How to manage Linux services using Systemd
One of the most important skills that any new Systemd user needs to learn is how to manage computer services. This article will teach you the basics: start, stop, enable and disable services from the Linux command line.
What is Systemd?
There are a number of Linux computers running Systemd such as in the Linux, Debian, Fedora, Red Hat and Ubuntu distributions that use Systemd by default. Some distributions will be difficult or impossible to run without installing Systemd.
- 10 Linux distributions you may not know yet
Systemd was designed to replace SysV's old init project, which has been used in UNIX distributions since the 1980s. Lennart Poettering's main developer has also stated that Systemd can do more tasks. init and can act as a development platform and link between individual applications, the Linux kernel.
How to start and stop units
Systemd starts, stops, turns on and turns off "unit". Units include services, mount points, devices and sockets on the computer. In these instructions, you will work with services (.service files), which represent programs on the computer waiting for access for a specific task.
Some Linux distributions have access to Hddtemp, a small utility that checks the temperature of the hard drive. Hddtemp has a .service file and can run as a daemon, so you can start it manually and allow it to activate at startup. This utility is small so you can download and try it with Systemd, you can delete it later if you want.
- Instructions for checking the temperature of CPU, VGA, hard drive of computer, laptop
Install Hddtemp on Arch with the following command:
sudo pacman -S hddtemp
and on Ubuntu with:
sudo apt-get install hddtemp
Now start the new utility with Systemd:
sudo systemctl start hddtemp.service
You can then restart, stop and see the status of man-db with the same type of systemctl unit. Notice that the 'unit' works like any 'unit.service' file that you will use.
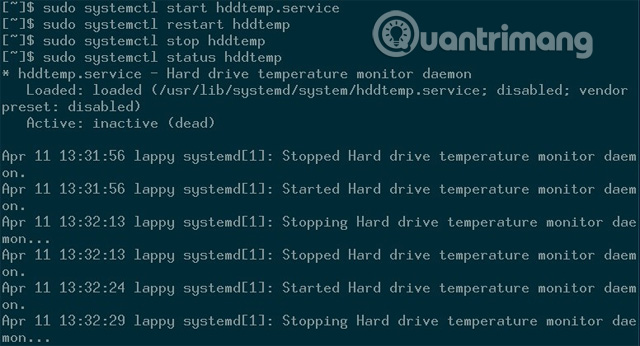
sudo systemctl start hddtemp commands, sudo systemctl stop hddtemp , and sudo systemctl restart hddtemp does not create output by default when it runs successfully.
You can get more service information with the following command:
sudo systemctl status hddtemp
In this case, this command will provide the name of the service, the status of the service (active or inactive) and start / stop made in minutes. If any of the above commands fails or causes an error, those problems will show up in the status report.
Activate and deactivate units
When starting or stopping a unit, you are completing a manual process that will likely only last for the current session. When restarting, the unit you start may not run automatically.
For units to boot, try turning them on with Hddtemp:
sudo systemctl enable hddtemp
The output will show that Systemd has created a symbolic link (symlink) to start Hddtemp automatically when the computer is in the boot process. The next time you can use the shortcut:
sudo systemctl enable --now unit
to activate and start a unit in a command.
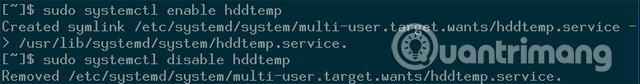
You can now disable Hddtemp easily with the following command:
sudo systemctl disable hddtemp
If you are unsure whether a unit is enabled, you can run the sudo systemctl is-enabled unit command.
Now you can remove Hddtemp from your computer if you want.
When using Systemd, the above commands will become useful when managing programs on the computer. Check the 'COMMANDS' section of the Systemctl man page with the command man systemctl to see the commands that start, stop, enable, disable, and other commands are more complex than the example above, but you should not worry about the commands. This command is very easy to use.
See more:
- How to manage Windows Vista services
- Disable unnecessary services in Windows 7
- All ways to open Windows Services on Windows 10/8/7