How to view all applied Group Policies in Group Policy Editor
Windows' built-in Group Policy Editor allows you to quickly apply system-wide or user-specific policies and features with just a few clicks. In fact, many Windows instructions often ask you to edit Group Policy Objects.
If you're someone who changes a lot of policies to make Windows work the way you want, it's important to keep track of all those policy changes. This is especially true for new users. Mainly because, if something goes wrong with the policy change process, finding the policy quickly will help you restore the system. Not to mention, having a quick view of all policies applied or changed helps you understand system configuration better.
So, in this quick article, let's look at how to find all applied group policies in Windows.
Use the Resultant Set of Policy tool
Windows has a built-in tool called Resultant Set of Policy . This tool only displays policies that are enabled or disabled. Since all policies that are applied or changed will be in one of these two states, you can use this simple tool to find applied policy groups.
1. First, open the Start menu , search for "rsop.msc" and click on the result. Or, open the Run dialog box with the keyboard shortcut Win+ R, type "rsop.msc" and press Enter.
2. As soon as you do that, the Resultant Set of Policy tool will open. It will immediately scan the system. It may take a few seconds.

3. Once done, you can see all the applied policies by expanding the folders on the left panel.

Very simple, right? You've got all the information you need about applied policies in a single tool.
Use Filter Options in GPEdit to find the applied policy
Instead, you can also use the filtering function in Group Policy Editor. The only downside to this method is that you have to filter all three main folders separately: Software Settings, Windows Settings and Administrative Templates that appear in the Computer Configuration and User Configuration sections . Most useful and configurable policies are located in Administrative Templates.
1. First, open the Start menu , search for Edit Group Policy and click the result to open Group Policy Editor.
2. In Group Policy Editor , right-click on the folder that appears on the left panel and select the Filter Options option.

3. In the Filter Options window , set the options in Select the type of policy settings to display as follows and click the OK button to save the changes.
- Managed → Yes
- Configured → Yes
- Commented → Any
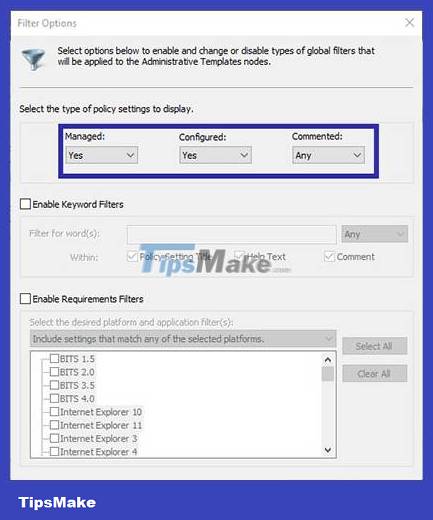
From now on, Group Policy Editor will only display enabled and disabled policies.
How to view group policy applied with PowerShell
Another method for determining which policy is applied to a Windows user or computer involves using PowerShell. If you are someone who likes to use command line tools to interact with or make changes to your computer, this method may be useful.
To view group policies applied using PowerShell, follow these steps:
- Press Win + S to open the search menu.
- Type powershell in the text box and select Run as administrator .
- Select Yes when the User Account Control (UAC) prompt appears.
- Enter the following command in the PowerShell window and press Enter :
gpresult /Scope User /v 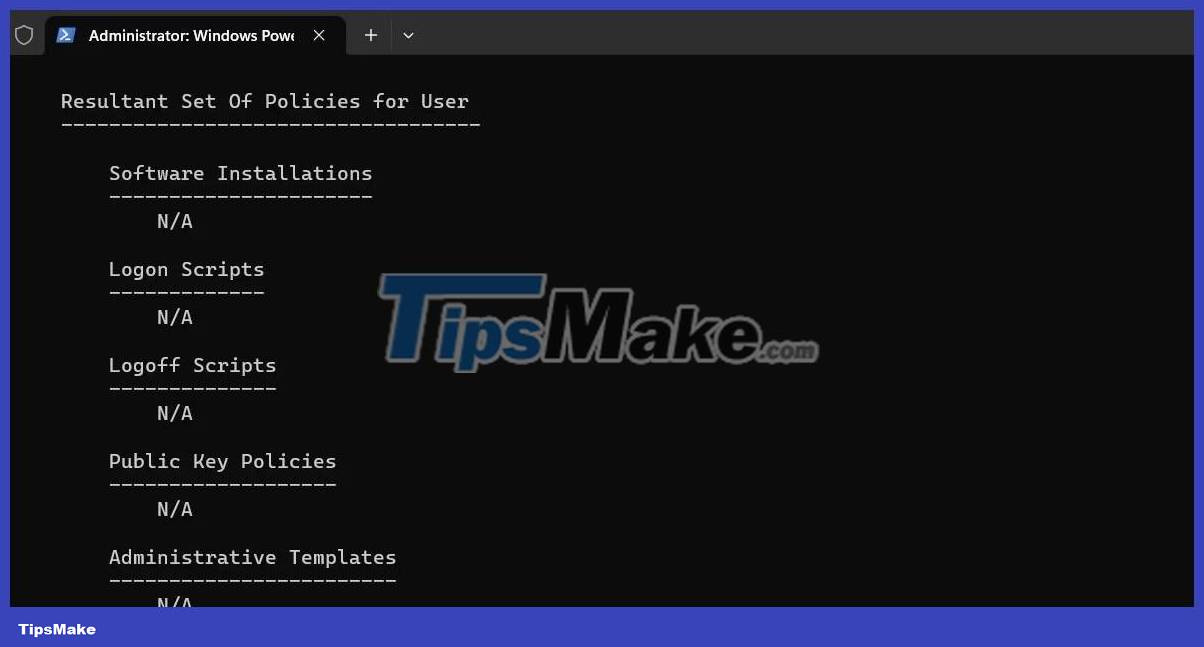
When you run the above command, you will see all the policies applied in the Resultant Set Of Policies for User section . If you want to see all policies applied to the computer, use the following command instead:
gpresult /Scope Computer /vFor more useful commands, be sure to check out TipsMake's guide to the best PowerShell commands for Windows.
Knowing how to check the policies applied to your Windows computer can be helpful when troubleshooting a problem with a program or feature or when you're concerned about your privacy or security. Luckily, this is easy with the methods mentioned above.
You should read it
- ★ Use Group Policy Filtering to create a NAP DHCP enforcement policy - Part 1
- ★ How to use Local Group Policy Editor to tweak your computer
- ★ How to apply Group Policy only to non-administrators in Windows 10
- ★ 8 'tweak' Windows Group Policy any Admin should know
- ★ Configure App-V with Group Policy Objects