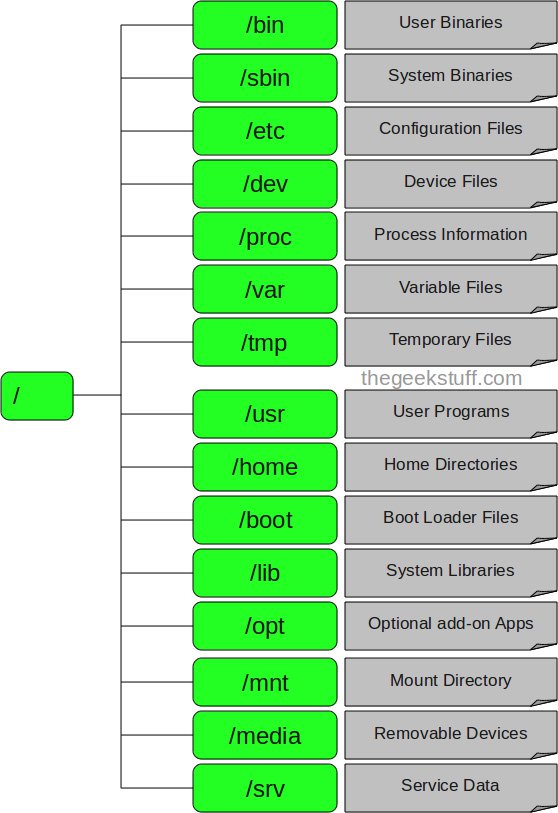
Directory tree structure in Linux
TipsMake.com - Have you ever wondered why some programs in Linux are stored under different directories like / bin, / sbin, / usr / bin or / usr / sbin?
For example, some are stored in / usr / bin. Why not / bin or / sbin? What is the difference between those directories?
In this article, we will review you about Linux's file system structure and the meaning of each main directory.
1. / - Root
True to its name: the root node is the starting point of all files and directories. Only root user has permission to write in this directory. Note that / root is the root user home directory, not /.
2. / bin - User's program
This directory contains executable programs. The general Linux programs used by all users are saved here. Examples include: ps, ls, ping .
3. / sbin - System program
Just like / bin, / sbinn also contains executable programs, but they are admin programs, for system maintenance. Examples: reboot, fdisk, iptables .
4. / etc - Configuration files
This directory contains the configuration files of the programs, and it also contains shell scripts used to start or shut down other programs. For example: /etc/resolv.conf, /etc/logrolate.conf
5. / dev - Device files
Hard drive, peripheral devices such as USB drives, external drives, or any device attached to the system are stored here. For example: / dev / sdb1 is the name of the USB you just plugged into the device, to open this USB you need to use the mount command with root privileges: # mount / dev / sdb1 / tmp
6. / tmp - Temporary files
This directory contains temporary files created by the system and users. Files saved in this folder will be deleted when the system restarts.
7. / proc - Information about the process
Information about running processes will be saved in / proc as a simulated directory file system. For example, the subdirectory / proc / {pid} contains information about the process with ID as pid (pid ~ process ID). In addition, this is also the place to store information about the current resources of the system such as: / proc / version, / proc / uptime .
8. / var - File about the program variable
Information about system variables is saved in this directory. Like information about log file: / var / log, packages and databases / var / lib .
9. / usr - User's program
Contains libraries, executable files, documentation and source code for the program running at level 2 of the system. Inside
- / usr / bin contains executable files of users such as: at, awk, cc, less . If you can't find them in / bin, look in / usr / bin
- / usr / sbin contains executable files of the system under admin such as atd, cron, sshd . If you can't find them in / sbin, look in this directory.
- / usr / lib contains libraries for programs in / usr / bin and / usr / sbin
- / usr / local contains user programs installed from source. For example, if you install apache from source, it will be saved under / usr / local / apache2
10. / home - User's directory
This folder contains all the personal files of each user. For example: / home / john, / home / marie
11. / boot - Boot files
All files required when starting as initrd, vmlinux. grub is saved here. Example vmlixuz-2.6.32-24-generic
12. / lib - System library
Contains library support for executable files in / bin and / sbin. These libraries usually have names starting with ld * or lib * .so. *. For example, ld-2.11.1.so or libncurses.so.5.7
13. / opt - Optional secondary applications
This directory name means optional (optional), it contains additional applications from other independent vendors. These applications can be installed at / opt or a subdirectory of / opt
14. / mnt - Folder to mount
This is a temporary folder to mount system files. For example, # mount / dev / sda2 / mnt
15. / media - Attached devices can be removed
This temporary folder contains devices like CdRom / media / cdrom. floppy / media / floopy or / media / Data hard disk partitions (understand as D: / Data drive in Windows)
16. / srv - Data of other services
Contains data related to server services such as / srv / svs, containing CVS-related data.