Wireless LAN security (Term 2)
Wireless LAN security (Term 1)
4. Structure of a wireless LAN
A wireless LAN consists of three parts: Wireless Client, Access Points and Access Server. The typical Wireless Client is a laptop with a wireless NIC (Network Interface Card) installed to allow access to the wireless network. Access Points (AP) provide coverage of radio waves in a certain area (known as cells) and connect to a wireless network. And Access Server controls access. Both 802.11b standards (11Mbps LAN at 2.4GHz frequency) and Bluetooth APs are supported here. An Access Server (such as Enterprise Access Server or EAS) provides advanced control, management and security features for Enterprise wireless networks.
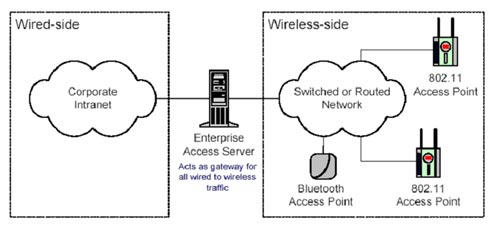
Enterprise Access Server in Gateway Mode
A wireless component can be connected to wireless networks that exist in a number of ways. The overall architecture uses EAS in 'Gateway Mode' or 'Controller Mode'. In Gateway Mode (see Figure 2 above) EAS is located between the AP network and the rest of the Enterprise network. So EAS controls all traffic flows between wireless and wired networks and acts as a firewall.
In Controll Mode (pictured below), EAS manages APs and controls access to the wireless network, but it does not involve the transmission of user data. In this mode, wireless networks can be divided into wired networks with regular firewalls or fully integrated in the Enterprise wired network.
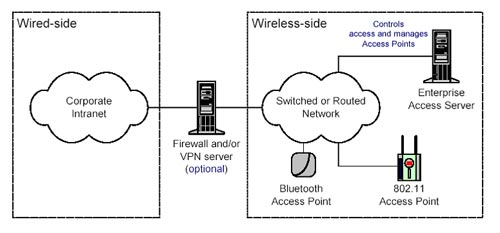
Enterprise Access Server in Controller Mode.
5. Wireless security model
Wireless LAN architecture supports an open and comprehensive security model based on industry standards as shown in Figure 4. Each element within the model can be configured according to the network manager to satisfy and match what they need.
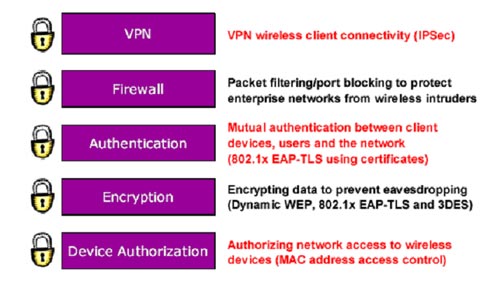
Security model not for wireless networks
Dievice Authorization : Wireless clients can be blocked by their hardware address (eg MAC address). EAS maintains a database of authorized wireless clients and separate APs that lock or flow appropriate traffic.
Encryption : WLAN also supports WEP, 3DES and TLS standards using encryption to prevent theft. WEP keys can be created per per user, per session basic.
Authentication : WLAN supports mutual authorization (using EAP-TLS 802.1x) to ensure only authorized wireless clients can access the network. EAS uses an internal RADIUS server for authorization by using digital certificates. These digital certificates can be obtained from an internal certificate authority (CA) or imported from an external CA. This has maximized security and minimized administrative procedures.
Firewall : EAS integrates customable packet filtering and port blocking firewall based on Linux IP series. The previous configuration allows common traffic types to be enabled or disabled.
VPN : EAS includes an IPSec VPN server that allows wireless clients to set up solid VPN sessions on the network.
See more: Wireless LAN security (Term 3)
Pham Van Linh
Email: vanlinh@quantrimang.com