How to format a hard drive into NTFS in Linux
If you are a user moving from Windows to Linux and vice versa or are cooperating with Windows users and need access to the same file, it is best to have a common partition in NTFS format, so that both operating systems are accessible.
Linux proves its versatility by supporting all storage formats supported by Windows. Of the three options, FAT32 will be too limited for current use, with a maximum file limit of 4GB. ExFAT is not much better because it is located between FAT32 and NTFS.
This makes NTFS the best option, and fortunately, it is easy to format the hard drive in NTFS format in Linux. There are many ways to do this, but one of the easiest is to use GParted.
Create NTFS partition with GParted
GParted is the most popular application of its kind in the open source world, so it may already be installed in your distribution. If not, find it in the software center, the app store, or install it via the terminal with:
sudo apt install gparted 
Run GParted and select the hard drive you want to format into NTFS from the drop-down list at the top right of the program window. Double check that you have selected the correct hard drive.
Create a new partition
For example there is a completely empty drive connected, so GParted calls its space unallocated. If you already have one or more files on it and make sure they don't contain the data you need, right-click on them and delete them one by one.
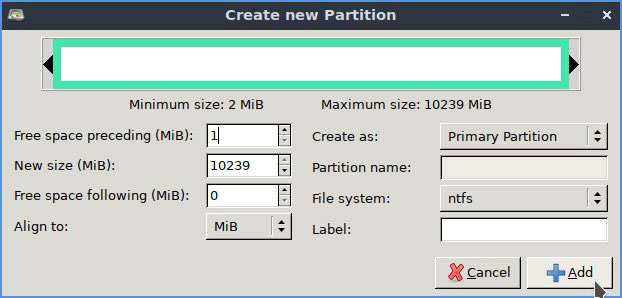
Right-click on unallocated space and select 'New' from the menu that appears.
Click the drop-down menu next to 'File System' and change its type to 'ntfs'.
The article recommends that you do not change the rest of the settings. It is recommended to use the entire HDD space for the primary NTFS partition that both Linux and Windows will recognize.
Please provide a name for it in the 'Label' label to make it recognizable. If you do not do this, the distribution will usually mount it using an unfriendly UUID.
Check and apply
GParted, by default, adds each operation to a batch but does nothing with the hard drive. All changes are virtual until you make it permanent.
Click 'Apply' to start the procedure. GParted will ask if you are sure you want to proceed - remember, choosing the wrong hard drive can lead to data loss. Click 'Apply' here too, and GParted will begin to perform its task.
If you want to check additional information for each step, you can expand the list in the 'Details' section of the 'Applying pending operations' window.
When done, click 'Close' and enjoy the new NTFS partition.
As a final note, if the distribution uses GNOME as a desktop environment, then it is likely that you have installed Gnome Disk Utility. You can usually find it in 'Disks' via the distribution's main menu, and it also allows you to format any drive to NTFS.
To do this, run it, select the drive you want to format into NTFS from the left panel, click the two-gear icon under the graphical representation, and select 'Format Partition…' . Set the format type to NTFS and proceed with the formatting process.