Learn the file system and folders on Linux operating systems
Linux and Unix file systems are organized in a hierarchy similar to the structure of a hierarchical tree. The highest level of the file system is the root directory, denoted by a slash '/' (root directory).
Part 1: Linux directory structure (system file structure)
1. Folders and file system
Linux and Unix file systems are organized in a hierarchy similar to the structure of a hierarchical tree. The highest level of the file system is the root directory, denoted by a slash '/' (root directory).
For Unix and Linux operating systems all devices connected to the computer are identified as files, including components such as hard drives, hard disk partitions and USB drives. This means that all files and folders are under the root directory, even the icon files for the hard drives.
For example, /home/nttvinh/nguyen/scnp.odt indicates the entire path to the scnp.odt file in the nttv folder is the subdirectory located in the home directory, just below the root directory (/).
Under the root directory (/) there are a variety of important file system directories that are recognized in all different Linux distributions. Below is a list of common directories seen under the root directory (/):

1. / - Root
- Open each file and folder from Root folder.
- Only root user has the right to write under this directory.
- Note that / root is the root directory of Root user.
2. / bin - User Binaries
- Contains binary executables.
- The popular Linux command is used in Singer-user mode in this directory.
- All users on the system located in this directory can use the command.
- For example: ps, ls, ping, grep, cp.
3. / sbin - System Binaries
- Like / bin, / sbin also contains binary executables.
- The Linux command is located in this directory used by the system Admin, for the purpose of maintaining the system.
- For example: iptables, reboot, fdisk, ifconfig, swapon.
4. / etc - Configuration Files
- Contains configuration of system configuration files, command files to launch system services ……
- Also / etc contains shell scripts startup and shutdown, used to run / stop individual programs.
- For example: /etc/resolv.conf, /etc/logrotate.conf.
5. / dev - Files device
- Contains files for identification for system devices (device files).
- Includes terminals, USB or devices attached to the system.
- For example: / dev / tty1, / dev / usbmon0
6. / proc - Process Information
- No information about System Process.
- This is a fake file system containing information about running processes. for example, the directory / proc / {pid} contains information about pid's special process.
- This is a virtual file system with information about system resources. Such as / proc / uptime.
7. / var - Variable Files
- Var is an abbreviation of variable file, saving the file to record variable data.
- Content files are expected to increase at this directory.
- Include: log file system (/ var / log), packages and data files (/ var / lib), email (/ var / mail), print queues (/ var / spool); lock files (/ var / lock); Temporary files need to be rebooted (/ var / tmp).
8. / tmp - Temporary Files (temporary files)
- The directory contains temporary files created by the system and the user.
- These folder creation files are deleted when the system is rebooted.
9. / usr - User Programs
- Contains applications, libraries, documents and source code for secondary programs.
- / usr / bin contains the files of the main applications installed for the user. If you cannot find the user binary in the / bin directory, you can find it in the / usr / bin directory. For example, at, awk, cc, less, scp.
- / usr / sbin contains application files for the system Admin. If you can't find the binary at / sbin, you can find it at / usr / sbin. Such as atd, cron, sshd, useradd, userdel.
- / usr / lib contains the / usr / bin library and / usr / sbin.
- / usr / local contains user programs that you install from source.
For example, when you install apache from source, apache is under / usr / local / apache2.
10. / home - Home directory
- The main directory stores personal files of all users.
- Example: / home / john, / home / nikita.
11. / boot - Boot Loader Files
- Contains configuration files for system startup.
- Kernel files initrd, vmlinux, grub are in / boot.
- Example: nitrd.img-2.6.32-24-generic, vmlinuz-2.6.32-24-generic.
12. / lib - System Libraries
- Contains library files that support directories under / bin and / sbin.
- Library file name can be ld * or lib * .so. *.
- For example: ld-2.11.1.so, libncurses.so.5.7.
13. / opt - Optional add-on Applications
- Opt stands for Optional (optional).
- Contains add-on applications from vendors.
- The add-on application is installed under the directory / opt / or / opt / sub directory.
14. / mnt - Mount Directory
- Mount temporary system folders (Temporary folders) where Sysadmins can mount system files.
15. / media - Removable Media Devices
- Mount the Temporary folders created by the system when a removable media is plugged into such as CDs, digital cameras .
- For example: / media / cdrom for CD-ROM; / media / floppy for floppy drives; / media / cdrecorder for CD writer.
16. / srv - Service Data
- Svr stands for service.
- Contains specific server services related to data.
- For example: / srv / cvs contains CVS related data.

2. Disk and Partition (partition)
- / dev / hda First IDE hard drive (main)
- / dev / hdb Second IDE hard disk drive (secondary)
- / dev / sda SCSI hard drive first
- / dev / sdb Second SCSI hard drive
- / dev / fd0 First floppy drive
- / dev / fd1 Second floppy drive

For example, if we run ls –l firstdoc.txt, we see the following result:
-rwxrw-r-- 1 User1 Testers 512 Oct 24 19:42 firstdoc.txt
The meaning of the fields is:
- File Access Permission: -rwxrw-r--
- Number of links: 1
- File Owner: User1
- Group: Testers
- File Size (bytes): 512
- Last modified: Oct 24
- Last Modification Time: 19:42
- File name: firstdoc.txt
Also, through ls –l, we will know firstdoc.txt is a file or directory based on:
- If the first character is (-), then this is the file.
- If the first character is d, then the object is the directory.
- If the first character is l, then full is a symbolic link pointing to another file (similar to the shortcut on Windows OS).
- If the first character is b, the object is a block device such as a disk drive.
- If the first character is c, the object is a character device like the serial port.
Object Ownership
In the above example we see that the files all have a group owner and the owner file. In case you want to change the ownership for another group or user, log in as root and execute the following command to change the ownership permission for the file payroll.doc for the user vp_finance
chown vp_finance payroll.doc
If you want to change ownership for group accounting, execute the command
chown vp_finance.accounting payroll.doc
In case you want to transfer ownership of all directories and internal files, execute the chown command with the option -R:
chown -R vp_marketing.marketing / marketing / June
chown -R .marketing / marketing / June
In addition, if you want to transfer ownership without root, you can use the chgrp command, but now you have to belong to a group that has ownership and group rights.
To manage files and folders on Linux, in addition to the Nautilus File System utility, we can install and use Webmin to manage files and folders using the web interface. However, it is recommended to use the latest version to ensure system safety. Download and install Webmin at www.webmin.com

Part 2: Exercises for installing WebMin under Task 3A4
On Windows we can see processes running with taskmanager, but for Linux systems we use the ps command to display active processes.

To see more details, use the aux option with:
- a— displays all processes.
- u — display additional user information
- x — expand the list of processes
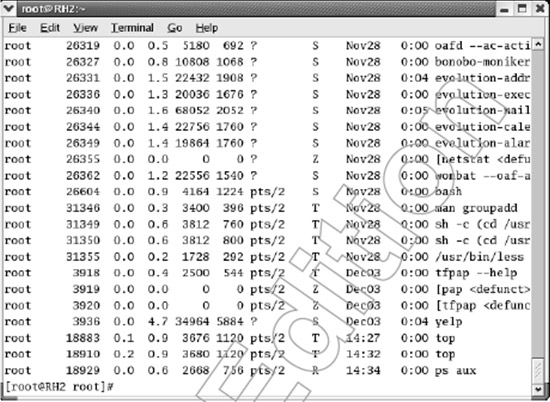
We can use the top command to see the list of active processes that are updated by the specified time. For example, to refresh the list of displayed processes after 7 seconds we use the command:
# top d 7
In addition, using the System Monitor graphical interface is also a good solution for managing and reviewing the operating processes as shown below:

View hard disk usage information using the df -h command:

2.1. Task Task 3A-5
Mounting device, drive
To be able to use drives like CDROM, FDD . we need to mount these drives with the mount command like:
# mount / dev / cdrom / mnt / cdrom
The order result will be :
Mount: block device / dev / cdrom is write-protected. mounting
read-only
However, for new Linux versions, the use of CDROM is mostly mounted automatically by the system. In addition, we can mount cdrom or usb drives, fdd to the directories we create as:
mkdir / cdrom
mount / dev / cdrom / cdrom
And after using it, we can use the umount command before removing the disk (there are many cases that the CD must be removed by turning off the power).
Access rights
All files of a Linux file system are linked with different access rights according to each user of the system, regarding read, write and execute operations. The system administrator (super user "root") has access to any file of the system. Each file is owned by a certain person and attached access restrictions depending on the user and attached to a user group.
So each file is secured by 3 sets of access rights that are attached to the following 3 user groups, in order from high to low:
- The user access rights of this group apply to file owners,
- group (user groups) the access rights of this group apply to the group attached to the file,
- other (these) access rights of this group apply to all others.
Each access set will specify the actual access rights to the files and directories as follows:
- read (read)
Right to view file contents or open files
permission to view the contents of the directory file - write (write, write)
The right to record and correct the file contents or delete the file
permission to edit the contents of the directory file - execute (execute)
This permission is attached to the command file, the user group that has received this permission can execute command files and permissions into the directories.
Permissions on Linux systems can be described through numbers from 0 to 7 in the decimal system. For example, a user or group has the right to R (read), W (write), E (execute) for 1 file / folder, which is denoted by 1, otherwise 0 if there is no corresponding permission (-). And with the conversion from binary to decimal we have the following table of values:
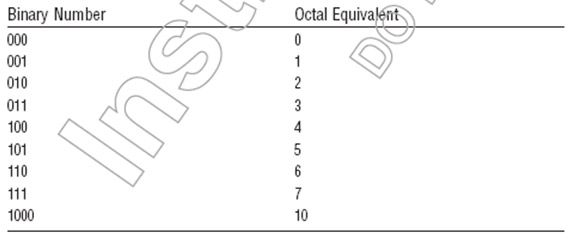
So if a user / group has rights to certain files / folders, it corresponds to establishment 111 in binary or 7 in the decimal system, so 777 is allowed to allow RWE for all.

Users and user groups
To add users, or groups of users, to the system, you can use the Users And Groups program, in the System menu -> Administration -> Users and Groups .
To add a new user, click on Add user , fill in the required information and then click the OK button. To edit the properties of each user, you can click the Properties button in the Users main window.
To add a new group of users, select the Groups tab tab and click on Add group . Specify the name of the new group and, if desired, change the number assigned to the group (Group ID). If you plan to use some already used Group IDs, the system will notify you.
To add users to the newly created group, simply select a user from the list on the left and click the Add button. Wanting to exclude a user from a group is as simple as adding: after selecting the user name in the right window, click on the button you have written.
Remove . When done, click the OK button to finish and actually create a new user group, along with the users of that group.
To edit the properties of a group of users, select the name of a group in the Groups window and click the button that says Properties .
To completely delete a user, or a group of users, from the system, select the user name or user group name you want to delete and click the Delete button .
Similar to the Windows system, when installing Linux (FC Core) will create an account with administrative rights and can be used to create other accounts, this is the most advanced account called root. . To grant access to the system we need to create user accounts, and each user account is assigned a UID. Accounts with the same attributes will be grouped as on Windows systems and each group will have its own GIDs.
On Linux systems we can view existing Users through the contents of the file / etc / passwd as shown below:
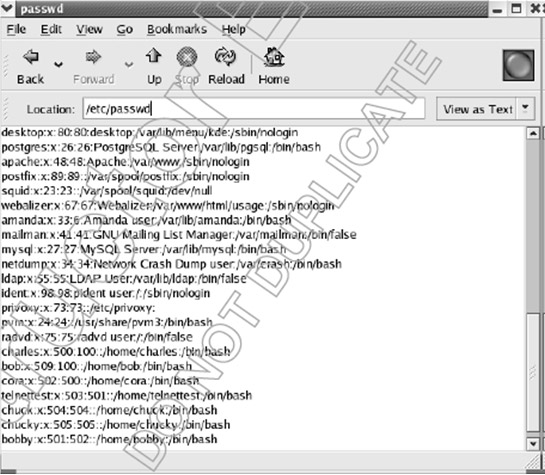
In this passwd file, we see that there are many different filed records such as:
- User Account Name: login name of user account.
- Password: login password of user account. If only the x character in this cell is found, the password is encrypted and protected in the shadow password file.
- User ID: user number (UID)
- Group ID: Grioup number where this user is a member (GID).
- Full Name: Full name of the user.
- Home Directory: the user's home directory after logging in.
- Shell: show command interpreter, for example bash.
When a new account is created it will be assigned a UID, starting from 500 onwards and increasing as new accounts are created.
As with Windows operating systems, after installing some default accounts and groups will be created as:
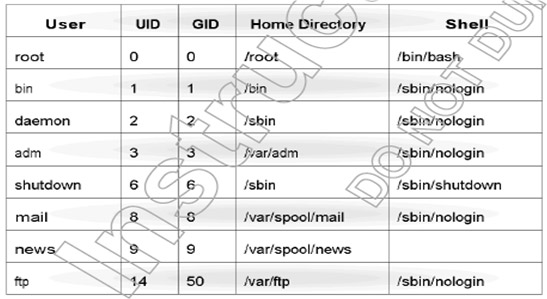
Default users

The default group
Create User and Group
We can create user accounts on Linux using the command line or graphical interface. To create a Linux1 user account using the command line, do the following:
useradd -g Users Linux1
passwd Linux1
New password: qwerty
Retype new password: qwerty
If you want to identify home folders and shells for users, you can use the -d and -s options
The following example will create a group with GID of 1024 (the -g option used to determine GID, if not using this option, the system will automatically determine the GID for the group in ascending order).
2.2. Exercise Add Linux User and Group
1. To Add a New User on a Linux system, click System => Administration => Users and Groups .
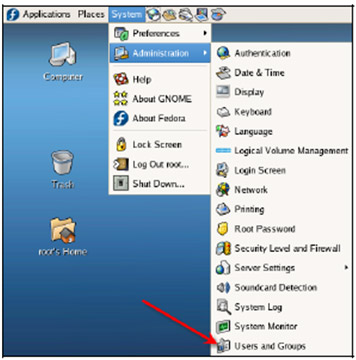
2. User management interface is as follows:
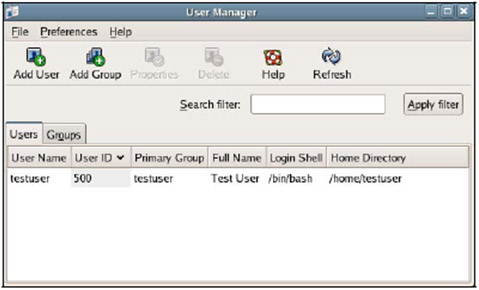
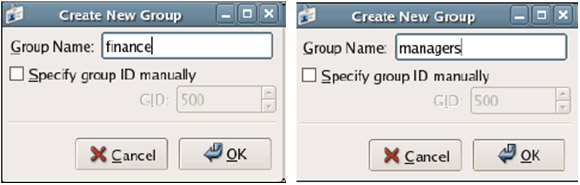
3. Click Add Group in the toolbar then create 2 group finance and managers as shown below:
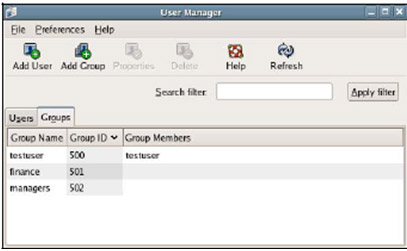
4. Select the Users tab and select Add User to create Sam Randolph accounts with the following information:
User Name srandolp
Full Name Sam Randolph
Password Fishing123
Confirm Password F ishing123
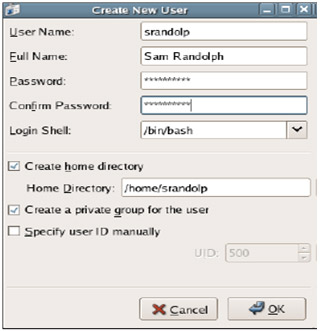
Click OK to finish
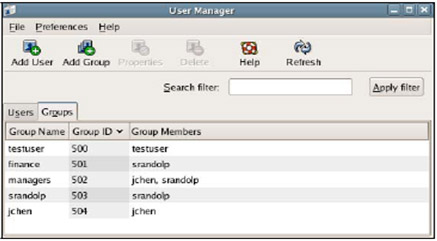
Assign rights on files and folders
1. Create a folder called Share by double-clicking the Computer icon and then opening File System . Right-click and select Create Folder .
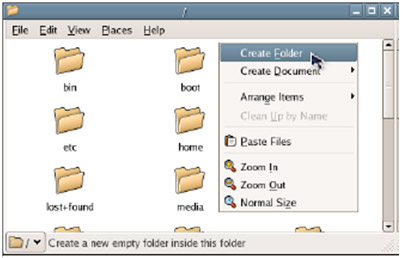
2. Enter the folder name as Shares and press Enter .

3. Next create two sub-folders: Finance Reports and Managers in Shares Folder

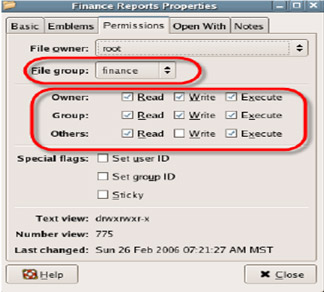
4. Now that we will assign the appropriate permissions to the users on the newly created folders, right-click on the Finance Reports folder and select Properties . On the computer window select the Permissions tab (if you do not see the Permissions tab, restart the system)
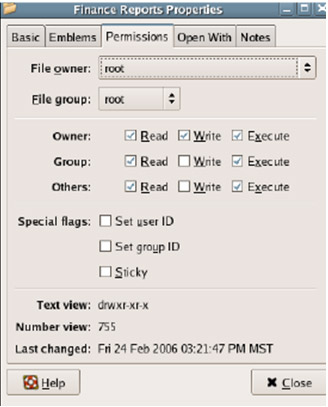
5. Change the permissions on this folder as follows:
File Group = finance
Group Permissions = Read , Write , and Execute
Other Permissions = Read only (if you want to browse the directory, select Read & Execute)
After assigning permissions as above, Group Finance can access this folder and other users only have Read permissions.
6. Similarly, assign permissions to Managers folder as follows:
File Group = managers
Group Permissions = Read , Write , and Execute
Other Permissions = (none)
To check the results of assigning permissions to folders and groups, log in with the respective accounts and perform file, folder, read or delete files .
Refer to some of the following articles:
- Ubuntu Bash tutorial on Windows 10
- Certain deadly commands never run on Linux
- How to access Linux partitions on Windows?
Good luck!