Quick fix tip when Internet connection is 'broken'
When browsing the web and the "The page cannot be displayed" message is displayed (the page cannot be displayed), the network connection may be corrupted. The following methods will help restore.
1. Restart the connection
The easiest way is to right-click the Local Area Connection icon in the system tray (or by right-clicking on the icon My Network Places > select Properties > Disable . Then, click Enable again.
If this is not possible, users can try out measures related to the IP address:
2. Get back the IP address
 If you subscribe to a DSL or cable, you may be using a dynamic IP address - which means that the address connecting the PC to the Internet will change each time you log on. This address is specified by the DHCP protocol. However, during the operation, DHPC may not grant a new address when the machine starts up and you will be "stuck" with the old IP address and cannot connect to the Internet.
If you subscribe to a DSL or cable, you may be using a dynamic IP address - which means that the address connecting the PC to the Internet will change each time you log on. This address is specified by the DHCP protocol. However, during the operation, DHPC may not grant a new address when the machine starts up and you will be "stuck" with the old IP address and cannot connect to the Internet.
Whether the system is directly connected via modem or router, the first step you must take is to get an IP address specified by right-clicking on the network connection icon in the system tray, selecting Repair. Windows will automatically remove the old address and request a new address from the router or service provider (depending on how the PC is connected). In most cases, this is quite effective. But if you can't fix it, you have to solve it manually.
Click on Start menu> Run > type cmd . (In Windows Vista, just type cmd in the Start Search dialog box). At the prompt to wait for the command on the DOS screen, type ipconfig to see the current IP address, subnet mask and default gateway for all adapters. Other adapters may include Wi-Fi and Bluetooth cards, although they will appear in a disconnected state.
This statement itself only displays information, not anything. To get another IP address, type add / release and / renew parameter after the word ipconfig and a space. ipconfig / release will control the DHCP server to delete the existing IP address of all adapters, whether Ethernet or wireless. Then, ipconfig / renew, if successful, a new IP address, a new subnet mask and a new default gateway will appear.
3. Check DNS cache
When you are still connected to the Internet but cannot access a page, it may cause problems with the DNS client cache causing this. DNS translated the Internet domain name text into IP number. For example Amazon.com became 207.171.171.132. The cache stores a record of the pages you have visited so that the next time, when you continue, will load faster. Sometimes, a part of the file is corrupted and makes the PC unable to retrieve the archive. Clearing cache is the way to solve this problem.
Type the command line ipconfig / displaydns to see a list of recently visited pictures. If you don't have the site name you need to enter, type ipconfig / flushdns to delete this list. After that, retype the web address in the browser.
4. Use additional parameters of ipconfig
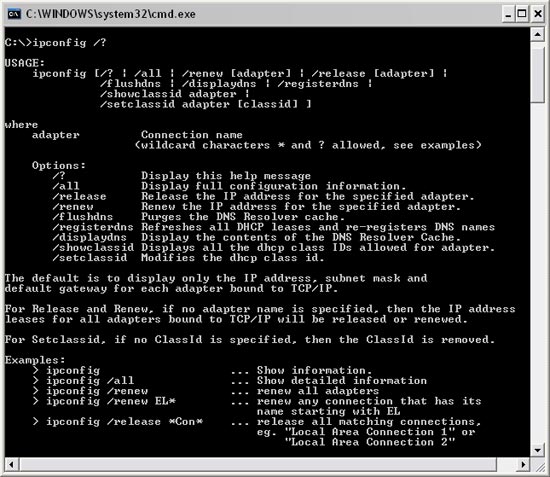
The parameters of the ipconfig command.
Ipconfig has many other parameters for troubleshooting at a higher level, and if you're lucky, you'll never need them. Type ipconfig /? for further research.
5. Ping the IP address
Also in the DOS window, the ping command acts as the computer's network connection. This ping sends the packet to the host, which can be like a submarine that sends sound waves to an underwater object to determine the distance, the ping command estimates the two-way travel time of the packet, returning it to and display any packet loss status.
First, look at the computer's IP address (for example 127.0.0.1) and type ping 127.0.0.1 at the command prompt, wait a few seconds for a response. Windows will try to ping the network card of the system to see if the device is working. If you get back the packet, it means that the network adapter is working properly. Now ping an external address by typing it, for example ping google.com . If there are returned packets, your network connection has been established.
However, if you do not receive this packet, try pinging the IP address of the default gateway. If this is not possible, your hardware (modem, router, wiring) has problems and must be checked again.
6. Check hardware
If the computer is connected directly to a DSL modem, check that the cables are securely attached to the connector, the modem light must be lit. Check the Ethernet port on the PC to see if the light is on. If the light is off while the cable is connected to the computer (turning on the power), it means changing the Ethernet port.
If the light is on and there is no connection, turn off your network devices and wait a moment and then turn it back on. Need to follow the following sequences.
- Turn off the PC, unplug the modem's power cord. If you are using a router, disconnect the router's power cord.
- Then restart the modem. After it has finished booting and has a connection indicator, turn on the router and wait for the router to restart.
- When this is done, turn on the PC, open the browser to check the connection.
If all of the above failed, it is time to call support from the service provider. Let them know you have done these things so they don't have to do it again and take time. The cause may be an error in the system or on the line from outside to your home.