How to check all services running in Linux
When using any Linux distribution, several processes and services will run together. Some services may run in the background without the user's knowledge. Running unnecessary services can consume a lot of system resources or cause security problems.
Therefore, it is necessary to know all the services that are running on the system. In this article, TipsMake.com will show you all possible ways to list the services running on Linux computers.
How to check the services running in Linux
First, understand the Linux services. If the service has a script, then it comes with three states:
- start (start)
- stop
- restart
This is all done with the - service command . For example, to restart service network-manager, run the following command:
sudo service network-manager restartThe service command references each service using the init script stored in /etc/init.d for Ubuntu and any other Debian-based distributions, and etc / rc.d / init.d for the distributions. Linux distribution is based on RedHat. Some service names vary by distribution. For example, the Apache web server service is httpd on CentOS and Apache2 on Ubuntu.
Many Linux distributions belong to the following init systems:
- System V (SysV) , is the original init system.
- Upstart
- systemd , is the newest init system as of the time of writing.
Check all services running in the System V (SysV) init system
Let's take a look at some of the Terminal commands you can use to list all services running on the SysV init system.
service --status-all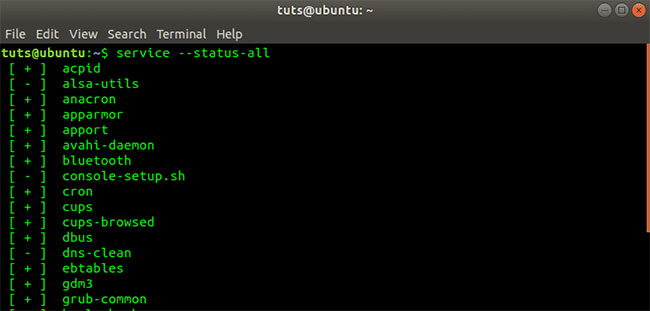 Service -status-all command output
Service -status-all command output The above command lists all the services running in the system. In case the service is running a lot, you can use the additional parameters - more and less to list the services in the view in an organized and clear manner.
service --status-all | less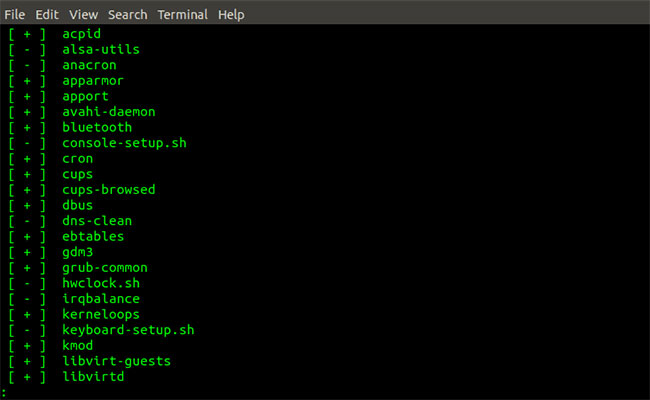 Service command output –status-all | Less
Service command output –status-all | Less service --status-all | more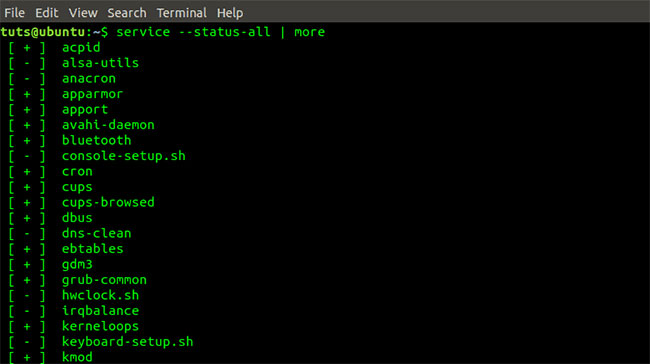 Service command output –status-all | More
Service command output –status-all | More To list only services currently running on the system, execute the command below:
service --status-all | grep runningTo view the status of a specific service, execute the command below:
service --status-all | grep [service_name] e.g service --status-all | grep httpdAlternatively, you can execute the below command to view the status of a specific service.
service httpd statusTo list all services that are activated during boot, execute the command below:
chkconfig --listCheck all services running in the Upstart init system
To list all services on Linux machines running the Upstart init system, execute the command below:
initctl listCheck all the services running in the Systemd init system
To list all services on Linux machines running Systemd init, execute the following command:
systemctl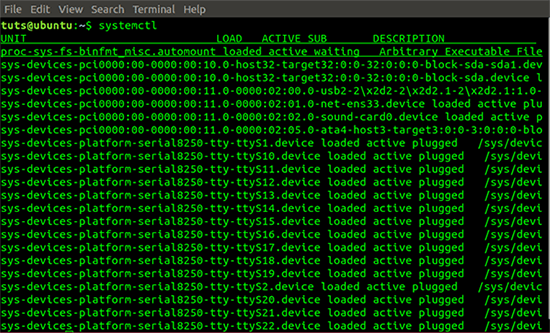 Systemctl command output
Systemctl command output From the above command, we see that the data is displayed in 5 columns, namely UNIT, LOAD, ACTIVE, SUB and DESCRIPTION .
You can also list running services based on their type with the following command:
systemctl list-units --type service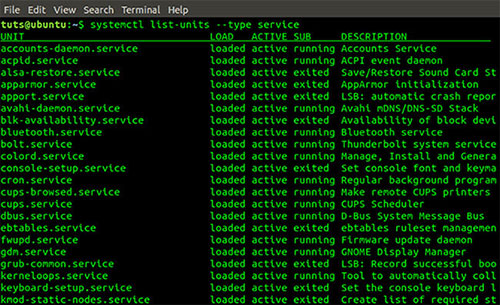 Output command systemctl list-units –type
Output command systemctl list-units –type You can also list services based on their current state. The result is quite similar to the output of the previous command but a bit simpler.
systemctl list-unit-files --type service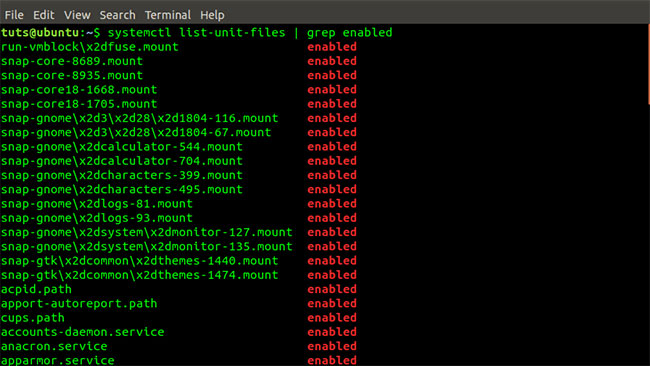 systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled
systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled To list the status of a specific service, execute the command below:
systemctl status [service_name] e.g systemctl status acpid.path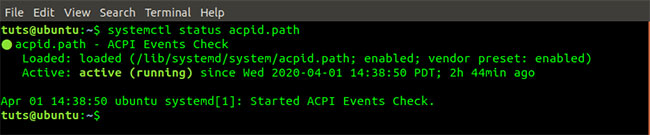 Systemctl status acpid.path command
Systemctl status acpid.path command To list only services currently running on the system, execute the command below:
systemctl | grep running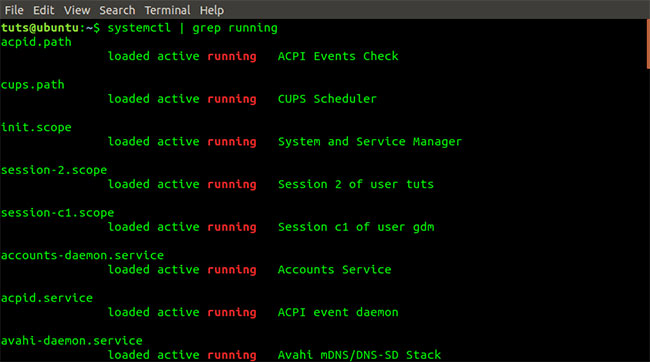 The systemctl command | grep running
The systemctl command | grep running To list all services that are activated during boot, execute the command below:
systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled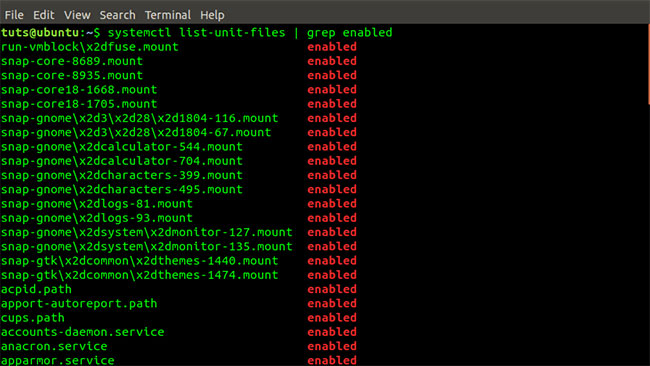 The command systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled
The command systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled You can also view the top control groups and their use of system resources such as I / O, CPU, Tasks and Memory using the systemd-cgtop command .
systemd-cgtop Systemd-cgtop command output
Systemd-cgtop command output It is also possible to use pstree to list all services running on the system. Pstree gets this information from the Systemd system output.
pstree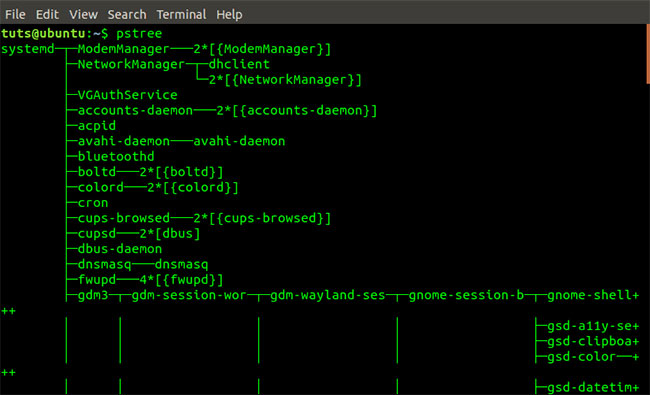 Pstree command output
Pstree command output Pstree can also be used with the System V int system. It takes the output from the SysVinit system.
pstreeYou can also use the chkservice utility to check all the services running on the Systemd system. This utility is not preinstalled. However, you can install it via Terminal using the command below:
sudo apt-get install chkservice Chkservice installation command
Chkservice installation command To start the chkservice, execute the command below. Note, you need superuser rights.
sudo chkservice The command starts chkservice
The command starts chkservice To see all the features that come with this great tool, press the key ?to open the Help menu .
 Press ? to open the Help menu
Press ? to open the Help menu