How to Get Root Rights on Ubuntu
Execute root with sudo command
Press Ctrl+ Alt+T to open a terminal window. Because Ubuntu locks the root account by default, you cannot use commands suto become a super user like in other Linux distributions. Instead, start your command with sudo.
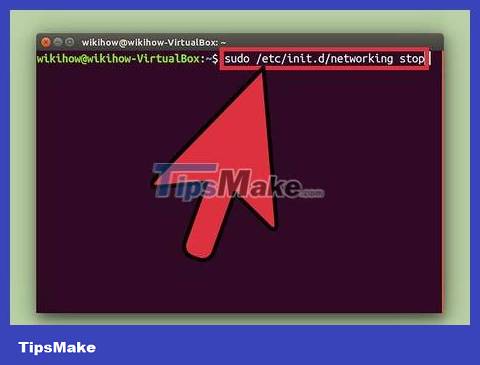
Enter sudobefore the command. 'Sudo' stands for 'Super User Do.' When you use sudo to start a command, the command will be executed as a super user.
For example, the command sudo /etc/init.d/networking stopwill stop network services, while the command sudo adduserwill add new users to the system. These tasks all require super user permissions.
You will be asked to enter your password before sudo executes the command. Linux will save your password for 15 minutes, so you don't have to enter it again and again.

Enter gksudobefore executing a command to open a program with a graphical user interface (Graphical User Interface, referred to as GUI). For security reasons, Ubuntu does not recommend using 'sudo' to open programs in the GUI. Instead, enter gksudobefore the program start command.
For example, you can type gksudo gedit /etc/fstabto open the file "fstab" using the Gedit editor program in the GUI.
If you use KDE Window Manager, use kdesudoinstead gksudo.

Emulates a high-level user environment (root shell). If you are an advanced user who needs real root shell access to execute specific scripts, you can simulate a high-level user environment with sudo –i. This command will give you super user access to root's environment variables.
Enter the command sudo passwd rootto create a root password, essentially 'activating' the account. Don't forget this password.
Enter sudo -i. Then enter the root password when prompted.
The command line interpreter will change the word$wall#, meaning you already have root access.
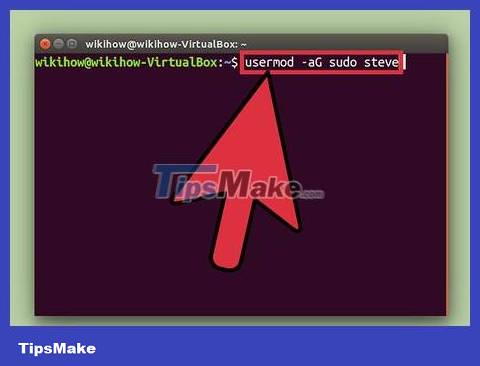
Grant access sudoto other users. If you're setting up an account for someone who doesn't have root privileges, you'll need to add their username to the sudo group. To proceed, type usermod -aG sudo username(replace 'username' with the specific username).
Enable super users
Press Ctrl+ Alt+T to open a terminal window. For security purposes (and to avoid damage), super user accounts are always locked by default. To safely execute commands as a super user, you should instead use sudoor gksudo. If you absolutely must have a separate root account (if it's required by a program your business uses, or if this dedicated computer is only used by a single user), you can Enable a super user account with a few simple commands.
Ubuntu does not recommend enabling super user accounts as this may pose risks to the system.
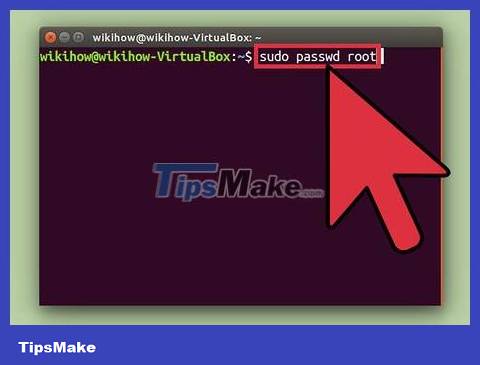
Enter sudo passwd rootand press ↵ Enter. You will be asked to set a new password for the super user account. Please remember this password.
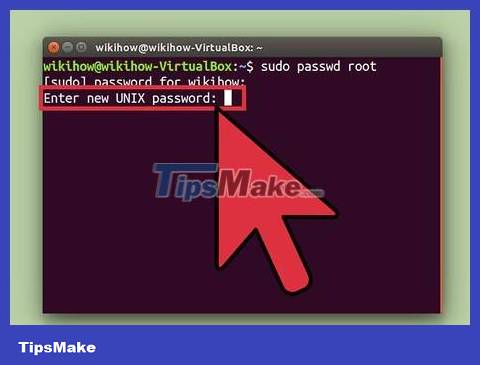
Enter the password, then tap ↵ Enter.
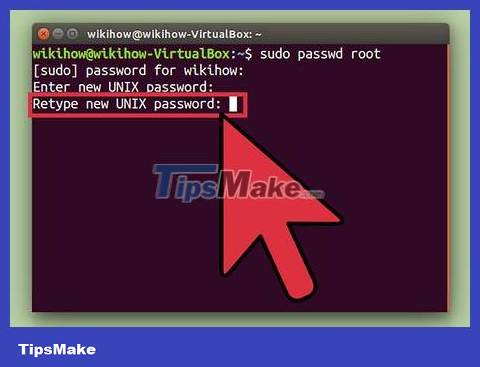
Re-enter your password when asked, then tap ↵ Enter. So the super user account has a password set.
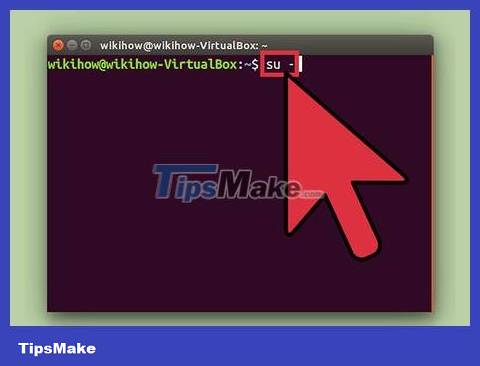
Enter su -then press ↵ Enter. Enter the root password when asked in the root prompt.
To disable the super user account, enter the command sudo passwd -dl root.