How to Create and Edit Text Files Using Terminal on Linux
Open Terminal
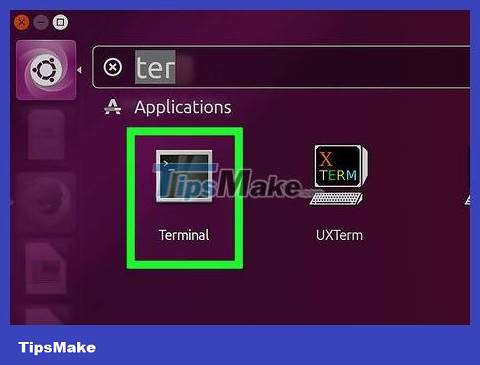
Open Terminal. To open the software, click on Menu , then find the Terminal software, which looks almost like a blackboard with a white ">_" symbol, and click on it. You usually find Terminal in the left sidebar of the Menu window.
You can click on the search bar at the top of the Menu window and type terminalto find Terminal.
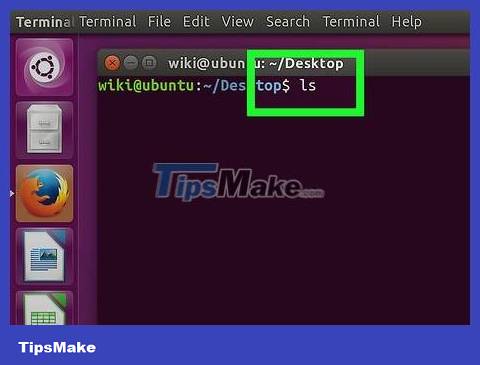
Type lsinto Terminal, then press ↵ Enter. Terminal will open the main directory, but the command lswill display all folders in the current directory. To create a text file in one of those directories, you need to change the current directory.
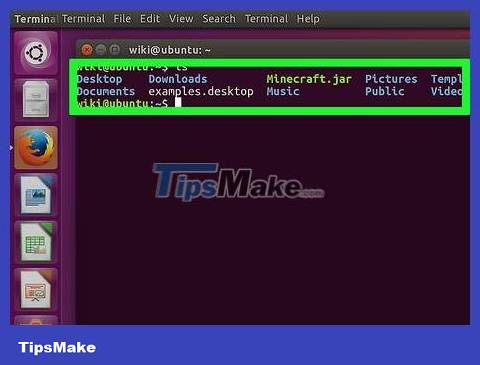
Find the directory you want to create a text file for. Any category name listed below the command ls(for example "Desktop") is a navigable location.

Enter cd directory. You replace "directory" with the name of the directory you want to create the file. This command will shift Terminal's focus from the current directory to the directory you name.
For example, you enter a command cd Desktopto move Terminal's command execution location to the Desktop category.
If you want to create a text file in a separate folder within the selected category, simply add "/" after the category name and then type the folder name. For example, for the "Misc" folder in the Documents category, you type cd Documents/Misc.

Press ↵ Enter. This executes a command, switching Terminal's target from the main directory to the directory you specify.

Decide on editing software. You can create simple text files quickly, or use Vim or Emacs for advanced file creation and editing. You have accessed the category where you want to create a text file, now let's create the file.
Create Text Files Quickly
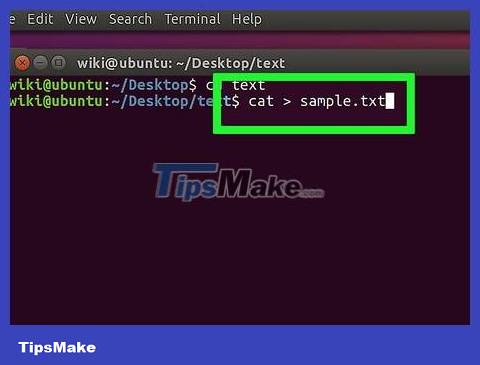
Enter cat > tên tệp.txtinto Terminal. You replace "filename" with the name you want to give the file (e.g. "report").
For example, when creating the file "kitty", you enter the command cat > kitty.txt.
Press ↵ Enter. This is the operation of creating a new text file according to the name just given in the current directory. The cursor will appear on a blank line in Terminal.

Enter text. You type text as you would any other document. To save the line of text you just typed and move to the next line, press ↵ Enter.
If the directory contains an open text file, simply double-click the text file when it appears to perform this step.

Press Ctrl+Z . This is the command key to save text and return to the command line in Terminal, allowing you to continue entering commands.
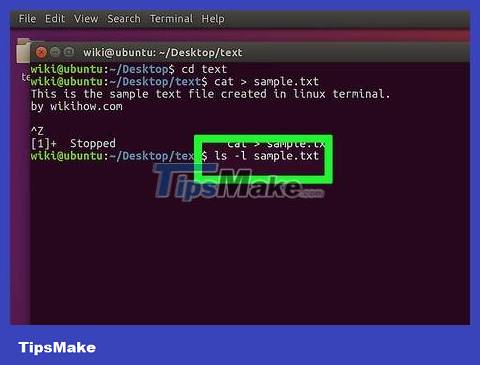
Enter ls -l tên tệp.txtinto Terminal. You replace "filename" with the name you intend to give the text file. This command will locate the file to ensure that it was created in the directory you choose.
For example, to open the file "textfile", you enter the command ls -l textfile.txt.
The letter in this command is a lowercase "L", not a capital "i".
Press ↵ Enter. This displays the time, date, and file name on the next line, indicating that the file was created and saved in the selected directory.
Use Vim

Enter vi tên tệp.txtinto Terminal. The "vi" part in this command is to choose to use Vim text editing software. You will replace "filename" with the text filename you want to assign to the new file.
For example, for the file "tamins", you enter the command vi tamins.txt.
If the current directory has a file with the same name, this command will open that file.

Press ↵ Enter. This is the operation of creating a new file and opening it in Vim software. You'll see a blank Terminal window, with a tilde (~) on each line and the filename at the bottom of the window.

Press key i. This puts the document into "Insert" mode so you can edit the text if needed.
You will see -- INSERT -- appear at the bottom of the window when you press the key I.
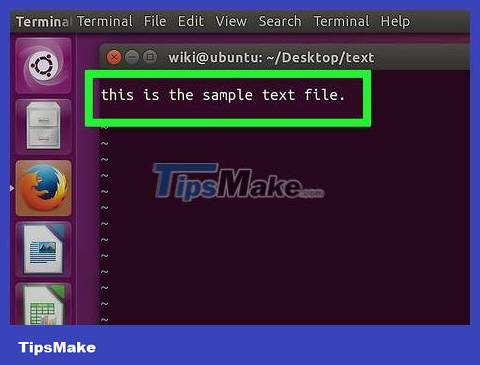
Enter text. You type text as you would any other document. To save the line of text you just typed and move to the next line, just press ↵ Enter.

Press key Esc. This key is usually located in the upper left corner of the keyboard. This key will put Vim into "Command" mode.
You will see the mouse pointer appear at the bottom of the window.

Type :winto Terminal and press ↵ Enter. This is the command to save the current document.
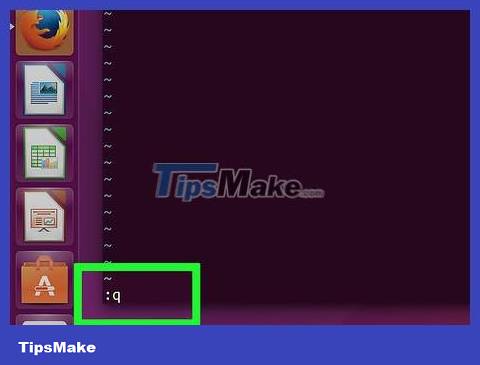
Type :qinto Terminal and press ↵ Enter. This is the command to exit Vim and return to the main Terminal interface. The text file is now in the specified directory.
You can check the text file by entering the command lsinto Terminal and pressing ↵ Enter, then find the file name.
You can enter commands :wqto save and exit in the same command.
Reopen the file in a Terminal window. Similar to creating a file, you enter a command vi tên tệp.txtto open the file. Now when you open the file, you will see that any changes you saved have been implemented.
Use Emacs

Enter emacs tên tệp.txtinto Terminal. You replace "filename" with the name you intend to give the text file.
Press ↵ Enter. As long as the file name does not overlap with an existing text file in the current directory, this command will open the new text file in the Emacs editor.
For example, a file named "newfile" would require the command emacs newfile.txt.
If you enter a file name that already exists, this command opens that file.
Learn Emacs commands. Emacs has a wealth of powerful commands that allow you to navigate documents, look up related or supporting information, manipulate text, and understand code. These commands are divided into two types: Control commands and Meta commands.
The Control Command has the form: C-
The Meta (or Exit ) command has the form: M-
A command written as follows C-a b(or M-a b) requires you to hold down the key Ctrl(or Altor Esc) while simultaneously pressing the first key (e.g. key a), release both keys, and then immediately press the second key (e.g. key b).
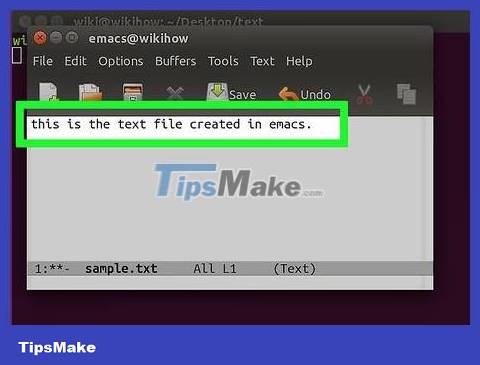
Enter text. You can type text as you would any other document. To save the line of text you just typed and move to the next line, press ↵ Enter.

Press the Ctrl+X key , then press again S. This is the file saving operation.
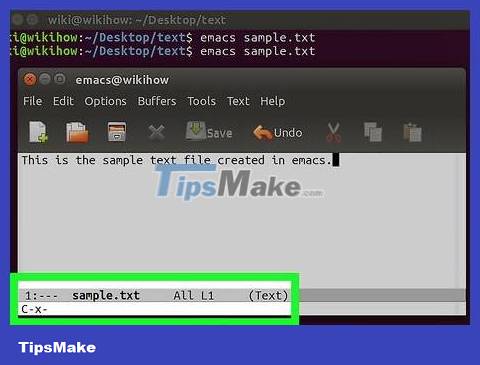
Press the Ctrl+X key , then press Ctrl+C again . This exits the Emacs editing software and returns to the menu in Terminal. The text file is saved under the name you just set in this directory.
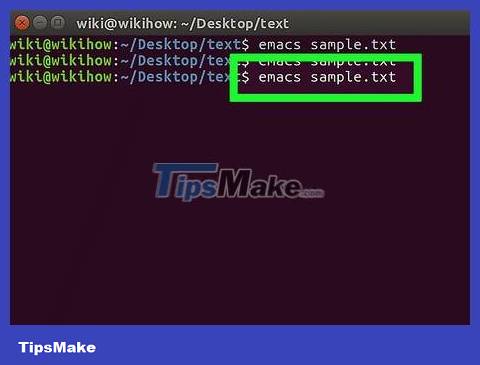
Open the text file again. To open the file, you enter the command emacs tên tệp.txtinto Terminal. As long as you're in the directory where the file is, this command can open the file in Emacs, so you can continue editing if you want.