Learn about how email works
QuanTriMang - Email - the daily work of most computer users needs them, they send and receive emai during working hours, leisure time with friends, family, exchange information with partners, customers . But do people understand the nature and operation of email? And in the article below, we will go together to find out about this issue.
So what exactly is email?
Email - Electronic mail (e-mail, email, E-Mail .) or email is a popular way of communicating and communicating the system based on computers. At a time a long time ago, the computer term used to refer to large-scale machines, users had to apply dial-up methods to access, and every computer was available. equipped with memory and storage devices for multiple accounts. Soon after, the inventors sought to make these machines 'communicate' with each other. The first application was born, but they only sent messages to other users in the same system until 1971. And as time passed, technology was developed to a new level when Ray Tomlinson became the first person in the world to send an email to others using the @ symbol. And that's the first foundation of the Email concept - we're talking about it.

At that time, emails were equivalent to messages in today's text. With the continuous development of technology, email has 'evolved' with the accompanying information such as details of senders, recipients, titles, content, attachments . But anyway, The whole process is not as simple as when we take a pen and draw a line between any two points A and B. Just like to launch a program or software, there are many processes that happen when users want to send or receive emails without them knowing.
Distance from sender to receiver:

When we want to send an email, we need to explicitly specify the recipient's address as user@domain.ext. As in the example above, freman.alpha@arrakis.com, email is sent from the client side with the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol - SMTP, which can be temporarily visualized as an intermediate post, with a task of checking Stamps and addresses on the letter for exact destination. But it does not understand domain - domain name, this concept is quite abstract and relatively confusing. At this step, the SMTP server will have to contact the Domain Name System server. This DNS server is similar to the phone or address book on the Internet, the main task is to compile domains like arrakis.com into IP addresses like 74.238.23.45. Then it will find any domain with an MX or mail exchange server on the system and temporarily mark that domain. To make it easier, imagine this process as follows: the post office where you send the letter will conduct a check on the map to determine the destination, contact the post office there to check the recipient with the box letter to receive or not.
Now, when the SMTP server has enough information, the message will be sent from that server to the domain's mail exchange server - Mail Transfer Agent (MTA). It will determine exactly where the incoming mail will be located, corresponding to the post office in the area where the recipient will deliver the mail to the most convenient address. And then, the friend will go to receive the mail, usually using the standard POP or IMAP protocol.
POP and IMAP?
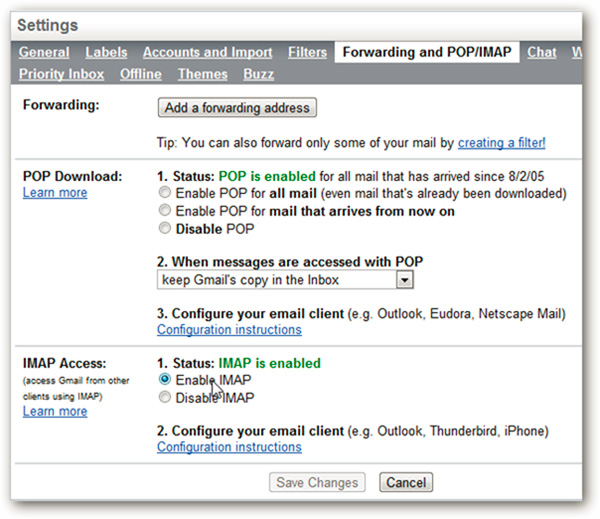
Here, we continue to mention the two most common terms in the setting of any form of sending - receiving emails. First is POP - Post Office Protocol, like the post office, you can come, go inside and receive all letters easily, then return home. Users do not need to be always connected, just leave 1 backup directly on the server, the whole process is extremely simple and fast. If the user does not leave a backup, it will not consume bandwidth and storage capacity on the hard drive. On the other hand, you can absolutely use POP to receive emails from many different accounts, and then combine them into a single block. Besides, POP also has certain disadvantages, because this is a one-way routing protocol and the information flow will flow in one direction only. It doesn't matter if you only access the mailbox from a certain place. But with today's business needs, many users of this protocol can still check email from anywhere: office, home, library, Internet access point tool . in many ways like Application on the phone, directly via the browser . The system will have trouble arranging and classifying emails every time there is a request from the user.

The remaining protocol standard - IMAP with a few basic differences. While POP can be considered completely user-oriented, IMAP is designed to work with other ways: on the server's request or vice versa. Usually, the client has two ways to communicate with the server. All messages will be stored on the server, through which multiple client accounts can be accessed and used. When the user needs to check email via phone, it will be marked as read and during the next interaction with the server, this status will be sent back, and the remaining clients will be updated. full.
Besides, IMAP also supports offline mode, all changes will be synchronized with the server when the user accesses the Internet. Or set up a mail server using IMAP to receive email from POP mailbox. But since the concept of cloud came into being, using IMAP to access the server and other online storage services may also have errors.
SMTP and MTA?
Unlike physical mailboxes, outgoing and incoming emails will be managed and monitored by 2 servers. There is not too much difference for the server taking on the role of email, any computer can become an MTA with a few simple and easy setup steps. Meanwhile, sending email is a different story, requiring SMTP server to have a static IP address, but most ISPs block port 25, so a large number of users cannot send email. Why so? Simply because spam is increasingly 'expanding' and accounts for most of their bandwidth traffic, and the MTA system needs to be reconfigured to prevent spam. Users can set up the client system using the ISP unit's SMTP server, but the point here is that you need both MTA and SMTP servers to combine, and each server must take on its own task.