How to manually mount/unmount USB devices on Ubuntu
When you connect a USB drive to your system, it is usually automatically mounted and a folder with your username is created in the media folder. You can also access the drive through your system's file manager. Unfortunately, this is not always the case; sometimes you need to manually mount the USB drive to your system to access it.
This guide will explain how to manually mount and unmount a USB drive to your system. The commands and steps described in this article will work on all recent versions of Ubuntu including Ubuntu 24.04 and Ubuntu 22.04 .
How to mount USB on Ubuntu
Follow these steps to manually mount the USB to your system:
Step 1 : Plug the USB into an available port.
Step 2 : Run the following command as sudo in the Terminal application to check the available storage devices on the system and the file system they are using:
$ sudo fdisk -l 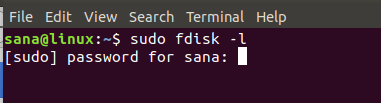
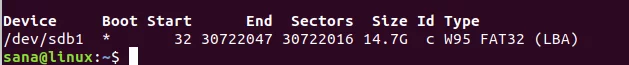
Your USB device will usually be listed at the end of the output, usually as sdb-(number) . In the example case, it is listed as sdb1 , running the FAT32 file system .
Step 3 : Create a mount point for your USB device using the following command:
Syntax:
$ sudo mkdir /media/[mountPointName]Note : Your mount point name cannot include spaces; you can separate words with underscores '_'.
For example:
$ sudo mkdir /media/USB 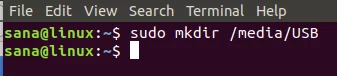
The mount point will be created now.
Step 4 : Now, we will mount the USB storage device to the created mount point. We will use the following command to mount the FAT32 device:
$ sudo mount -t vfat /dev/sdb1 /media/USB -o [securityoption]The security option is required and allows you to grant/receive access to the USB by specifying one of the following values to grant permission:
- uid=1000
- gid=1000
- Utf8
- dmask=027
- fmask=137
This example grants access control to a user (current user) by specifying the user id:

For NTFS, use the following command:
$ sudo mount -t ntfs-3g /dev/sdb1 /media/USBStep 5 : The USB is now mounted. You can access it through your media folder.
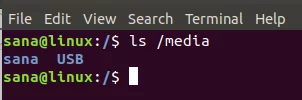
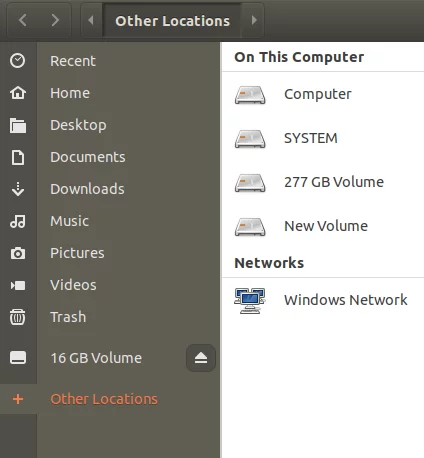
You can also access the USB through the file manager. In the following image, the 16 GB Volume listed just above Other Locations is the mounted USB storage device.
How to unmount USB on Ubuntu
If you have mounted the USB manually, it is best to also unmount it manually.
Step 1 : Use the following command to unmount USB:
$ sudo umount /dev/sdb1Or:
$ sudo umount /media/USBIn the above command, specify the mount point if it is different from the 'USB' mount point used.
The USB will be unmounted from your system:
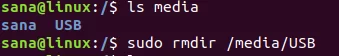
Step 2 : You will need to manually delete the USB mount point folder as follows if you do not plan to use it again in the future:
Step 3 : Remove USB from the system.
After following the steps described in this article, you should be able to successfully mount and unmount USB storage devices in and out of your system. This will help if your system does not automatically allow USB access and use.