Instructions for automatic VPN connection on Linux
There are many ways to connect to VPN from Linux operating system. However, if you want to connect without a GUI or connection to run automatically, follow the article below.
Most of the best VPN services will be built on OpenVPN. OpenVPN is a free and open source VPN server that you can use to set up your own VPN. However, you only need the OpenVPN client to be sufficient.
When installing OpenVPN on Ubuntu, the client will also appear. You can use the OpenVPN client to connect to any OpenVPN server. OpenVPN is a service, so it can run when you start your computer, which means you don't need to remember to start it and do not need to configure separate connections for each user.
- 11 best VPN software
- The fake IP method helps you access anonymously
- How to use Opera VPN to fake IP, create VPN
Install OpenVPN
Before you can connect to the VPN service, you need to install OpenVPN on Ubuntu. It may be available in your device, so use apt to receive it.
sudo apt install openvpn
You can also install OpenVPN from the package manager, regardless of which distro you are using.
Download VPN configuration
Most VPN providers have profiles available for OpenVPN. Check to see if your VPN provider supports OpenVPN and review their configuration files.
VPN packages are usually in the form of .zip or if they are personal files, they are usually set to the server location and end with the .ovpn extension.
Copy configuration
Once you have the OpenVPN archive file, you will need to put it in the OpenVPN folder. If you need to extract the files from the zip file, do it first.
unzip openvpn.zip
Copy the file to the OpenVPN folder and rename it to ' openvpn.conf '.
sudo cp ~ / Downloads / OpenVPN / 'Northeast US.ovpn' /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf
Your path and file name will be different. However, you can use the example above.
Automatic login
Fortunately, OpenVPN supports logging in with just one file.
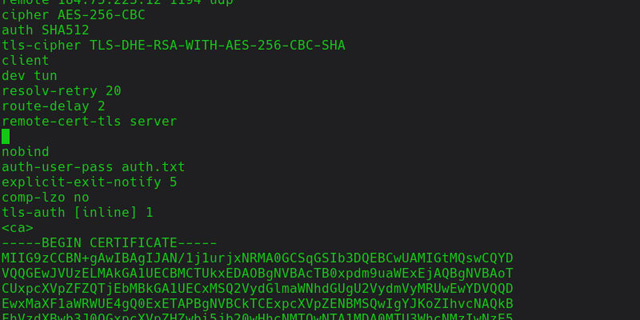
Open ' /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf "with sudo. Search for the line containing' auth-user-pass '. Then add ' auth.txt ' on the same line. Save the file and close it.
Create a new file in ' / etc / openvpn ' called " auth.txt ". On the first line of the file, set your username to include the password in the second line. Then save and close the window.
Reboot and check
That's all you need to do to connect to your VPN. Restart the OpenVPN service for changes to take effect.
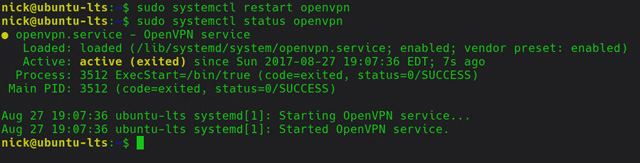
sudo systemctl restart openvpn
To ensure that OpenVPN runs at the same time the computer boots, activate it with systemd.
sudo systemctl enable openvpn
Finally, check your VPN connection with dnsleaktest.com. When you reach the website, you will see your IP address and VPN location. Click the button below to test and check if DNS information is leaked.
It is done! Now you can connect VPN on Linux easily.