What factors determine the strength of a CPU?
CPU (Central Processing Unit) or also known as central processor, microprocessor, chip, is the electronic circuit in a computer. This part executes the instructions of the computer program through arithmetic, comparison, logic or basic input - output (I/O) operations proposed by the code.
For computers, the CPU acts as the brain, helping to operate and process most of the tasks you perform on the computer. The selling price of CPUs is differentiated according to the processing power as well as the technology used on them. So what factors affect the strength of the CPU? Let's find out with HANOICOMPUTER in this article!
There are 7 main factors that directly affect the processing power of the CPU. These factors include:
- Number of cores (also known as multiplier)
- Pulse
- Hyper-Threading
- Cache
- Word Size
- Address bus width
- Data bus width
So how do these factors affect the strength of the CPU? Let's find out right away!
Number of CPU cores
A core is a unit of CPU or we can also understand that a core can be considered a separate CPU. Each core has its own execution and fetch cycle, thereby helping the CPU operate more efficiently. The computers we use today all use dual-core or quad-core CPUs, which means the CPU has 2 cores or the CPU has 4 cores. Or the Intel Core i9-10900K CPU, which was just released in May 2020, has up to 10 cores.

CPU Intel Core i9-10900K (3.7GHz turbo up to 5.3GHz, 10 cores 20 threads, 20MB Cache, 125W) - Intel LGA 1200 Socket
Not only that, the biggest advantage that multi-core processors bring to users is the ability to multitask. On multi-core CPUs, each task will be processed on one core. The remaining cores will enter a state of rest until there is another task that needs to be processed. On single-core CPUs, when a program fails, the entire system will not work.
One of the biggest benefits of multi-core technology is multitasking. With a multi-core CPU, each task will be handled by one core, the remaining cores will go into idle state until another task requires it. Whereas if the CPU only has one core, all tasks will be processed on that core. This is very risky because when a program fails, the whole system will freeze.
Online games, graphics, and video editing software can take full advantage of the CPU's multi-core capabilities. You can see a clear difference in video rendering speed between a 4-core processor and a 6-core processor.
CPU clock speed
Clock speed is a parameter that represents the working speed of the CPU. One clock cycle is equivalent to 1Hz, which is one cycle per second. The clock speed of modern microprocessors today ranges from 2 to 5GHz. That is, in one second, the CPU performs billions of cycles.
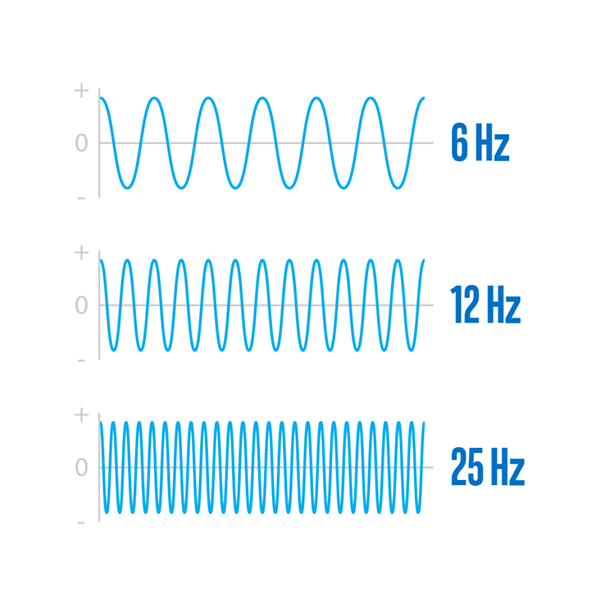
In general, the higher the clock speed, the faster the CPU's processing speed. However, a CPU with a high clock speed also consumes more energy and generates more heat. When the temperature generated by the central processor is greater than its heat capacity, the clock speed will automatically decrease to reduce the temperature. From there, the computer's working speed will also decrease.
Hyper-Threading
Hyper Threading is a technology that allows a physical CPU to act as 2 CPUs by dividing it into different processing threads. This allows the CPU to handle multiple tasks at the same time, thereby increasing the processing speed of the system.

The effects of hyper-threading technology are most evident for users using 3D modeling software, video editing applications, and scientific research applications. Hyper-threading technology on the CPU can help increase the performance of the machine by up to 30%.
CPU Cache
Cache memory, also known as buffer memory, is a small, high-performance RAM memory built into the central processor. Data and instructions that are used frequently will be stored in this memory. This data plays an extremely important role like a signpost in the system, contributing to shortening the time the CPU accesses and retrieves information in the main memory. The role of cache memory is most clearly demonstrated when the CPU processes games, edits videos or other heavy applications.

Word Size
Word size is the number of bits that the CPU can process at a time. For example, a 32-bit processor is faster than a 16-bit processor simply because it has a larger word size.
The word size of a computer system today ranges from 32 to 64 bits. Modern computers manufactured in recent times usually have CPUs with word sizes of 64 bits.
Address bus width
Address bus width refers to the number of memory locations that the system can have. For example, if you have a 32-bit address bus, this means that you can have a maximum of 2^32 (4,294,967,296, over 4 billion) addresses. These addresses or memory locations can hold 1B, which is a total of 4GB of writable memory.
Data bus width
The data bus is the internal electrical path that allows the CPU to exchange data with the cache. The width of the data bus can be roughly understood as the number of bits (electrical paths) that make up the bus. Normally, the data bus will be the same size as the address bus, but there are exceptions. If the data bus is 16 bits and the address bus is 32 bits, the data will be fetched in groups of 2 x 16 bits.

Above are 7 factors that affect the strength of the CPU. However, to compare the power of central processors produced in recent years, you only need to pay attention to the first 4 factors including number of cores, clock speed, hyper-threading and cache memory. Hopefully you have learned many interesting things when reading this article!