25 interesting things about hard drives you may not know
All large and small computers have different types of hard drives and most of us know that it's part of the hardware that stores software, music, videos and even the operating system. But maybe there are many things about hard drives that you don't know, let's discover 25 interesting things later.
- Instructions for fitting the second hard drive to the computer
1. The world's first hard drive is called 350 Disk Storage Unit, released by IBM in September 1956. It has a capacity of 3.75MB and the size of a refrigerator.

2. When the hard drive is commercialized, it is rented for $ 1,000 a month and purchased for about $ 35,000. The price per memory is about 8,500 USD / MB, equivalent to the average of 5 cents / GB today, 170 million times more expensive. At that price, a 256 megabyte storage device will cost $ 200,000.

3. While price differences make today's hard drives seem like a big jump in scientific discovery, in fact, modern hard drives are very similar to old hard drives, they contain one the number of platter plates, where information is read by the read / write head.
4. But how has the archive developed today? Most tech savvy people will tell you that HDD hard drives swap speeds for storage and SSD drives swap storage capacity for data speed. Although this is absolutely true, today's largest capacity drives belong to SSD. The Samsung PM1633a is the largest 16TB hard drive released in May 2017.
5. Many of you may have heard of Moore's Law, every two years, the system's computing power and storage space doubled. Unfortunately, Moore's law stopped working with HDD, because the technology is reaching its physical limit. There are several methods to fix, but rapid progress has shifted to SSD.

6. Hard drive disc is made of expensive materials, such as platinum because of its thermal properties, as well as ruthenium because of its magnetic properties. However, do not try to map hard drive plates because these expensive materials form only a tiny layer on the top of the aluminum plate or glass plate.
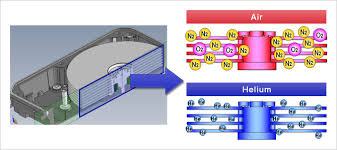
7. Contrary to what you often hear, hard drives are not airtight. However, they have filters to prevent dust around them which could seriously affect your data.
8. Traditional hard drives have a limited capacity because the air and power requirements limit the number of discs that a drive can hold. Different aerodynamic processes make it difficult to push multiple platters onto a hard drive, while other principles along with power requirements make it difficult to spin discs over 15k RPM.
9. The hard drive is also limited by space on the read / write disk plate to read the information. A magnetic encoded area of a diskette that is too small can lead to data not being read.
10. Although all of this seems to make the future of HDD hard to become bleak, there are also creative solutions to these problems, such as Helioseal technology. WD's Ultrastar He12 helium hard drive replaces the air inside the baffle with helium, thus increasing the limit of the number of discs that can fit in one case, making the 12TB storage unit more compact.
11. Talking about compact storage, remember that the first hard drive is about the size of a refrigerator. When compared to modern storage hard drives, the 350 Disk Storage Unit hard drive accounts for about 10 billion times the space per MB compared to the current average hard drive.
12. Most of the data is circulated in social networks and video platforms. For example, Facebook hosted about 300PB (petabytes) in their data center in 2013, which means that now this number has increased greatly. YouTube, is estimated to have 15 years of video history uploaded daily, storing about 500PB of data in 2015.
13. These figures are only rough estimates, according to Moore's law, the amount of data stored by industries doubles every 1.2 to 2 years.
14. All of this information is stored in data centers, large establishments contain rows of hard drives and servers. And while you feel that using a computer doesn't take a lot of power, a large data center can consume as much power as it does for a small city.
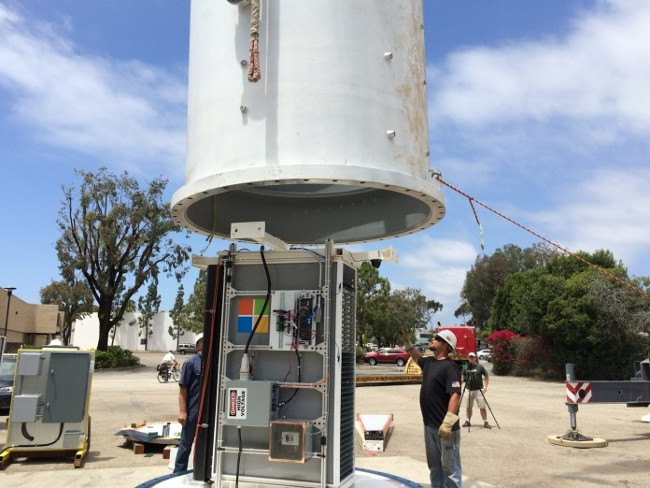
15. Today, we have a lot of space for data centers, building in places that are less suspicious than underwater can bring some unexpected benefits. For example, in the testing of Microsoft's underwater data center in 2015, a large lid filled with servers was sunk in the ocean. This can help cool the system as well as speed up data transfer because half the world lives next to the coast. Iceland's data tower project also intends to use nature to cool its data centers.

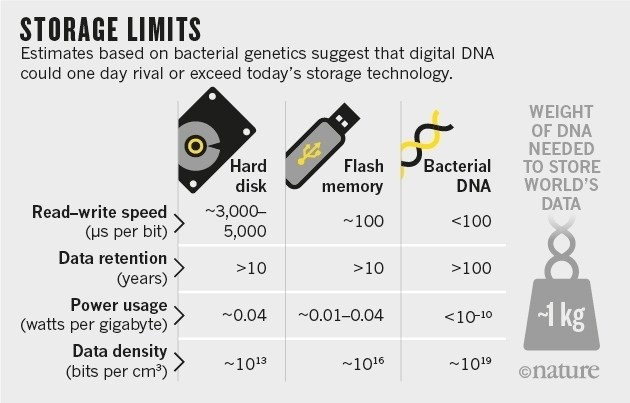
16. In this list, all metrics are displayed in bytes, however, sometimes you may notice the amount of data measured in bits. Bit and byte are not the same! A bit is either 1 or 0, while a byte consists of 8 bits, putting in a sequence of identifiers for the computer. This means that 1TB (terabytes) of information, for example can also be measured into 8Tb (terabits), but the bits are mainly used to measure bandwidth for interfaces.
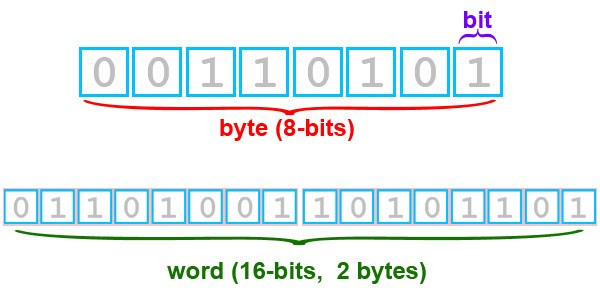
17. People still say one gigabyte is 1,000 megabytes, but that's not true. Because the computer uses a binary numbering system, 1GB is not 1000MB but 1024MB (or 2 ^ 10).
- Basic measurement units in computers
18. The file data does not disappear completely when you delete them. The computer specifies the space where those files can be reused but cannot access them on the computer, they can be recovered by some very sophisticated data access methods. So if you want to completely delete something, use the software to scan the drive or smash the hard drive.
19. However, the best way to delete your data is to place it under a super strong magnet. Magnets can damage or completely destroy data on the hard drive because the information is stored by magnetizing small parts of the disk plate surface.
20. While destroying data is not an easy task, it is easier to protect your hard drive with a password than you think. In fact, you can set up any password you want by accessing the BIOS. Before downloading the operating system, the computer will allow you to access the boot options by pressing Esc or one of the function keys. In the BIOS menu, go to the security section to set a password for the hard drive. Make sure you remember it because every time you turn on your computer, you will have to enter the password for the operating system to boot.

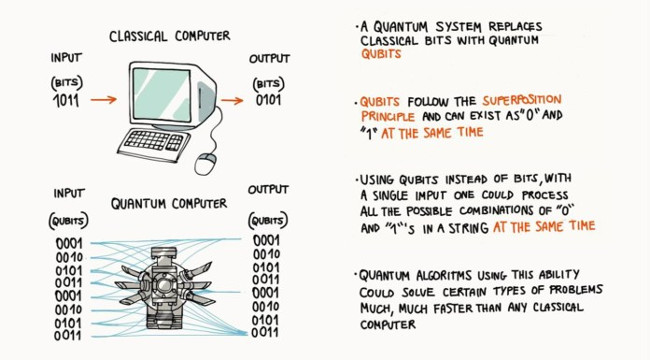
21. Conventional transistor electronics, including HDD and SSD, will reach their limits in the future because of quantum phenomena such as superparamagnetism and quantum tunneling ( quantum tunneling). In short, both phenomena can make data cells change their state at random if they are too small, even on a disk plate or in the NAND SSD port.
22. HHD hard drives can be completely replaced by SSDs in the future, but we will still see them for a while because of innovative solutions. Previously we mentioned helium drives that can reduce mechanical force on hard disks. However, there are more complex technologies such as Shingled Magnetic Recording (SMR), which allows storing older information "below" new information to make the storage system more compact.
23. There are several completely new methods for storing data, one of the so-called 5D memory methods stores information in a glass plate. The main advantage of this method is good durability. It is estimated that a small 5D glass disk can hold data for 13.8 billion years at an average temperature of 375 degrees F (190 degrees C). Although it is still difficult to access data at a reasonable rate, this technology is still being developed, bringing more expectations in the future.
24. Previously, quantum computers were mentioned a lot, but in recent years it has rarely been mentioned. However, quantum computing studies continue with success in both processing and the first step in the storage system. A few years ago, a research team led by Andrea Morello presented their progress in storing information on an atom. Information is stored in different quantum states of the grain, as opposed to the entire "pack" of particles as in semiconductor electronics. Although there are a lot of obstacles in storing information for a longer time, many other companies like Google and Microsoft are investing in research. Therefore, in the future, we can hope to own supercomputers.
25. Quantum storage is still not enough? So try hologram storage. The Holo archive will store the same information as how it is done now but the particle packages will be sorted in such a way that more information can be stored in one place. Does this still not impress you? So what about storing DNA? Although this may be a normal form of data storage in the distant future, it is certainly a potential storage device. Experts in this field predict that only a few pure DNA strands can contain all the data we have created so far in human history!