Linux
Vi is actually a Terminal application, so you will have to boot from the corresponding Terminal window. Use the vi / path / to / file syntax to open the text file available with Vi, and the command will also work if the specified text file is not available, instead Vi will create a text file with that name. .

Note that we need to use the sudo command if we want to modify the file system, for example, if we want to edit the system's Fstab file, type:
sudo vi / etc / fstab
If you use a non-Ubuntu operating system version of Linux, replace sudo with su .
Command mode
Here is the image when we open the file with Vi, it looks like we can type the character here, but it's not really. Vi is actually a drafting application, and is opened in Command mode:
When in Command mode, we can move the cursor by pressing the arrow key, pressing x to delete the character just below the cursor, and pressing dd to delete the entire character line. Besides, you can choose, copy, cut and save the text in this mode. Move the cursor to the left or right of the letter to copy and press the v key, press x to cut the text, then place the cursor where you need to move the text and press p to paste:
Insert mode
This is Vi's operating mode that allows users to insert characters into the text. Just press the I button we have switched to Insert mode after defining the cursor position in Command mode:
When entering the necessary text, press the Escape key to return to Command mode.
Saving and Quiting
You can save and exit the application in Command mode (press Escape to make sure we are in this mode). Type: wq to save the file after changing and closing Vi, or executing it separately into 2 steps: w to save the file and: q to exit the program without saving the changes:
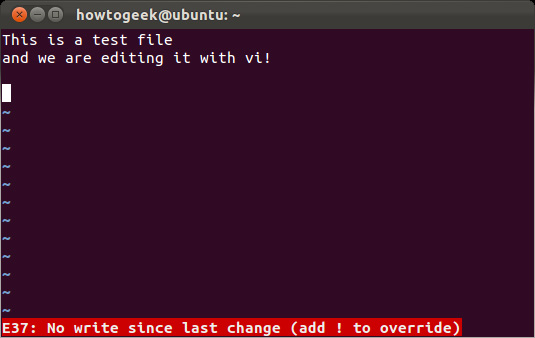
But Vi will not let the user close the application if it has changed since the last save, type: q! And press Enter to ignore this warning:
Write a very small C program using Vi
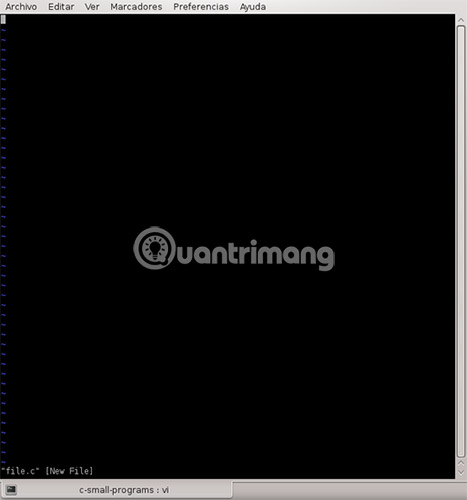
Open a Terminal.
Please enter:
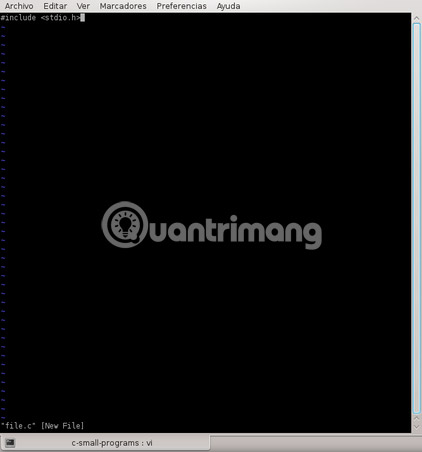
vi file.c This will create a new file.
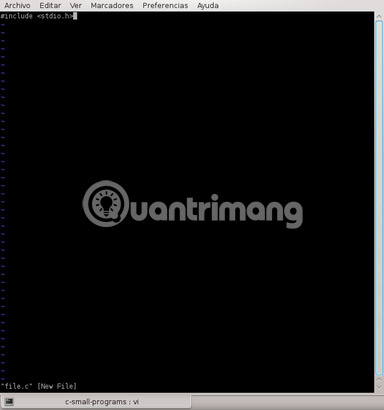
Vi in Command mode by default. So if you want to write something, you can't do this.
Type 'i' to be able to write your code.
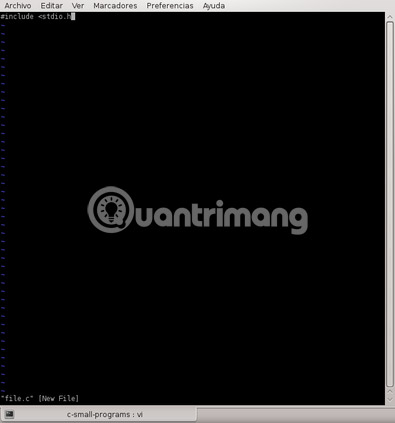
Now, you will be in Insert mode , but if you want to delete a character, you cannot do it.
Type ESC to change to Command mode.
In Command mode, type 'x'. This will delete the character under the cursor.
You can insert a character to the left of the cursor by typing 'i'.
You can insert the character to the right of the cursor by typing 'a'.
Insert a '>' in the text.
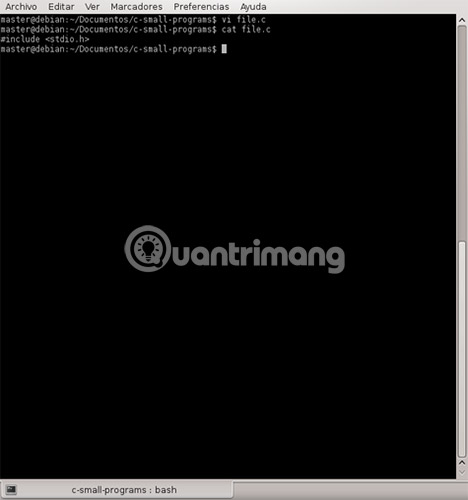
Return to Command mode and type : wq, then return:
wq Now you are at the command prompt. Please see the contents of your file using cat.
You may be thinking that Vi is very complicated, but in reality it is not. Vi is a fairly simple editor, but it can only work in a single mode at a time.
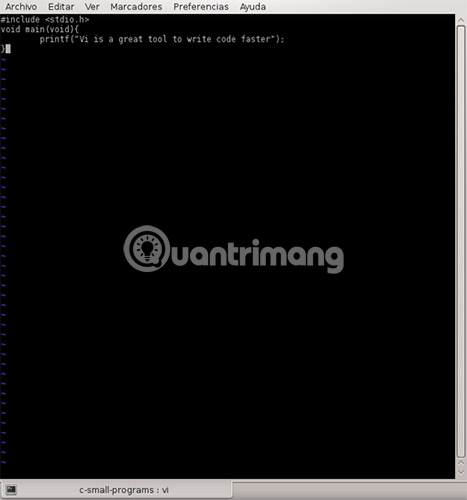
Re-open your file ( vi file.c ) and write the following code:
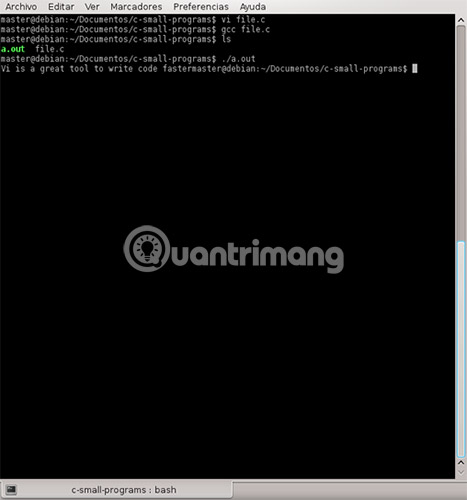
void main(void){ printf('vi is a great tool to write code faster '); } Save your file and if you have gcc installed, you should compile and run it.
Common options for opening files in Vi
- vi file: Create a new file if it does not exist. If not, it will open the existing file.
- vi -R file: Read-only mode (Read only)
Move between characters
- You must be in Command mode.
- You can use the keys: Up, down, left and right arrows.
Alternatively, you can use other keys:
Common commands in Vi
Note : You must be in Command mode.
Copy and paste command in Vi (Practice!)
Create a new file named "linux-distro".
Write the following list:
- Ubuntu
- Linux Mint
- Debian
- Slackware
- Red Hat
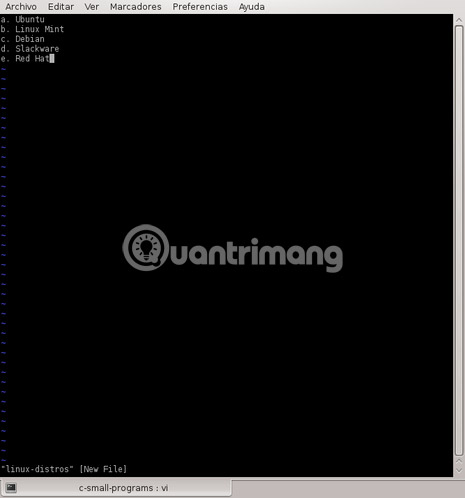
Change to Command mode (ESC).
Move the cursor to "Ubuntu".
Type yy (this is a command to copy a line).
Type G.
Insert a new line by typing o.
Change to Command mode (ESC).
Type P (This command is for pasting lines).
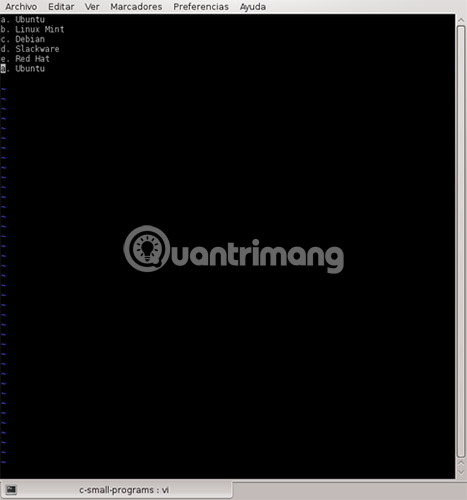
Type 1G
Type 4yy.
Type G.
Type P.
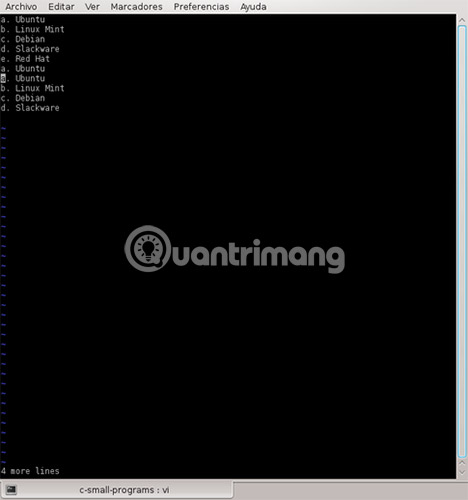
Alternatively, you can use other copy - paste commands:
- yw: Copy from current.
- p : Set the copied text after the cursor.
Advanced micro command
Work with two or more files (Practice!)
Open the linux-distros file
In Command mode, type:
:e unix Write " UNIX is a good OS " and save it.
Go to the linux-distros file with the command:
:e # Exit Vi by typing:
:q Good luck!
See more:
- Basic Shell commands in Linux
- Certain deadly commands never run on Linux
- How to use the Vim editor
- 5 best free code editors