How to prioritize specific network traffic on a Wi-Fi router
Just because you have fast Wi-Fi doesn't mean you'll always get the best speeds possible. As more and more devices connect to your network, you'll see the importance of prioritizing network traffic.
What are QoS settings?
Most modern routers will have Quality of Service (QoS) settings in their advanced settings. QoS settings help you control how your available bandwidth is divided among the devices and applications running on your network. When your network is congested and many devices are competing for bandwidth, these settings will prioritize certain devices and applications over others.
Let's say you're playing a game while someone else in the house is streaming Netflix on the TV. Generally, routers handle such cases on a first-come, first-served basis, meaning that if packets from Netflix arrive at the router sooner than packets from your game server, Netflix gets priority while the game has to wait.
This is especially true when there are many different data packets coming into your router at the same time. Since the router can only handle a certain amount of data at a time, packet loss occurs as packets sit in a queue for the router to properly distribute them among the many devices connected to the router.
With enough devices (or bandwidth-draining apps), this will start to show up as lag in games while Netflix runs fine, or lag in both games and Netflix, depending on how the router handles the traffic. However, with properly configured QoS settings, the router will know which types of packets to prioritize. So if you have QoS set up on your router to prioritize games, PCs, or consoles, your experience will be fine, but others may see their content cached.
Depending on how you set up your QoS settings, you can have a better online gaming experience, better audio and video call quality, a better streaming experience, or anything else you want to prioritize over other traffic.
What QoS settings does your router support?
Most modern routers have QoS settings, but they can be a bit difficult to find. Furthermore, not all QoS settings are the same, and different routers implement them with different names and rules. In general, the following two QoS settings are the most common:
- Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) : As the name suggests, this feature monitors Wi-Fi traffic and prioritizes multimedia apps like Netflix or Spotify over other types of traffic. It works automatically and is usually available as a simple toggle.
- Bandwidth Control: This is a more useful feature that allows you to specify devices and applications by and port to tell the router which traffic to prioritize in what order.
If you're buying a router, make sure it supports Bandwidth Control and WMM. WMM is great if you stream a lot, and is usually enabled by default. However, it lacks the flexibility you need if you want to prioritize anything other than streaming. There are other features to look for when buying a router, so be sure to do your research.

To check which QoS settings your current router supports, you'll need to access its settings. Typically, you can access these settings from a preset IP address like 192.168.0.1. Keep in mind that these settings vary from device to device, so it's best to check the label on the back or bottom of your router to find the correct IP and login information.
They may not be in the same place either. For example, on the TP-Link Archer C5 router, the WMM toggle is hidden under the router's advanced wireless settings (and can't be disabled for some reason), while Bandwidth Control has its own section.
On the older D-Link DIR650N, there was a separate QoS section with Bandwidth Control and WMM, so you'll likely have to dig around in your router to find the right settings.
Use QoS to prioritize specific traffic
Since WMM doesn't offer much control over which traffic you can prioritize and is just a box you need to check, there's not much to do other than enable a feature. Bandwidth Control, however, is a different story.
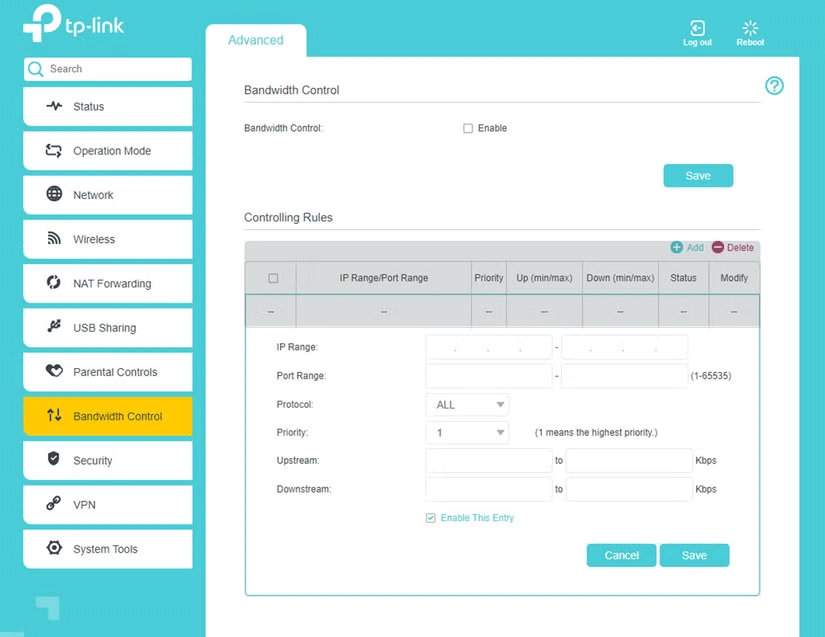
While the exact settings you need to change will vary depending on the IP address your device of choice receives from your router and the specific ports your game or program needs when connecting to the Internet, here's a general summary of everything you need to set up.
- IP Range : This is a list of IP addresses assigned to the bandwidth settings you are deploying. If you are only changing the settings for one device, enter the same IP address as the start and end points of the range. It may be helpful to set static IP addresses for your devices first.
- Port Range : This is the range of TCP and UDP ports that the specific program or game you are trying to connect to prefers to use to connect to its server. This range varies depending on the program you are using and you can usually find them with a simple search on .
- Protocol : This option will choose whether the port you select uses TCP, UDP, or both. Most programs have different port ranges for either type.
- Priority : This setting allows you to set the priority for the rule you are creating. In general, you can choose up to 10, where 1 is the highest priority and 10 is the lowest priority.
- Upstream/Downstream Speed : This is where you can enter the upload or download speed allocated to the device. If you want to use the full bandwidth of your internet connection, enter the upload and download speeds provided by your ISP. However, you can experiment with lower numbers to save some bandwidth for unmanaged devices on your network.
On most routers, the five settings mentioned above will provide all the QoS control you need. Once set up correctly, your router will know which types of traffic to prioritize over others and how much bandwidth to allocate to a particular device.
High-speed Wi-Fi is great, but if you use it on multiple devices, it can quickly slow down. Setting up the right QoS network priority settings helps avoid this and ensures you get the best possible experience on the devices, games, and programs that really matter.