Forward from Exchange 2000/2003 to Exchange Server 2007 (part 2)
Review part I
Install Exchange Server 2007
This is the next installment of a series of three tutorials on how to forward a server from Exchange 2000 or 2003 to Exchange 2007, deployed in the same Active Directory Forest. For the purposes of this article, we will only install an Exchange 2007 Server, with a standard installation program (Typical). Since Exchange 2007 (Typical) has Mailbox, Hub Transport and Client Access Server are installed on the server respectively, so before you start Exchange 2007's Setup program, you must meet the following Windows software and component requirements.
Software requirements
• Microsoft .NET Framework Version 2.0 (including this update)
• Microsoft Management Console (MMC) 3.0 (note that MMC 3.0 is installed by default when using Windows Server 2003 R2).
• Windows PowerShell V1.0 (can be found here, or on the Exchange 2007 DVD).
Windows components
Mailbox Server
• Allow COM + network access.
• Internet information services.
• World Wide Web Service (WWW) service.
When installing Mailbox Server, you must make sure you have installed the hotfixes that are mentioned in the MS KB article (904639 and 918980).
Client Access Server
• World Wide Web Service (WWW) service.
• Remote procedure call (RPC) via the Windows Proxy Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) component. (Only required if you are deploying clients using Outlook Anywhere functionality, formerly known as RPC over HTTP).
• ASP.NET v2.0.
Hub Transport Server
The Hub Transport Server does not require installation of any additional windows components. However, you must make sure that the SMTP and NNTP services are NOT installed.
Attention
Listing hardware requirements for Exchange 2007 is beyond the scope of this series. For more information, see the following article in the Exchange Server 2007 Online Guide.
Once you have the Exchange 2007 installation files online or after inserting the Exchange Server 2007 DVD, double-click Setup.exe . A large screen appears, taking up the entire desktop space as shown in Figure 2.1 . Click Step 4: Install Microsoft Exchange (Step 4: Install Microsoft Exchange).
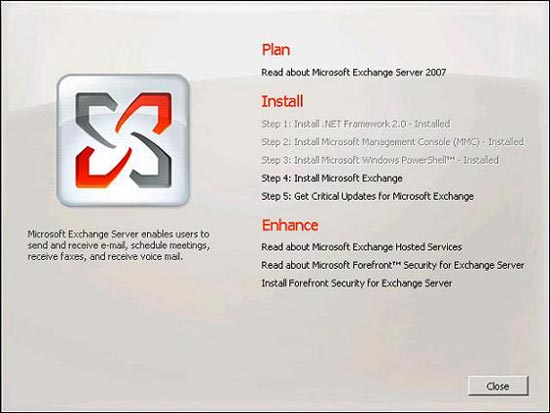
Figure 2.1 : Large installation screen of Exchange 2007
The installer will copy the necessary files and quickly start the initialization value. The initial value is completed, the first step in the Installation Wizard appears: the Introduction page. You should click Next .
The provisions in the end user copyright agreement (EULA) are given. If anyone has an English language background, check out some of their terms, even if the License Agreement is always a very interesting thing. If not, check the box I accept the terms in the license agreement (I agree to the terms of the license agreement ), then click Next . The Error Reporting page appears. You choose whether to allow this to be used, then click Next .
As you can see in Figure 2.2 , now is the time to choose the type of installation you want to perform. From the beginning we talked about Typical (standard) installation, check this option and click Next .
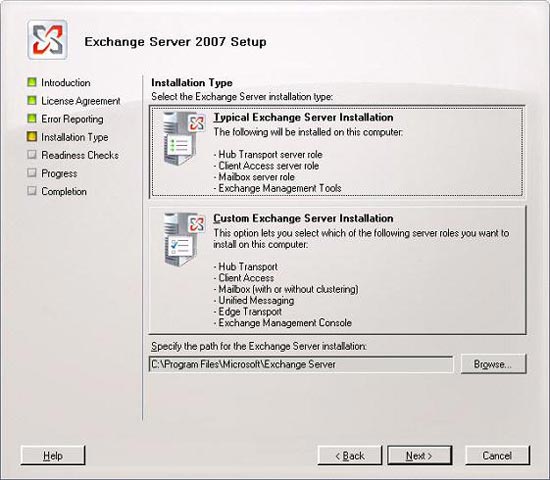
Figure 2.2 : Select Typical installation type for Exchange Server
To set up the main mail flow between Exchange 2000 or 2003 and Exchange 2007 routing groups, we need to create a routing group connector ( Figure 2.3 ). Click on Browser , select the Exchange 2000 or 2003 header server as you wish to connect to Exchange 2007, and then click Next .
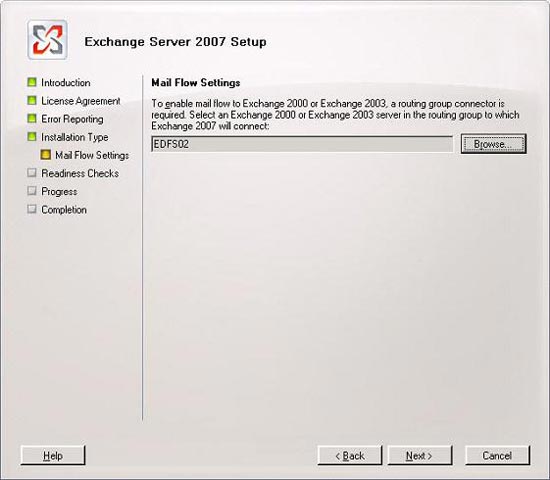
Figure 2.3 : Description of Exchange 2000 or 2003 routing group
Now Exchange 2007 Setup will check a series of prerequisites to see if Exchange is ready to install. If you have installed all necessary software, windows components, and hotfixes, the program will be complete without giving any warning or error messages. If there is a lack of a request, you should review the issue and click the Recommended Action link to see an explanation or a solution to the situation being stopped.
When all problems are resolved, click the Install button to Exchange Setup copy the necessary Exchange files and install and configure each component on the server.
Attention
If you do not run any preparatory changes as mentioned in Part 1, the Exchange 2007 Setup Wizard will prepare the Active Directory before starting to install each of the main components on the server in turn.
When Setup finishes installing completely, click Finish ( Figure 2.4 ).
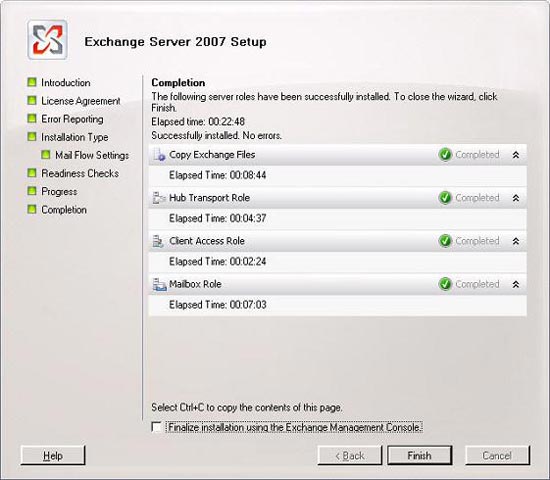
Figure 2.4: Complete the Exchange 2007 installation.
Through final implementation
After installing and correctly Exchange 2007 Server, we start the Exchange Management Console (EMC). Note that the first time EMC is started it will show you the Finalize Deployment tab (via final deployment) under the Microsoft Exchange node as shown in Figure 2.5 . You should check each task deployment in the list below and implement the deployments to suit your environment.

Figure 2.5 : Finalize Deployment Tab in the Exchange Management Console
Every deployment task is explained step by step so we don't go into details about them here.
End-to-End Scenario activities
Next to the Deployment Tasks tab above there is an End-to-End Scenario tab ( Figure 2.6 ), providing a list of optional activities to configure the component. You should skim through each component and consider whether these activities are appropriate for your Exchange environment.
Figure 2.6 : End-to-End Scenario tab in the Exchange Management Console
Each activity under this tab has quite a few self-explanatory sections. Detailed introduction of their content is beyond the scope of this series.
Global Settings
Global Settings configured on the Exchange 2000 or 2003 server will be automatically transferred to the Exchange 2007 server because these settings are stored and read from Active Directory. This means that the recipient policy, Internet Message Format, SMTP connector, and Exchange delegate rights are also applied to the mailbox of each user stored on Exchange 2007. Figure 2.7 below shows the main Default policy (Default Policy) is created from the beginning on the Exchange 2003 server.
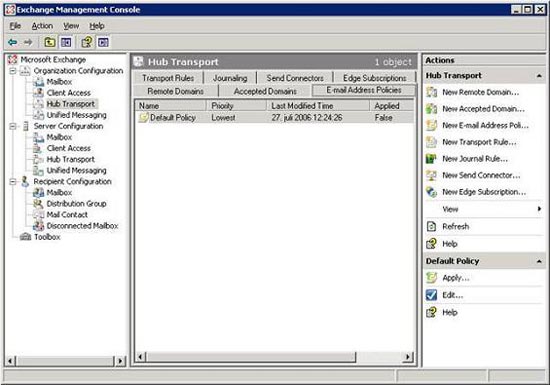
Figure 2.7 : Default Policy in the Exchange 2007 Management Console
Also note that, when the Exchange 2007 Server is deployed in a legitimate Exchange organization, any organization level setting will be managed using Exchange 2007 Management tools (such as EMC or EMS) in time. coexistence.
The second part ends here, the third part will quickly come to you in the next few days. In Part 3 we will replace the public folders, move mailbox mailboxes and a few other things before we completely shut down the Exchange 2003 server. Welcome to invite you to read!
You should read it
- ★ Installing, configuring and testing Exchange 2007 CCR on Mailbox Server (Part 1)
- ★ Backup for Exchange Server with DPM 2007 (Part 1)
- ★ New Outlook Web Access features in Exchange 2007 SP1
- ★ Backup for Exchange Server with DPM 2007 - Part 3: Backup process
- ★ Checking Exchange Server 2007 with MOM 2005 (Part 1)