How to Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux
Part 1 of 3:
Preparing Your Ubuntu Linux System
-
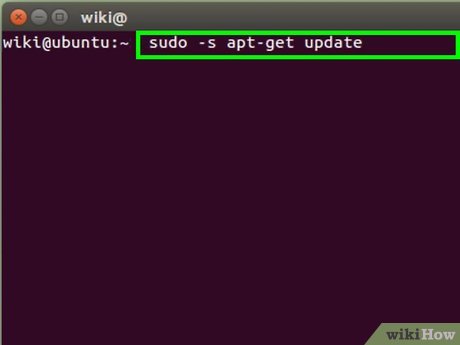
 Issue the following commands below in order to prepare your Ubuntu Linux system to capture embedded Adobe flash videos from websites.
Issue the following commands below in order to prepare your Ubuntu Linux system to capture embedded Adobe flash videos from websites.- Type: sudo -s apt-get update. This will update your repository sources.
- Type: sudo -s apt-get install perl. This will install the Perl, programming language, you will need Perl in order to run your FlashVideoCapture.pl script.
- Type: sudo -s apt-get install lsof. This will install lsof if it is not already installed.
- Type: sudo -s apt-get install firefox. This will install the Mozilla Firefox web browser.
- Type: sudo -s apt-get install vlc. This will install the VLC multimedia player in order to playback your captured *.flv videos.
- Important Note: You must use the Firefox browser to view your FLV videos because this does not work in Google Chrome.
-
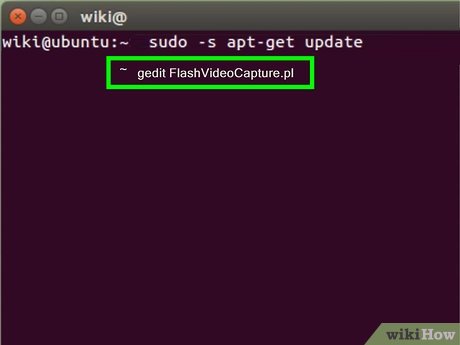
 Open up a text editor such as gedit or nano.
Open up a text editor such as gedit or nano.- Type: gedit FlashVideoCapture.pl
- Type: nano FlashVideoCapture.pl
-
 Type the following perl script located in the box below and save it as FlashVideoCapture.pl:
Type the following perl script located in the box below and save it as FlashVideoCapture.pl:#!/usr/bin/perl[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 1 Version 5.jpg|center]] #Filename: FlashVideoCapture.pl use strict;[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 2 Version 5.jpg|center]] ################################################## #Setup the variables[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 3 Version 5.jpg|center]] ################################################## my $PROGNAME = $0; $PROGNAME =~ s|.*/||; my $LSOF = 'lsof'; my $FIND = 'flash'; # Find flash files my $POST = 'flv'; # Postfix to save to #Where we save files[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 4 Version 5.jpg|center]] #%f is $FIND[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 5 Version 5.jpg|center]] #%d is the next available number[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 6 Version 5.jpg|center]] #%p is .$POST my $DEST = "found%f.%d%p";[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 7 Version 5.jpg|center]] ################################################## #Usage[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 8 Version 5.jpg|center]] ################################################## sub fatal { foreach my $msg (@_) { print STDERR "[$PROGNAME] ERROR: $msgn"; } exit(-1); } sub usage { foreach my $msg (@_) { print STDERR "ERROR: $msgn"; } print STDERR <<USAGE; Usage:t$PROGNAME [-d] Copies deleted flash files currently open in your browser's cache -d Set debug mode -find What to search for [default $FIND] -post Postfix for saving files [default $POST] -dest Or just specify full destination [default $DEST] (see the script for meanings of %f, %d, %p) USAGE exit -1; } sub parseArgs { usage("You need to be on a system that uses /proc") unless -d '/proc'; my $opt = { find => $FIND, post => $POST, dest => $DEST, }; while (my $arg=shift(@ARGV)) { if ($arg =~ /^-h$/) { usage(); } if ($arg =~ /^-d$/) { $MAIN::DEBUG=1; next; } if ($arg =~ /^-find$/) { $opt->{find} = shift(@ARGV); next; } if ($arg =~ /^-post$/) { $opt->{post} = shift(@ARGV); next; } if ($arg =~ /^-dest$/) { $opt->{dest} = shift(@ARGV); next; } if ($arg =~ /^-/) { usage("Unknown option: $arg"); } usage("Too many files specified [$arg and $opt->{file}]") if $opt->{file}; } usage("You need to specify a destination with -dest") unless $opt->{dest}; usage("You need to specify something to search for with -find") unless $opt->{find}; $opt; } sub debug { return unless $MAIN::DEBUG; foreach my $msg (@_) { print STDERR "[$PROGNAME] $msgn"; } } ################################################## #Main code[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 9 Version 5.jpg|center]] ################################################## sub findFiles { my ($opt) = @_; my @found; #'lsof /' (The '/' just does files, no sockets, and is faster) open(LSOF,"$LSOF /|") || usage("Can't run [$LSOF]"); while () { next unless /delete/i; next unless /Q$opt->{find}E/i; next if /.adobe/; # Ignore adobe 'flash' db files chomp;[[Image:Capture Adobe Flash Videos on Ubuntu Linux Step 10 Version 4.jpg|center]] #procname pid user fd usage("Found it, can't parse it [$_]") unless /^S+s+(d+)s+S+s+(d+)/; push(@found, [$1,$2]); } usage("Couldn't find any deleted cached $opt->{find} files") unless @found; @found; } sub procPath { my ($pid,$fd) = @_; my $path = "/proc/$pid"; usage("Couldn't find $path") unless -d $path; $path .= '/fd'; usage("Couldn't find $path") unless -d $path; $path .= "/$fd"; usage("Couldn't read $path") unless -e $path; $path; } sub destPath { my ($opt) = @_; my $p = $opt->{dest}; $p =~ s/%f/Q$opt->{find}E/g; $p =~ s/%p/.Q$opt->{post}E/g; my $num = 0; my $path; do { $path = $p; $num++; $path =~ s/%d/$num/g; } until ! -f $path; $path; } sub main { my $opt = parseArgs(); my @found = findFiles($opt); foreach my $found ( @found ) { my $src = procPath(@$found); my $dest = destPath($opt); print "$src -> $destn"; system("/bin/cp",$src,$dest); } } main();
Part 2 of 3:
Configuring a Capture Directory and Enabling the FlashVideoCapture.pl Script
-
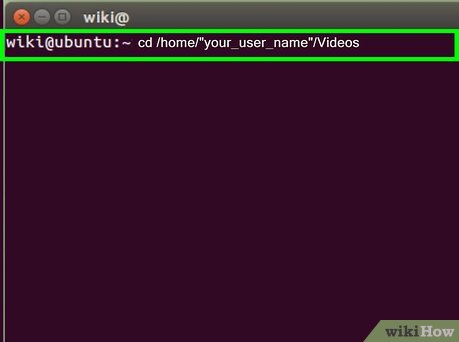
 Copy the FlashVideoCapture.pl script to your /home/"your_user_name"/Videos directory.
Copy the FlashVideoCapture.pl script to your /home/"your_user_name"/Videos directory.- You will either need to change into your Videos directory or create a dedicated directory where you store your multimedia videos.
-
 Create a directory. If you don't have a Videos directory on your system, the command below will allow you to create one.
Create a directory. If you don't have a Videos directory on your system, the command below will allow you to create one.- Type:mkdir -p /home/"your_user_name"/ Videos.
- This command will create your Videos directory.
- Type: cd /home/"your_user_name"/.
- Change into your home directory.
- Type: cp -r FlashVideoCapture.pl /home/'your_user_directory'/Videos
- Copy the FlashCaptureVideo.pl script to your Videos directory.
- Type: cd /home/'your_user_name'/Videos.
- Once the FlashVideoCapture.pl script is in your Videos directory, you will open up terminal and change into your Videos directory.
- Type: chmod +x FlashVideoCapture.pl.
- This command will make the FlashvideoCapture.pl perl script executable.
- Type:mkdir -p /home/"your_user_name"/ Videos.
Part 3 of 3:
Capturing Your Flash Video
-
 Start up your Firefox web browser and go to a site which has embedded flash videos in it.
Start up your Firefox web browser and go to a site which has embedded flash videos in it. -
 Allow the Flash video to play/load in the web browser until it is completely loaded into the browsers cache. You can tell the video has completely loaded by the grey bar at the bottom of the Flash video, which will usually indicate the load and completion of the video. Once the grey bar load cycle is complete and 100% of the video has been loaded it's time to capture the video stored in your web browsers cache.
Allow the Flash video to play/load in the web browser until it is completely loaded into the browsers cache. You can tell the video has completely loaded by the grey bar at the bottom of the Flash video, which will usually indicate the load and completion of the video. Once the grey bar load cycle is complete and 100% of the video has been loaded it's time to capture the video stored in your web browsers cache. -
 Keep your Firefox web browser open with the video completely loaded. Return to your open terminal and run the FlashVideoCapture.pl script by issuing the following command:
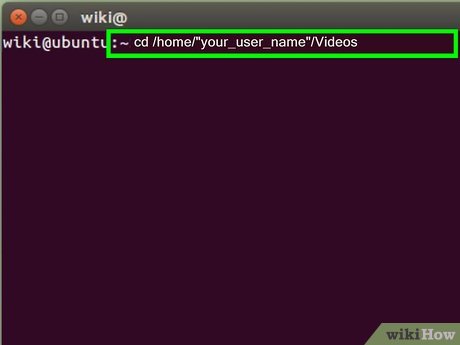
Keep your Firefox web browser open with the video completely loaded. Return to your open terminal and run the FlashVideoCapture.pl script by issuing the following command:- Type: cd /home/"your_user_name"/Videos
- This will change you into your Videos directory, make sure you are in the Videos directory and you have the FlashVideoCapture.pl script in this directory.
- Type: ./FlashVideoCapture.pl
- This command will execute the FlashVideoCapture.pl script and capture the *.flv video files to your /home/"your_user_name"/Videos directory.
- Type: cd /home/"your_user_name"/Videos
-
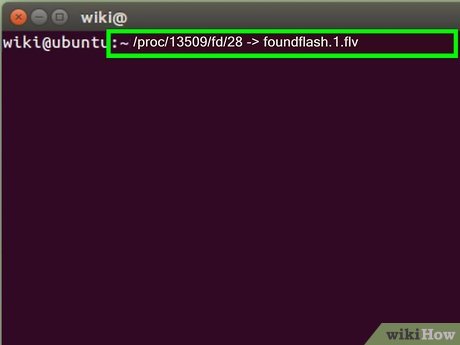
 Review the results. If this was done correctly, you will see a statement such as this:
Review the results. If this was done correctly, you will see a statement such as this:- /proc/13509/fd/28 -> foundflash.1.flv
- This means the flash video was captured as foundflash1.flv. In order to view the video you can use the VLC mediaplayer to view the captured *.flv file.
- /proc/13509/fd/28 -> foundflash.1.flv
-
 Play back your captured *.flv video files. Make sure you are in the /home/"your_user_name"/Videos directory before running the following commands.
Play back your captured *.flv video files. Make sure you are in the /home/"your_user_name"/Videos directory before running the following commands.- Type: cd /home/"your_user_name"/Videos
- Type: vlc foundflash1.flv.
- or
- Type: vlc *.flv
- This will playback all *.flv video files stored in your /home/"your_user_home"/Videos directory.
-
 Rename the foundflash1.flv to anything you like. So that you can view the captured *.flv video over and over again using the VLC media player without loading it from your Firefox web browser.
Rename the foundflash1.flv to anything you like. So that you can view the captured *.flv video over and over again using the VLC media player without loading it from your Firefox web browser.
Share by
Marvin Fry
Update 04 March 2020