How to delete a drive cannot be deleted with Disk Management
In many cases, you may need to delete an existing drive (it is also called partition in older versions of Windows operating systems such as Windows XP and Server 2003), to free up space or delete all drive to convert dynamic to basic (basic to basic) or MBR to GPT drives. Normally, it is easy to delete the drives with the Disk Management utility of Windows (right-click the drive you want to delete, and select " Delete Volume " from the menu).
Warning: Deleting a drive will cause all data stored in this drive to be lost, so back up the necessary data in advance.
However, when deleting the C drive in Disk Management, you will encounter a situation where the 'Delete Volume' feature is grayed out, as follows:

In fact, the C drive is not the only drive that cannot be deleted in Disk Management. Boot disk, drive file page storage (Page file is a special mechanism that helps Windows never run out of RAM), file errors or files that store information from memory used by Windows for Hibernate, manure Protected EFI system areas, recovery partitions, OEM partitions and mobile device partitions cannot be deleted in Windows Disk Management. Let's find out the reasons and solutions for this problem through the following article.
How to delete a drive cannot be deleted with Disk Management
- Why can't some drives be deleted in Disk Management
- Why can't drive C be deleted?
- Why can't the EFI system drive be deleted?
- Why can't Recovery partition be deleted?
- Why can't OEM partition be deleted?
- Why can't the drive store error files, Hibernation and Page files cannot be deleted?
- Why can't partitions on mobile devices be deleted?
- How to delete a special drive
- How to delete a drive on a mobile device
- How to delete OEM partitions and Recovery partitions
- How to delete the system drive, boot drive, and drive to save page file, hibernation file and error file
- Steps to delete the drive using the MiniTool Partition Wizard
Why can't some drives be deleted in Disk Management
Why can't drive C be deleted?
In general, Windows file system drives are always assigned by C by default, when you install the first operating system. If the Windows operating system is saved in the running C drive, you will not be allowed to delete this drive, since deleting it will lead to a lot of errors and confuse the system.
To be more precise, the drive that is loaded with the Windows operating system cannot be deleted, not just the C drive. For example, if you dual-boot Windows 7 and Windows 8, with Win7 stored in drive C and Win8 in drive D, you can delete the C drive but cannot delete drive D when Windows 8 is running.
Why can't the EFI system drive be deleted?
Currently, after successfully installing Windows or Mac OS X on a GPT PC drive, the EFI system partition (abbreviated as ESP) can be created and not displayed in Windows Explorer or Macintosh. Explorer. To view it, you must enter Disk Management or Disk Utility. Normally, you cannot delete it in Windows (the Delete Volume option is grayed out):
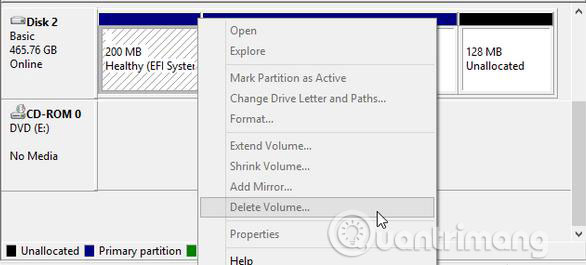
What is the reason? To answer this question, you need to know what it is saving. According to Wikipedia:
ESP contains boot loader programs for all installed operating systems (contained in other partitions on the same storage device or other device), device driver files included in the computer used by firmware at boot time, in system utility programs (running before the operating system is booted) and data files such as error logs.
To protect all these important files, Windows does not specify this drive with the drive letter, and users cannot see it in Windows, nor can it delete it, because deleting it will cause the system to installed cannot start.
However, in some cases, the user wants to delete it because it takes up some space in the drive. For example, users may want to delete the EFI system partition created on the Mac hard drive after uninstalling Mac OS X. At this point, how to delete the system drive in Windows? The solution will be introduced in the following section.
Why can't Recovery partition be deleted?
After installing Windows 7, Windows 8 or other systems, you can see that some Recovery partitions are created on the system drive, taking up space from several hundred MB to tens of GB. After right-clicking on the Recovery drive, you will only find a specific "Help" feature available and there is no option to delete it:
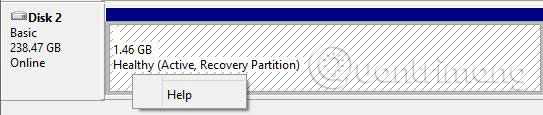
What is the reason?
Recovery partition is created by PC manufacturers, not Windows operating systems. Therefore, Windows does not provide any functionality to operate it, except for 'Help'. It stores files and driver programs that can help restore the computer to the state when Windows was originally installed. So keeping it is essential. However, if you own a Windows installation drive or have created a backup for the system, there is no need to keep this partition, especially on small capacity hard drives like SSD.
Why can't OEM partition be deleted?
The OEM partition is also created by PC manufacturers, so Windows Disk Management does not provide the functionality to delete it:
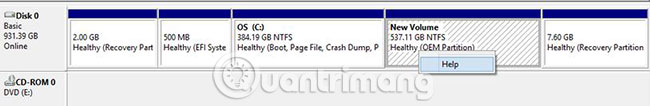
It stores backups for system restore with a key, and the so-called restore with a key is completed in this partition. Not having a system recovery feature is impossible. However, if you have backed up the system, there is no need to keep this partition.
Tip : Although you cannot do anything on the Recovery partition and the OEM partition (because they are hidden) in Disk Management, there is a way to see what content these partitions are saving. Please type the following commands in Diskpart (end each command by pressing the Enter key ):
list disk
select disk n1
list partition
select partition n2
set id = 07 override
exit
In particular, n1 is the number of drives where Recovery partition or OEM partition is set, n2 is Recovery partition number or OEM partition.
You can then see and open the hidden drive in Windows Explorer.
Why can't the drive store error files, Hibernation and Page files cannot be deleted?
First of all, see what a crash dump file, hibernation file and page file.
1. Crash Dump File : In case of a system failure (instead of any application errors), the state of the operating system information will be recorded and this type of information is called is the error file. Once these files are lost, it will be difficult to detect what error your computer is having. That may be the reason why Windows does not allow the drive to save these files. The settings for the error file are configured in Control Panel and saved in C drive by default. Here is an example in 32-bit Windows 7:
Go to Control Panel .
Select View by small icon , then select System.
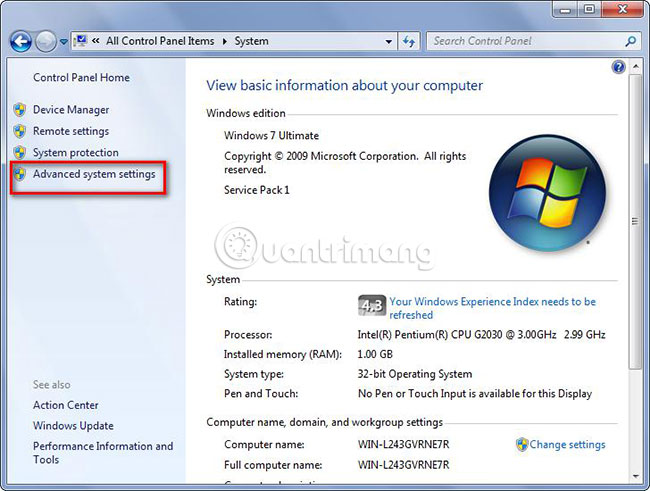
Click Advanced System Settings .
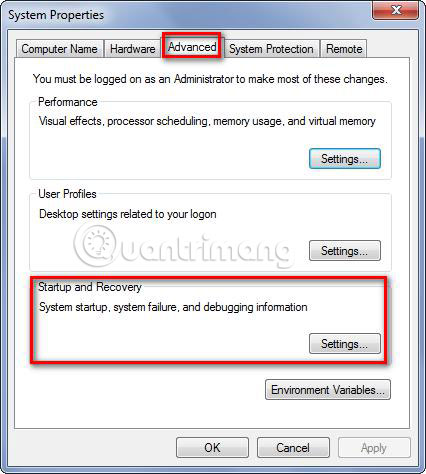
In the Advanced menu , select Settings in the Startup and Recovery section .
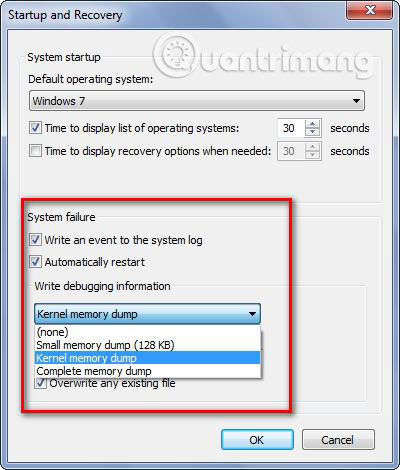
Now we can see the details of the error files.
2. Page File : Page File is a type of virtual memory on the hard drive. It is always in drive C but can be transferred to another drive, like drive D or F.
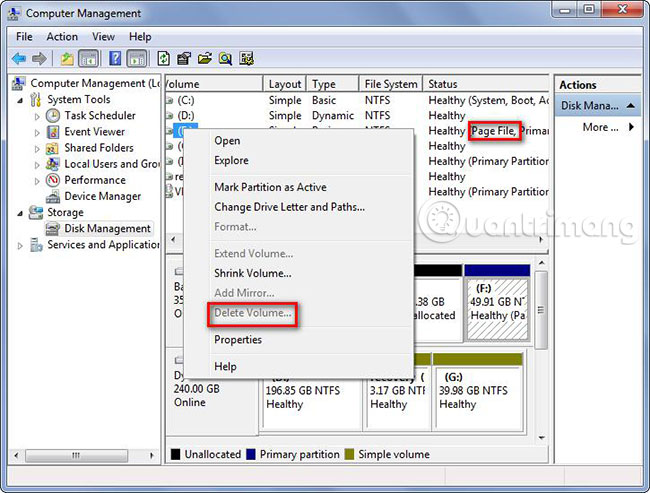
You cannot view the page files, unless you turn off the " Hide protected operating system files " option in Folder Options . When RAM is full, Windows will transfer some data from the RAM back to the hard drive, placing it in the page file. Disabling the page file may lead to some errors. If all available memory is used up, the running programs will start to fail because they cannot be swapped out of RAM into the page file. Furthermore, applications require a large amount of storage space to refuse to run when RAM runs out of space. Therefore, Windows does not allow users to delete drives that save page files.
3. Hibernation File (file that stores information from memory used by Windows for Hibernate mode): There are two modes of power management: Sleep mode and Hibernate mode, in That hibernation mode uses the hiberfil.sys file to store the current state of the PC. This file is located in the root of the drive where the operating system is installed, and Windows Kernel Power Manager preserves the file when you install Windows. It is managed by Windows so users cannot delete the drive containing the hibernate file in the usual way.

Why can't partitions on mobile devices be deleted?
As you know, USB flash drives, SD cards and optical drives are removable devices (the fact that a specific device is fixed or removable is determined by the driver). Such storage media do not require partitions, or should only contain one partition, because the use of more than one partition confuses mobile storage service. Removing a single partition on a mobile device will make the whole device unavailable. That may be the reason why Windows does not allow users to delete drives on mobile devices.

Note : The above is just a reason why it is not possible to delete EFI system drives, recovery drives, OEM drives, removable device drives, etc., by finding the file type saved, so They may not be 100% accurate.
In fact, although you are not allowed to delete these drives in Disk Management, there are other solutions.
How to delete a special drive
How to delete a drive on a mobile device
To do this, you can use the 'clean' command in Diskpart. This example will delete the partition on the USB flash drive.
1. Run Diskpart as admin to get the following window:
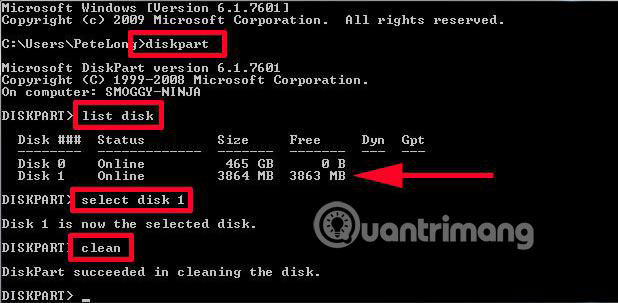
2. Type the following commands in turn, each command ends by pressing the Enter key
list disk
select disk 1
clean successively
In particular, disk 1 is a USB flash drive.
After Diskpart shows that it has successfully deleted the drive, the entire device will not be allocated in Disk Management. At this point, you can create a drive containing all the space of the mobile device.
Warning : All data will be lost after deleting the device, so choose the correct drive to delete and back up the necessary files first.
How to delete OEM partitions and Recovery partitions
This can also be done in Diskpart.
In Diskpart, type the following command and press Enter:
list disk
Then type:
select disk N
(N is the number of drives where the OEM partition or Recovery partition is located) and press Enter. Next, type:
list partition
and press Enter, then type:
select partition N
(now N is the OEM partition number or Recovery partition) and press Enter. Next, type:
xoá bỏ phân vùng phân vùng
and press Enter. Finally, type:
exit
and press Enter to exit Diskpart.
How to delete the system drive, boot drive, and drive to save page file, hibernation file and error file
Unlike mobile devices, you cannot delete the hard drive with the "clean" command if it is the current boot drive, the system drive, etc.
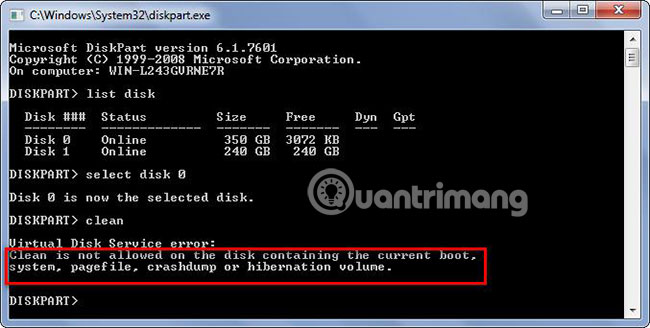
But there are also some solutions.
1. Put the hard drive in another computer. Then, delete the drive in Disk Management of that computer.
2. If you have more than one operating system, start an operating system that is saved in the drive that will not be deleted, and then delete the target drive in Disk Management.
3. Delete the drive using third-party partitioning programs, working with any type of drive mentioned in this post.
Note : The EFI system partition may not be deleted with the previous two solutions, but the third way is possible.
Professional partition programs have the ability to delete a specified drive without causing any damage to the data stored in other partitions. Here, you may consider using the free MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Note: It is only free for non-Windows users as servers. To support the server, you need to buy a special version.
Steps to delete the drive using the MiniTool Partition Wizard
1. Run the MiniTool Partition Wizard and select "Launch Application" to get the following window:
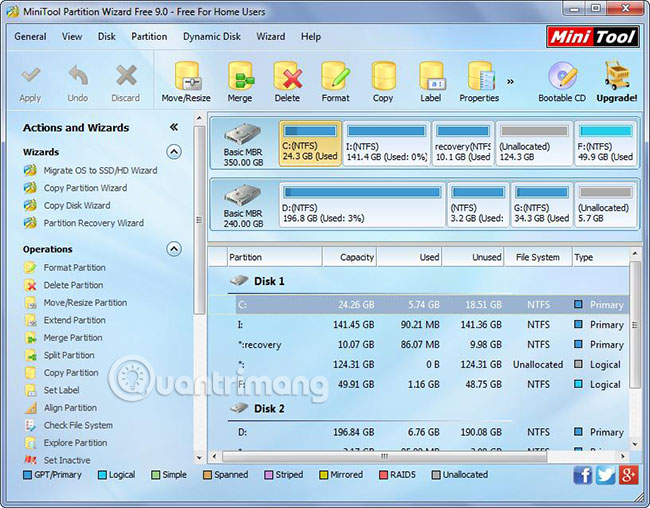
2. Select the partition to delete and select the Delete Partition feature on the left. Here, for example, we want to delete drive C. Also, because C drive stores Windows system files, the MiniTool Partition Wizard will ask you to confirm whether to delete it and just press 'Yes'.

3. Now, you can see that C drive has become an unallocated space. At this point, please click the Apply button to make changes. However, when the C drive saves Windows is running, you will be asked to restart the computer. Please do so, and then all changes will be made in startup mode.
Now, you already know how to delete the drive that cannot be removed in Disk Management. If you are troubled by this type of problem, try one of the solutions introduced in this article. Of course, you can also use MiniTool Partition Wizard Bootable CD, a tool that can operate the hard drive without booting Windows.
See more:
- How to format the hard drive on Windows
- Delete the virtual drive in Windows 7
- Delete and assign any Windows drive letter to Diskpart