How to record system audio on Linux
One of the most interesting, Linux is an incredibly viable 'candidate' as a creative workstation. For example, for audio creation, there are some great standard tools available to users, like Audacity and Ardor. Overall, this is a powerful and flexible system. This tutorial shows you how to record audio in Linux, both from microphone and system, using Audacity and PulseAudio.
Install Audacity
Audacity is available in a lot of distributions. It is usually available in the main archives.
For Ubuntu / Ubuntu / Ubuntu-based distributions:
sudo apt install audacityFor Fedora:
sudo dnf install audacityFor OpenSuse:
sudo zypper install audacityFor Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S install audacityIf you like Snaps or Flatpaks, both are available.
flatpak install flathub org.audacityteam.AudacityOr:
sudo snap install audacityInstall PulseAudio Volume Control
This is the app you'll use to record audio from the system. It's a great way to collect audio from videos, songs, or other media for later use. If you've ever wondered how people get high-quality sound samples, here's one way to do it.
PulseAudio Volume Control is available in most large archives. You will use the same commands as above to install it.
For Ubuntu / Ubuntu / Ubuntu-based distributions:
sudo apt install pavucontrolFor Fedora:
sudo dnf install pavucontrolFor OpenSuse:
sudo zypper install pavucontrolFor Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S install pavucontrolPulseAudio Volume Control is also available as Flatpak but not as Snap.
flatpak install org.pulseaudio.pavucontrolRecord audio from microphone
Once you've plugged in the microphone into the system, open Audacity. It will automatically find the hardware and open it for recording.
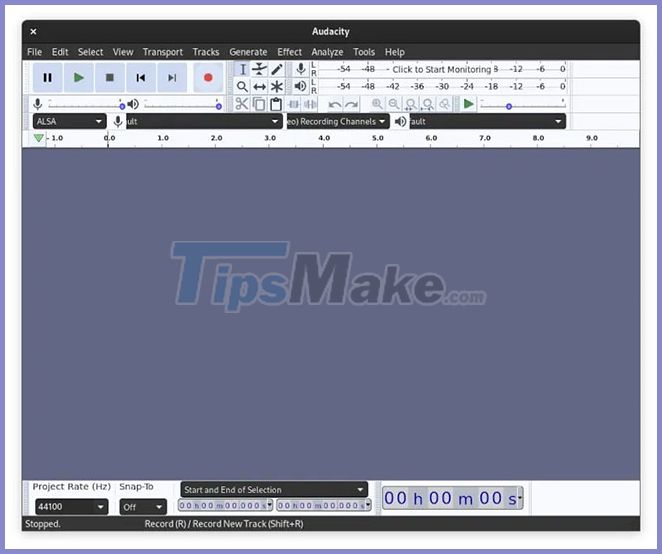
Just click the big red record button. Everything is as simple as that! Audacity is a simple tool to use, so it's hard to make mistakes.

Record audio from the system
This is a bit more complicated. Press the record button, just like above. This will start recording from the microphone. Once you've recorded it, open PulseAudio Volume Control and navigate to the 'Recording' tab .

Click the drop-down menu that says: 'ALSA plug-in [audacity]… from' .
Select the option that says: 'Monitor of Built-In Analog Stereo' . This will track the information the application is sending to PulseAudio and record that information instead of the sound coming from the microphone.
From there, go ahead and play whatever sound you want, and you'll see that sound show up in Audacity as it plays. You can stop recording and process whatever audio you're recording, just like any other audio input into Audacity.

Hope you learned a few useful things about Audacity and PulseAudio Volume Control. Now you know how to record your system sounds in Linux!
You should read it
- Listen to the strange sound obtained from planets in the Solar System
- The researchers first obtained the volcano's 'thunder'
- How to play Ambient Sounds on HomePod
- How to customize sound effects on Mac OS
- How to turn off automatic tab sounds on Chrome and Firefox
- How to change ringtone and incoming call on Facebook Messenger
 How to install Deepin desktop environment on Ubuntu
How to install Deepin desktop environment on Ubuntu How to change screen resolution in Ubuntu
How to change screen resolution in Ubuntu Is Linux the operating system or the kernel?
Is Linux the operating system or the kernel? How to Install Gradle on Debian 10
How to Install Gradle on Debian 10 How to access Linux Ext4 partition from Windows
How to access Linux Ext4 partition from Windows What is Linux Hosting?
What is Linux Hosting?