How to Completely Delete Any Windows File Using SDelete
Files deleted from your PC may still be recoverable, at least for a short time. To make sure they're gone forever, you can use SDelete. This command-line utility securely erases data, making it unrecoverable.
What is SDelete?
When you delete a file, your computer simply marks the space it occupied as unallocated. This means that until another application writes data into that space, the contents can be recovered using data recovery tools.
SDelete can ensure that deleted files cannot be recovered. This command-line utility not only deletes existing files, but also removes previously deleted data that remains in unallocated areas of the drive. It securely erases data using the DOD 5220.22-M strong data deletion standard, recommended by the U.S. Department of Defense. It works by overwriting file data on disk clusters.
How to install SDelete
To get started, visit the Microsoft Sysinternal site. Click Download SDelete to save the compressed file to your local drive. Right-click the downloaded file, select Extract All , select a destination folder, and then click Extract .

Since SDelete is a command-line utility, it does not work like a regular application with a graphical interface. To set it up, first move the unzipped SDelete folder into the C:Program Files folder . Once done, follow these steps:
1. Click Start , type view advanced system settings and open the best match.

2. Select Environment Variables .

3. In System variables , select the Path line and choose Edit .
4. Select New to add a new line, then click Browse . Navigate to C:Program Files and select the SDelete folder .
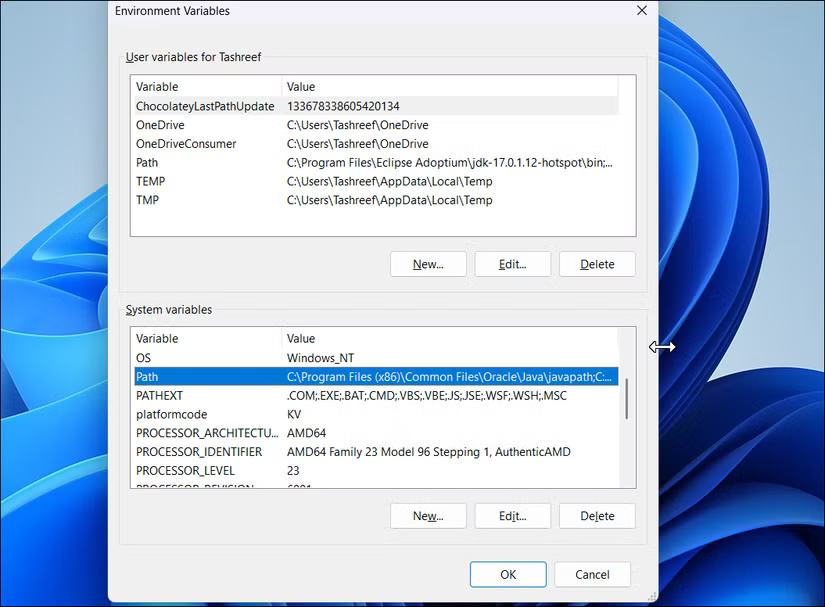
5. Click OK on all open dialog boxes.
After configuring SDelete, launch the tool and see how it works.
1. Click Start , type cmd , right-click Command Prompt and select Run as Administrator .

2. Type SDelete and press Enter in the Command Prompt window to launch the tool. You will also see the SDelete License Agreement dialog box when the tool is run for the first time. Click Agree to close the dialog box.

How to use SDelete to delete files permanently
Before you begin, you should back up your data. Also, consider testing SDelete on a virtual machine first to minimize the risk of accidentally deleting important files. If you don't already have a virtual machine, you can easily set one up on a Windows PC for testing.
To get started, launch Command Prompt with admin privileges. In Command Prompt, type SDelete and press Enter to launch the tool. This will display a list of parameters and arguments that you can use with the SDelete command to securely delete files and free up disk space.
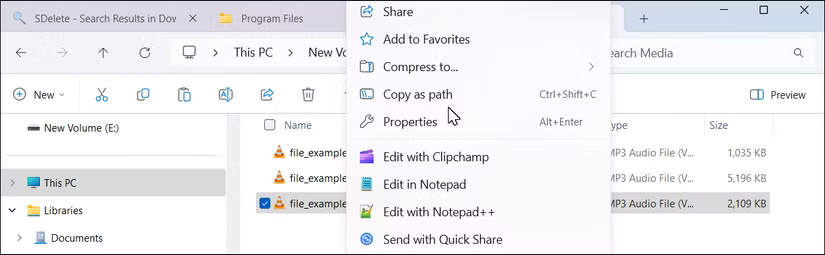
For this tutorial, we will be securely deleting an MP3 file located in the C:Media folder . Open File Explorer, locate and right-click the MP3 file, then select Copy as Path to copy the full file path of that file.
Next, in the Command Prompt, type SDelete followed by the file path. For example, the full command would look like this:
SDelete C:MediaOneMP3.mp3 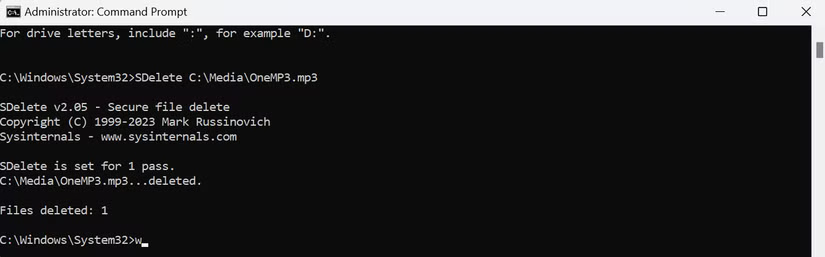
Press Enter to execute the command. If successful, you will see the output:
Files deleted: 1Next, try deleting the Media folder located in C: .
When deleting a directory, you need to include its subdirectories and handle any read-only attributes to ensure everything is cleaned up properly. To do this, use the SDelete command with the -s parameter to include subdirectories and -r to remove read-only attributes.
The full command would look like this:
SDelete -s -r C:MediaAfter running the command, the output will show the number of folders and files that have been deleted.
