The OFFSET function returns a reference in Excel
The OFFSET () function is a function of the reference and search function group in Excel. Functions are used quite a lot when processing and calculating data in spreadsheets. The following article helps you better understand the OFFSET () function you guys follow along.

The article describes the syntax and usage of OFFSET () function in Excel.
Description
The OFFSET () function returns a reference to a range, a cell or a range of cells with the number of rows and columns specified by you.
The return reference can be a cell or a range of cells that you can specify the number of rows and columns to return.
Syntax
= OFFSET (reference, rows, cols, height, width)
Inside:
- reference: is the reference area that you want to rely on to create a new reference area. The reference must be referenced to a consecutive cell or range of cells, otherwise the function will return an error value.
- rows: is the number of rows, up or down the reference, counting from the first cell of the reference. The row number can be a positive number (below the reference) or a negative number (above the reference).
- cols: is the number of columns, left or right of the reference, starting from the first cell of the reference. The column number can be positive (right reference) or negative (left reference).
- height: is the height calculated by the number of rows you want to have the reference returned.
- width: is the width calculated by the number of columns you want to have the reference returned.
Note
- Height and width must be positive numbers.
- If omitting height and width, the OFFSET () function will default to the height and width of the reference.
- If rows and cols cause the reference area to go beyond the range of the worksheet, the OFFSET () function will report the #REF! Error.
- The OFFSET () function does not move or change any selected part because the function returns only a reference. You can use the OFFSET () function in combination with functions that require a reference argument.
For example
1. In cell B8 returns the value of cell E6 through the base reference cell B5.
- In cell B8 you enter the formula: = OFFSET (B5,1,3,1,1)
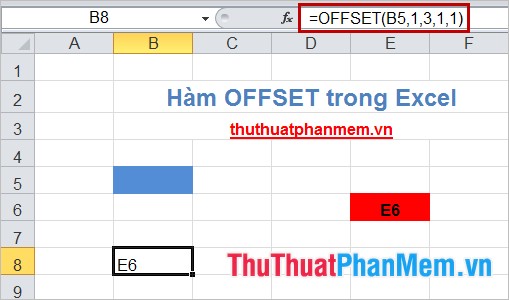
2. Combine the OFFSET () function with the SUM () function.
For example, the total salary and bonus for Nguyen Thi Dung's employees start from cell B6 (salary of the first employee).
Applying the function: = SUM (OFFSET (B6,3,0,1,2)) you will get the following result:
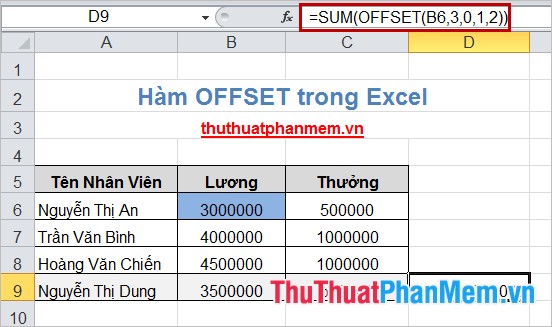
The OFFSET () function can be combined with many other functions to calculate and process data in Excel. Functions will help you a lot if you know how to apply functions and combine them effectively. Good luck!
You should read it
- ★ ISREF function - The function returns True if the value is a valid reference value in Excel
- ★ How to use ADDRESS function in Excel
- ★ Function Address - The function returns the address of a cell in Excel (usage, examples, examples)
- ★ CHISQ.TEST function - The function returns the independence test in Excel
- ★ How to use the IF function in Excel