Decode the specifications on the laptop
Machine check is an important step when you decide to take a laptop home. People often will check the configuration details of the machine, the capacity of the machine, speed, . to decide which type to suit the needs of each user. So you know how to check the specifications on your laptop? In this article, Network Administrator will show you how to read all the specifications of a laptop.
First of all, to check computer hardware information, please download and install the professional support program CPU-Z according to the link below:
- Download CPU-Z software for free
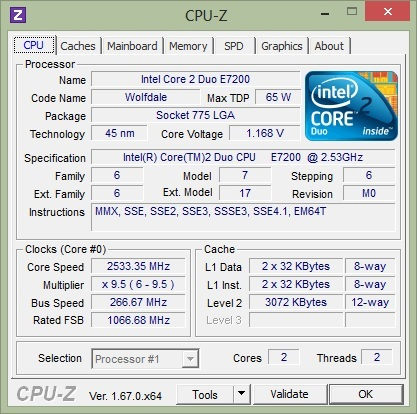
1. Meaning of parameters on CPU:
- Name : Name of processor chip - (Intel Core i5 3470).
- Code name : The name of the CPU architecture or CPU generation - (Ivy Bridge).
- Packpage : CPU socket (Socket types like 478, 775, 1155 . this parameter is very important when you want to upgrade your CPU. You cannot bring 1 socket 775 CPU chip attached to another socket (1155, 478 .) and vice versa.
- Core Speed : CPU clock speed, also known as CPU speed.
- Technology : Transistor technology, for example here is 22 nm, ie Transistor, each Transistor inside CHIP is 22 nm in size. Please note that the smaller the size of Transistor, the cooler your CPU is, very good for your computer.
- Core Voltage : That is the voltage for the core of CHIP. Current chips often adjust the clock and consumption voltage to save power.
- Specification : The full name of the CPU you are using.
- Stepping : This part is quite important, it tells us that the chips were launched in the market. The example here is 9, the higher the Stepping is, the better the fixes from previous versions. It is similar to the patches of those software or Windows.
- Revision : Is the version information, the same as in Stepping section.
- Instructions: These are scripts for the chip to process.
- Core Speed : CPU clock, this pulse constantly fluctuates to save power.
- Level 2 : The cache specification, the higher the parameter, the less CPU bottlenecks when processing.
- Cores and Threads : Number of cores and number of CPU threads. This number is usually even and commonly called: 2-core CPU, 4-core CPU, 6-core CPU .
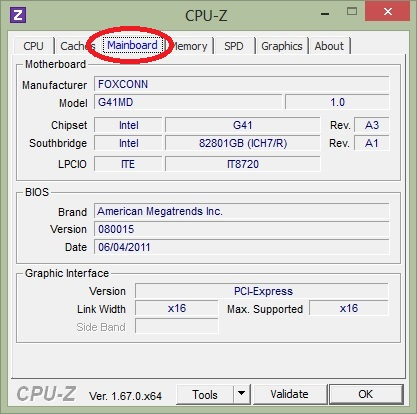
2. Meaning of mainboard parameters:
- Manufacturer : The name of the manufacturer of the motherboard (eg manufacturers such as Gigabyte, Asus, Foxconn .)
- Model : is the model of the mainboard. This information is very important in the process of finding drivers, without having to open the case to view directly. Next cell 1.0 is the version information, the higher the better.
- Chipset : Information about the chipset of main. Example: 945, 965, G31, G41, H61 .
- BIOS : Displays BIOS vendor information, production date and Version of BIOS.
- Graphic Interface : Information about graphics card slots on the mainboard, the most popular currently available are AGP and PCI-Express x16.
- Width : The width of the bandwidth.
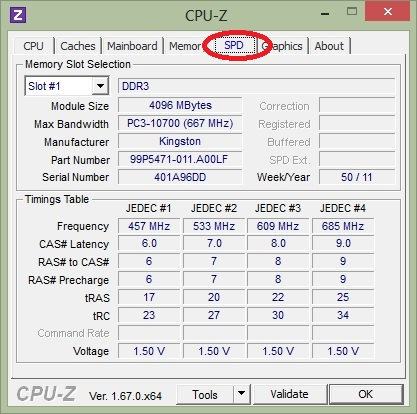
3. Meaning of parameters on RAM:
- Type : Display the type of RAM (RAM life) in use on the device (There are RAM types such as DDR, DDR2, DDR3 .)
- Size : The total amount of RAM used on your device.
- Channel : If the display is Single that means you are attaching a RAM or main does not support dual channel mode, if Dual is currently running RAM in dual channel mode (faster speed) this also means you attaching 2 or more RAM modules.
4. Meaning of SPD parameters (number of RAM slots):
- Slot # 2 : Pressing the drop-down arrow will show the number of RAM slots. Usually the computer will have 2 or 4 Ram slots. Slot # 2 means that the RAM is plugging in the 2nd slot.
- DDR3 : That is Ram testing, there are different types of DDR2, DDR33333 .
- Module Size : RAM capacity in the slot being viewed. Unit is MB (1GB = 1024MB). Like my device here is using 4GB ram bar.
- Max Bandwidth : This is actually the RAM bus parameter. You just need to multiply the clock part in parentheses by 2, which will output the current RAM bus. Example: 800Mhz x 2 = 1600 >> Bus RAM is 1600
- Manufacturer : Name of the manufacturer.
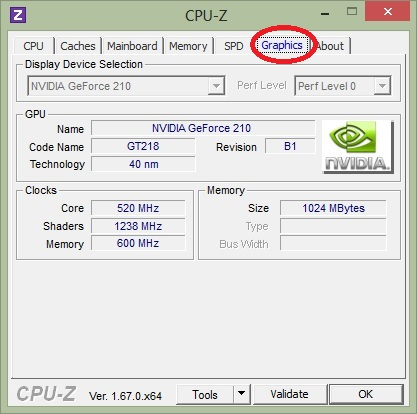
5. Graphics - View information about graphics cards with CPU-Z:
- Display Device Selection : If there are multiple video cards, this section will light up and you select the corresponding card. If there is only 1 card, this part will fade away as shown in the picture.
- Name : The name of the graphics chip manufacturer, the most popular is Ati and Geforce
- Code name : The name of the graphics chip running on the computer.
- Size : Capacity of the graphics card.
- Technology : Just like in the CPU section I said, this parameter is as small as possible.
- Type : Processing type, for example: 64-bit, 128-bit, 256-bit. The higher this parameter, the higher your card and the better graphics processing.
In addition, readers can also refer to the article 3 simple ways to check the configuration and hardware information of computers and laptops. With this article, you will understand the parameters of the machine from which to choose to buy the device as well as choose the appropriate replacement parts.
Refer to the following articles:
- How to check the temperature of CPU, hard drive, VGA computer, laptop?
- 2 simple ways to update VGA driver for computer monitor, laptop
- 5 basic ways to update, update drivers for computers
Hope the above article is useful to you!
You should read it
- ★ How to check the number of charges and laptop PIN bottle
- ★ How to check the battery level of the laptop battery without software
- ★ How to check the bottle of Laptop Battery without software
- ★ How to check laptop battery bottle with BatteryMon
- ★ How to use KeyboardTest to check the computer keyboard