Guide to building an Ultimate Wireless Network
Network administration - Wi-Fi standards can be a fickle object and are a lot of messy, especially when manufacturers engage in the battle of common words related to the latest features. Ignore most marketing terms - especially as copyrighted terms. Ignoring the missing components, let's take a look at what to know to choose a wireless router, configure a network and start working.
How to choose a wireless router

Today, you should buy a router using 802.11n. However there are a few issues here for this standard. This Wi-Fi protocol is compatible with 802.11g and 802.11b standards; so if you or a visitor uses a laptop built on older technologies, this computer will work with your new router as long as you configure the router to allow it. The 802.11n specifications allow further coverage (reach) and data transmission faster than the other two Wi-Fi methods, but it has not yet received the standard license.
The final 802.11n specifications are expected to appear in 2010, so technically you should buy a router that supports this technology. While it is still possible that existing routers will not work with the final standard, companies that agree with 802.11n will support this problem. They will release an upgrade software for the router to accommodate the final approved specifications.
Also a good way to choose a dual-band router. Such routers will divide the traffic into two different wireless spectrum regions, 2.4GHz and 5GHz. This arrangement basically opens up another lane for communication so that the network can manage more data at a time and give faster transmission speeds. Many routers, such as the Linksys Simultaneous Dual-N Wireless Router (WRT610N), can split traffic on two SSIDs (service set identifier), allowing the use of lower and slower 802.11b security devices. Other routers, such as Netgear Dual Band Wireless-N Gigabit Router (WNDR3700) allow you to isolate traffic on two wireless networks together.
You leave part of the decision to buy your device on the router's ports. Although in theory you can set up a wireless-only system, the reality is that a network will consist of a mix of wireless and wireless devices. While wireless connectivity has many advantages, wired connections will still be an option of speed, simplicity, reliability and security.
Many wireless routers still have the standard 100Base-T ethernet instead of the standard for higher speeds (1000Base-T). So you should look for a model that incorporates high speed. The goal is to use in many cases that require good traffic, such as high-definition video streams, you can share other files without being slow. For many advantages, you must use gigabit ethernet computers, but then you will need to upgrade 100Base-T clients as they (here are 10Base-T clients) will still work with hardware faster. Routers generally consist of four ports. You can choose routers that have more ports if needed or use the Switch to increase the number of ports.
Some routers have USB ports. Refer to the technical model documentation, you will consider appropriately, for example, you can connect a USB port to a printer or some hardware to make these devices connect to your network. If those features fit your needs, the extra cost is absolutely legitimate. If not, focus on the possibilities discussed above.
If scope is an important issue in the installation, make sure that you own a router that has an external antenna port, not simply relying on the broadcast distance advertised on the packaging. There are many factors that affect the scope of the router, such as the structure of the surrounding building and the interference from nearby sources. If you want to cover the entire house - or backyard - you can buy a second access point.
Configure the router
Most routers come with an installation disc, but let's leave it there and configure your router yourself through a web browser. Installation CDs often provide a lot of convenience for beginners, but you will be able to access other advanced installation options through the browser interface. In addition, you can access that interface from any connected computer without having to use the installation disc. Once you know how to configure the network through the browser, you'll be more confident if something goes wrong with your network later. The exact process will depend on the brand of the manufacturer or between modems, but the menu options on most leading brands are quite similar and this is the way to go.
To get the largest range, place the router on a high shelf or mount it somewhere near the top of the central wall. Connect an ethernet cable between the broadband modem and the router. To ensure high quality throughput, use Cat-5e or good cables for all connections. Don't choose cheap cables. Connect a second ethernet cable between a certain LAN port of your router and your computer. If you use a laptop to configure your router, disconnect this cable at the end of the process, which is when you're ready for wireless connectivity.
The first detail you need to know about your router is its IP address. Sometimes this address is printed on a certain point on the router. If not, you can find it in the Windows Network Connections control panel. The list of Local Area Connection will display 'Connected', because your router will set DHCP default (dynamic host configuration protocol). Double-click this connection and select the Support tab. Remember or write the IP address of the Default Gateway. (It could be 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
Open the web browser and enter the router's IP address into the address field. You will be prompted for your name and password. Look up printed router documents to get detailed information.
Once inside, you can control all router settings. First, change the router's admin password, because anyone can access your router (and network) simply by entering a series of default logins still in use. Check in the Administration tab, where you will make the change. Enter the password and then save your changes. Next, you will be presented with the login screen; log back in with your new password.
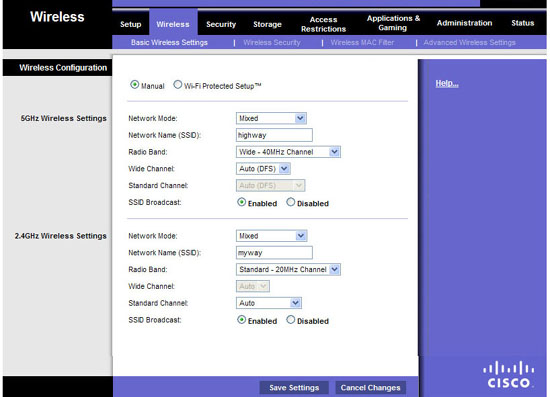
Next, change the internal IP address and subnet. This will give you an additional middle layer of security, but more importantly it will help you avoid IP address conflicts on complex networks. Enter the basic settings area and change the IP address to 192.168.x.1, where x is a number between 1 and 254. Write this number on a sheet of paper and save the changes, log in Return to the router, use the new IP address as a URL (You may need to wait a while while the router restarts).
Now change the SSID and enable Wi-Fi encryption for your first security layer. Observe the wireless configuration area and security settings; Disable Fi Protected Setup if needed. Change the network name to something. In addition, you can disable SSID Broadcast mode; This action acts as a thin layer of extended security, the reason that only serves as a thin layer of security here is that experienced users can easily find hidden networks, However, at least your network does not appear to any computer by default. If you use 802.11n hardware on computers and routers, activate 40MHz, broadcast broadband. (Disable it or set it to auto if you have network problems; it may be due to interference from the nearby networks). Click the Save button to save the changes.
Wi-Fi traffic without passwords will not be encrypted, which means that someone in your network's vicinity can block and read your data. You can block this vulnerability by enabling WPA2 Personal security mode, usually in the Wireless Security tab. Enter a long password with a combination of numbers and letters in it. Then save the changes you just created.
If your router or client device only supports WPA or WEP, you can use one of those standards instead. Be aware that both of these standards are less secure than WPA2. Another solution is that you can use multiple access points or a single point, but you can promote multiple SSIDs, then place your risk-free hardware on each of its individual networks.
Connect the client device
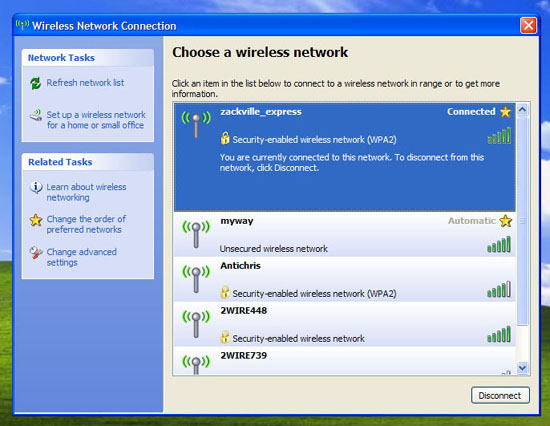
Wireless clients often have configuration software from Wi-Fi hardware companies as well as Windows Control Panel applications. You can connect clients to their programs, but we will focus on the Windows tools provided.
Open Network Connections Control Panel, right-click Wireless Network Connection. Select Properties . Then select the Wireless Networks tab, click Add . Enter the SSID for the network and check the box labeled Connect even if this network is not broadcasting . Select WPA2 for the Network Authentication section. Set Data encryption to AES , then click OK twice. Then double-click Wireless Network Connection in Control Panel and select the wireless network. Click Connect . Enter the network password and click Connect . The computer will save the password and it will then reconnect automatically.
Control other connections using MAC Address Filtering
There is an extra layer of security known as "address filtering", its method is to check the devices connected to your list of allowed items; After that, even if someone has a network password, the router does not allow this unauthorized hardware to access your network. This list is based on the unique MAC address assigned to each hardware device right from the factory. Like other security layers, this is also an unstable security layer. Theoretically, attackers can still change their MAC addresses later to match one of your friendly IDs. However, such an attack is unlikely to succeed if you incorporate MAC address filtering with the above security steps.
Address filtering requires an extra step in the process of connecting new devices to your network, but when you are done with this step, you will feel more at ease in terms of security. However, it is not considered that address filtering is equivalent to encryption: It cannot prevent those who deliberately want to block and steal your transmission like what WPA2 does.
To do so, connect all of your wireless clients to the network, using your WPA2 password. Remember the group of computers, smartphones, wireless entertainment systems, media-streaming hardware and other linked devices.
Go back to the configuration page for your wireless router, then enter the admin password to login. Look for the option to configure MAC address filtering (sometimes called "network filtering"), most of which are within the wireless settings area of the router. Activate the filter and set it to allow only certain MAC addresses to access the network. Many routers have a button to show all connected devices and allow you to add them automatically. Without this type of router, before you enable the filter, copy the MAC address from the DHCP client table; It is usually listed here, under Status (or Wireless Status). Save the changes and wait for the router to restart if necessary.
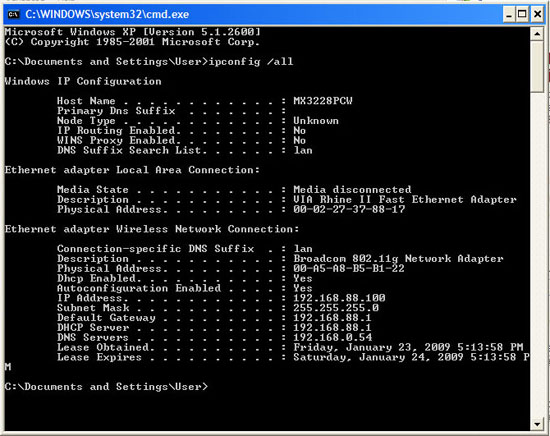
Later, you will have to type MAC addresses for any new device that wants to access the network. You can quickly look up a laptop's MAC address by clicking Start , Run , typing cmd and clicking OK . Then type ipconfig / all and press Enter . Search for a set of 6 pairs of numbers and characters in the Wireless Network Configuration area.
Security firewall
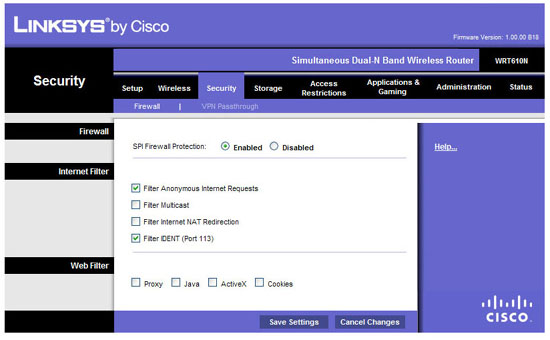
Your router may also have a firewall consisting of two parts: network address translation (NAT) and stateful packet inspection (SPI). In most cases, NAT is turned on by default. This routing method allows Internet traffic to connect to the router with an external IP address; The router controls which internal computers send and receive information. SPI performs a little deeper, ensuring that incoming data will reach requests from internal computers. Turn on the SPI firewall in your router configuration page (usually in the security tab). When the SPI is enabled, the router ignores the traffic that you didn't request.
Sometimes, these settings can block traffic - such as a game or another application - you want. If you encounter this problem with certain programs, change port-forwarding port settings. In essence, it is adding an extra port to the program that the computer is locking, and entering the IP address for that PC. (You can find many commonly used port numbers on the network).
Use the Switch to add ports

Very rarely home networks need more than 4 ethernet ports as they are still designed by default on typical routers. However, in small office networks, the number of ports may need more than this. Additional computers and network-equipped printers may need these ports. Instead of buying multiple routers, you can use a simple and inexpensive way to use the switch. Technically, you can use hubs to divide more ports, but we will experience traffic problems: because hubs cannot transmit and receive data and data simultaneously. Data is broadcast to all machines. As a result, there is a conflict and need to send a packet again and again, which slows down the speed of your network. Instead of using a hub because of its disadvantages, you should use a switch.
Switches can send and receive data at the same time. You should buy a switch that has the necessary port numbers for you. However, if you run out of your room, you should add another switch. The best way to do this is to choose a switch using gigabit ethernet. Even though you use 100Base-T hardware, you can still speed up faster with new devices later. Avoid 10Base-T switches. The installation process is simple: you just need to connect an ethernet cable between the router and switch, then connect the new devices to the rest of the switch.
Extend wireless network for wired devices
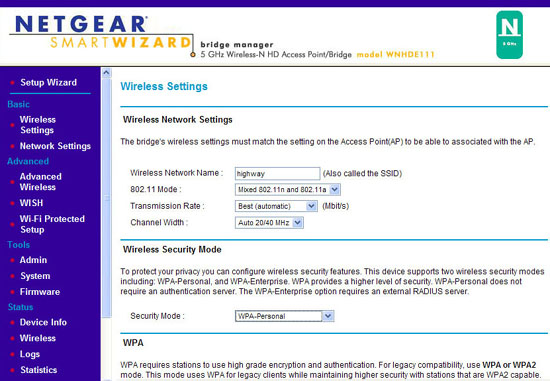
If you own devices that only support ethernet, you need to connect to your network wirelessly, in which case you can use a bridge instead of a series of cables. The wireless bridge method can work very well with Xbox 360, TiVo or other wired devices. Here's how.
The process is almost like installing a wireless router. You must first connect a computer directly to the bridge via an ethernet connection (temporarily disable your computer's Wi-Fi if necessary). Because the bridge will not broadcast the DHCP address, you still need to manually configure the ethernet details of the computer. Open the Network Connections Control Panel and right-click Local Area Connection. Select Properties . Double-click Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) , and select the Use the following IP address option .
Look up the bridge document to see which address it uses by default. Enter an IP address with the same first three sets of numbers but a different fourth set. For example, the Netgear 5GHz Wireless-N adapter (WNHDE111) uses the default of 192.168.0.241, so we need to set the IP address for the computer to 192.168.0.2. (You can choose any number from 2 to 254). Leave Subnet mask 255.255.255.0, since Windows has assigned it with a new number. Click OK twice.
Enter the bridge's IP address into the web browser, connect to its configuration page. Configure its wireless settings to match your network requirements, apply the same SSID details and encryption details. How can I receive DHCP details from the router.
Start the bridge and switch the computer back to DHCP by opening the Local Area Connection again in Network Connections Control Panel. Double-click Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) and click Obtain an IP address automatically . If the computer can be online, disconnect the ethernet cable, then plug the bridge to your wired-only device. If you run out of ports, add with a switch, as if you would be on a wired segment in your network.