COUNTIFS function - The function performs counting the number of cells in a data table that satisfy many conditions in Excel
The following article introduces you to the COUNTIFS function - one of the functions in the statistical function group is very popular in Excel.

Description: The function to count the number of cells in a data table satisfies many conditions.
Syntax: COUNTIFS (criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], .)
Inside:
- criteria_range1: The first range of condition 1, is the required parameter.
- criteria1: The condition that identifies a cell or reference to be counted, which is a required parameter.
- criteria_range2, criteria2: The second data range you want to count corresponding to the second condition ( criteria2). Are optional values containing up to 127 pairs of ranges and conditions.
Attention:
- If the criteria condition refers to an empty cell -> the function considers that cell to be 0.
- Use the characters?, * To combine in counting conditions.
For example:
Calculate the total number of items described in the table below:
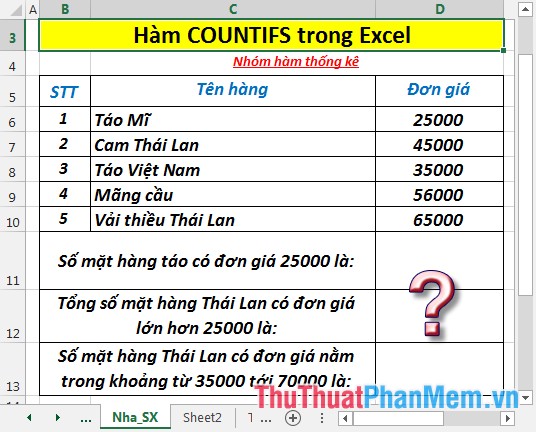
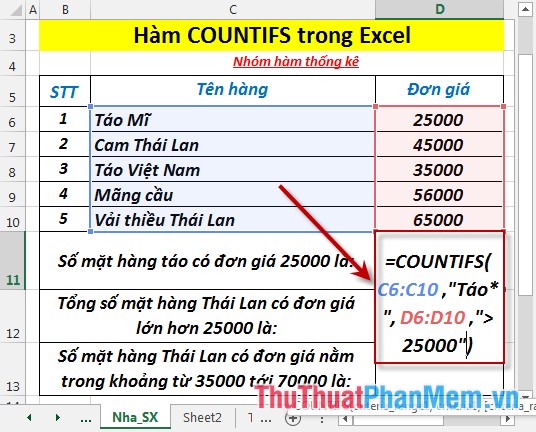
1. Calculating the total number of apple products with unit prices greater than 25000.
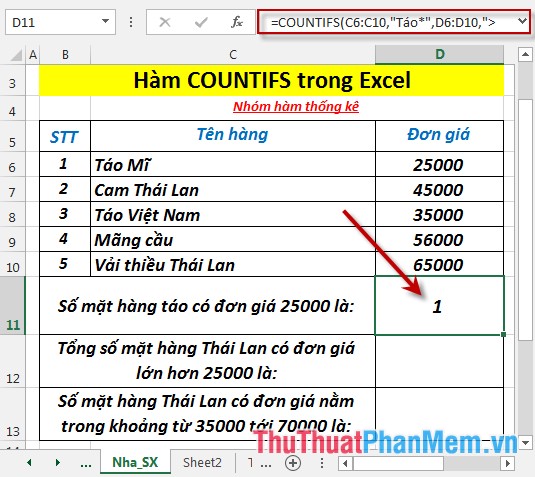
- In the cell to calculate, enter the formula : = COUNTIFS (C6: C10, "Apple *", D6: D10, "> 25000")
Press Enter -> the total number of apple items with unit price greater than 25000 is:
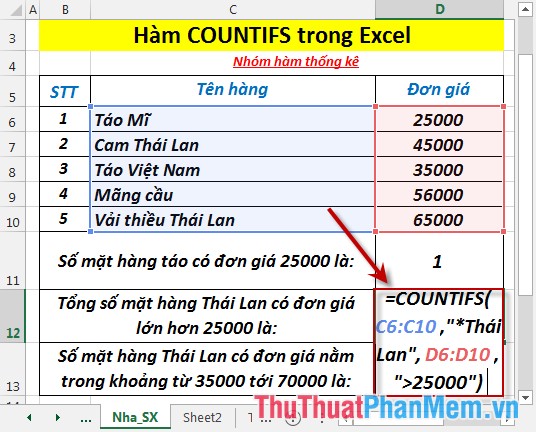
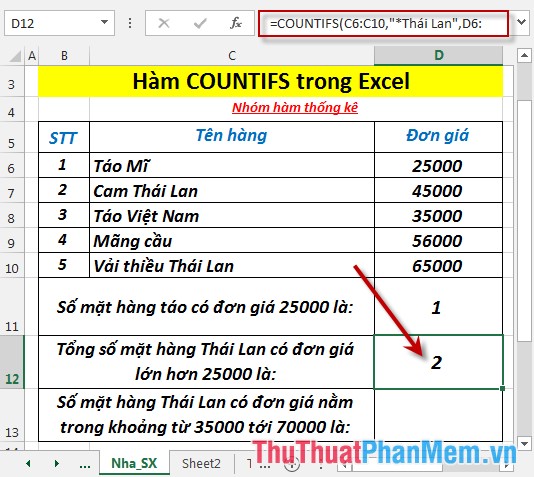
2. Calculate the total number of Thai products with unit prices greater than 25,000.
- In the cell to calculate enter the formula: = COUNTIFS (C6: C10, "* Thailand", D6: D10, "> 25000")
- Press Enter -> Total items of Thailand with unit price greater than 25000 are:
3. Calculate the total number of Thai products that have a unit price between 35,000 and 70000.
- In the cell to calculate enter the formula: = COUNTIFS (C6: C10, "* Thailand", D6: D10, "> 35000", D6: D10, "<70000")
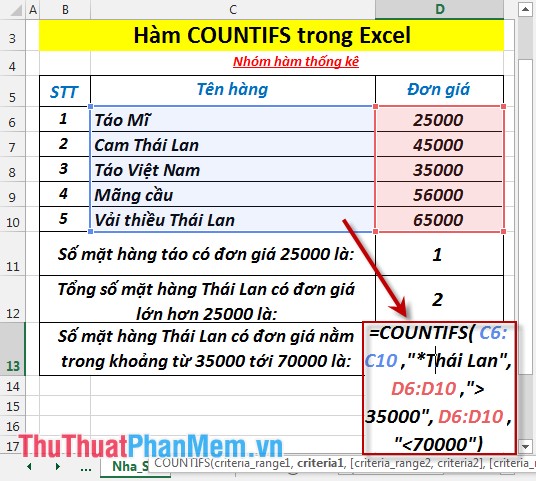
- Press Enter -> The total number of Thailand products with the unit price range from 35,000 to 70000 is:

Above are instructions and some specific examples when using the COUNTIFS function in Excel.
Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ The COUNTIFS function, how to use the cell count function according to multiple events in Excel
- ★ Cell counting function with data in Excel - Enclose example
- ★ COUNTA function - The function performs counting non-blank cells in the list of arguments in Excel
- ★ COUNTBLANK function - The function performs counting empty cells in the list of arguments in Excel
- ★ How to use Hlookup function on Excel