Guide to network operation for Linux users: 11 commands to know
TipsMake.com - Terminal on Linux is the same as cmd on Windows, it is a command line environment that allows users to interact with the system through commands.But the command on the terminal is more and it is not the same as the command on Windows cmd.So, if you just start using this operating system, you will have to learn terminal commands on Linux.[New Linux should use which distro?]
Linux supports commands for users to download files, diagnose network problems, manage network interfaces or view network statistics on the command line interface (command line).Here are some common Linux commands to work with, please consult.
curl and wget
Use the curl or wget command to download a file from the internet without a terminal. With the curl command, type curl-O the path to the file. Users can use the wget command without any additional options. The file will appear at the link.
Curl-O website.com/file
Wget website.com/file

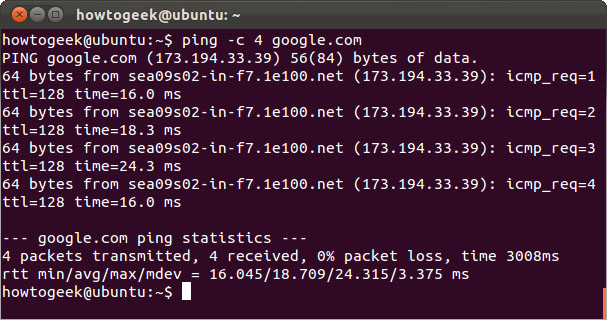
ping
The ping command sends ECHO_REQUEST packets to the specified address. The command is to check if the computer can connect to the Internet or a specific IP address. However, there are many systems that are configured to not respond to ping commands.
Unlike the ping command on Windows, the ping command on Linux will maintain sending packets until you finish it. It is possible to specify the maximum number of packets sent by typing the -c option.
ping –c 4 google.com
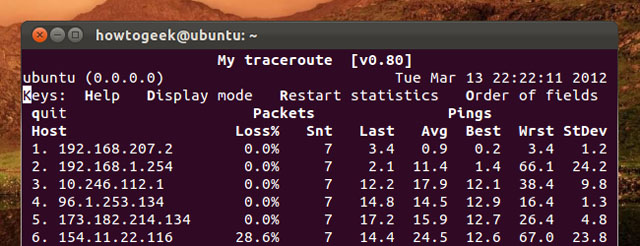
Tracepath and traceroute
The tracepath command is similar to traceroute, but it does not require administrative rights. It is also installed by default on Ubuntu and tracerout is not. The tracepath command traces the route on the network to a specified destination and reports each vertical node ( hop ) along the way. If network problems occur, the tracepath command can indicate the location of the network error.
Tracepath example.com

mtr
The mtr command is a combination of ping and tracepath in a single statement. mtr will send packets continuously and display ping times for each network node. The command also helps detect some network problems. In this case, it can be seen that the 6th button lost more than 20% of the total number of packages.
mtr howtogeek.com
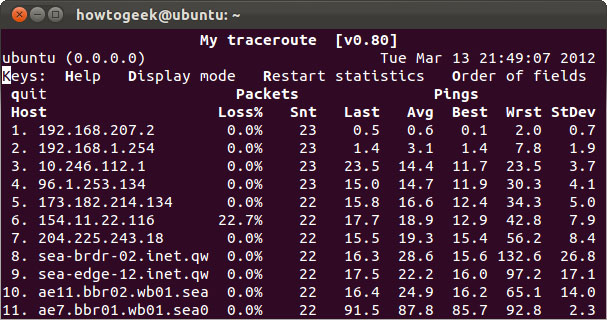
Press q or Ctrl-C to exit when you're done.
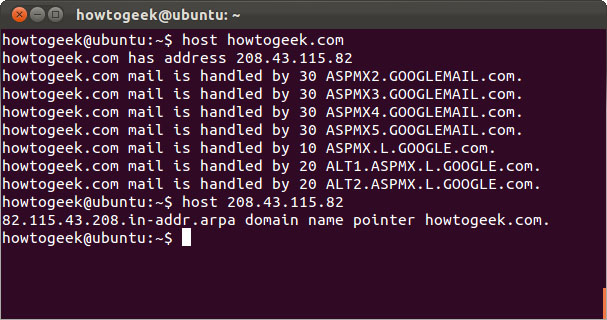
host
The host command will perform a DNS search. Enter the domain name when you want to see the attached IP address and vice versa, enter the IP address when you want to see the associated domain name.
Host howtogeek.com
Host 208.43.115.82
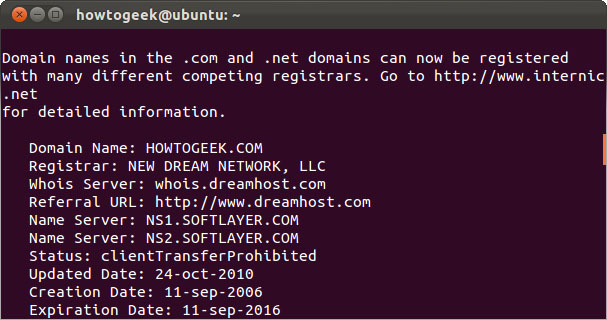
whois
The whois command will issue records on the whois server (whois record) of the website, so you can view information about the person or organization registered and own that website.
whois example.com
ifplugstatus
The ifplugstatus command helps check if the cable is plugged into the network interface. This command is not installed by default on Ubuntu . Use the following command to install it
sudo apt-get install ifplugd
Run the following commands to see the status of all interfaces or just view the status of a specific interface.
ifplugstatus
eth0 ifplugstatus
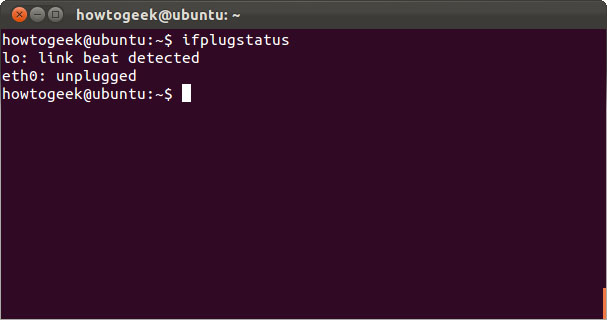
' detected ' link link means the cable has been plugged in and ' unplugged ' means the cable is not plugged in.
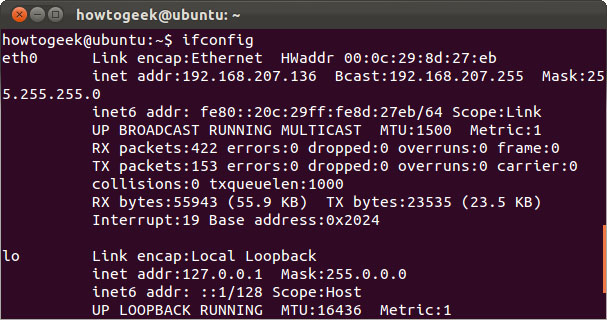
ifconfig
The ifconfig statement has many options for configuring, adjusting and detecting errors on system network interfaces. This is also a way to quickly see IP addresses and other network interface information. Type ifconfig to see the status of the currently active network interfaces including their names. You can also specify an interface name to view information on that interface only.
ifconfig
ifconfig eth0
ifdown and ifup
Ifdown and ifup statements are like ifconfig up or ifconfig down . The two statements execute on or off the specified interface. This requires administrative privileges so you must use the sudo keyword on Ubuntu.
sudo ifdown eth0
sudo ifup eth0
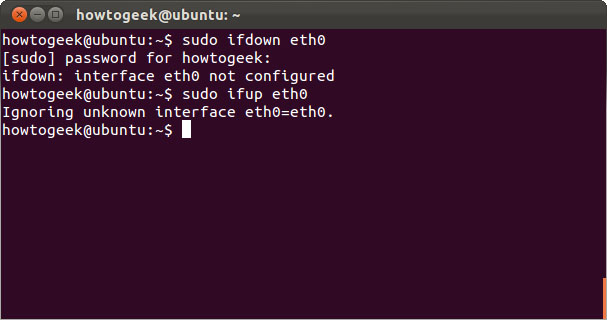
The Linux screen will report an error when these commands are entered. It often uses NetworkManager to manage network interfaces. However, these statements will still work on servers without using NetworkManager.
If you really need to configure NetworkManager from the command line interface, use the nmcli command .
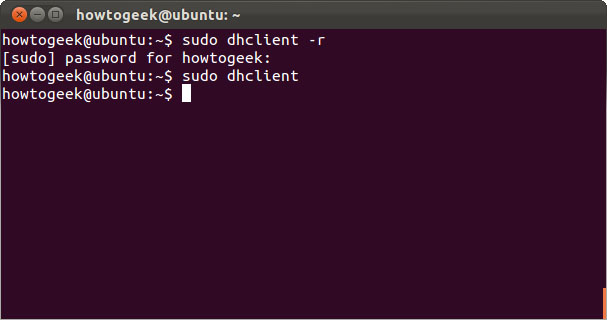
dhclient
The dhclient command helps refresh the IP address on the machine by freeing the old IP address and receiving a new address from the DHCP server. This job requires administrative rights, so use the sudo keyword on Ubuntu. Run dhclient to get a new IP address or use the -r option to release the current IP address.
sudo dhclient –r
sudo dhclient
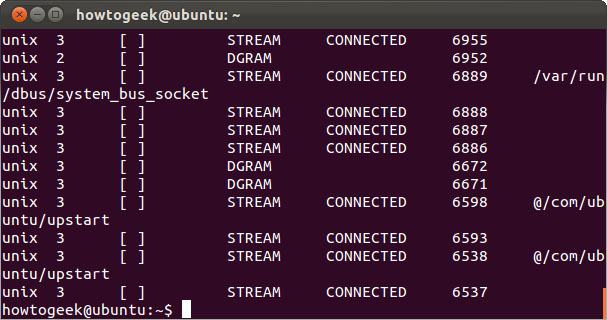
netstat
The netstat statement provides different statistics for the interface, including open sockets and routing tables.
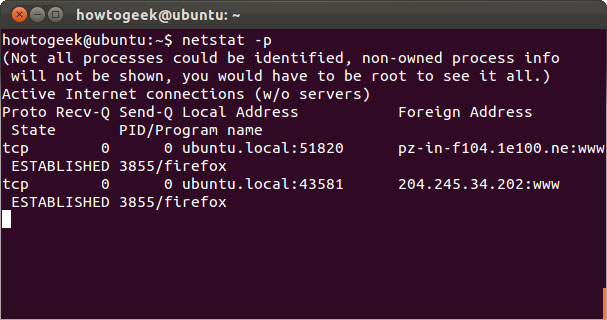
Use the netstat -p statement to see programs that come with open sockets.
See detailed statistics for all ports with the netstat –s statement.

The above are common commands to manipulate the network that Linux supports users. Through these commands, users can easily check for incidents or network-related information.
You can refer to other basic Linux commands here: Basic Linux commands everyone needs to know