ctype.h in C
ctype.h in C
The header file with the name ctype.h of the C Library declares some pretty useful functions for checking and mapping characters.
All of these functions receive the int function as a parameter, but the value must be EOF or can be represented as an unsigned char.
All this function returns true (different from 0) if parameter c satisfies the condition described, and false (0) if not satisfied.
Note : To understand character classes (for example, the class of Punctuation characters, graphical character classes, control character classes, etc.) which characters are included, please follow them at the bottom of this page. .
Functions defined in ctype.h
Here are some functions defined in ctype.h in Library C. Follow the link to find out the details of these functions.
Description function int isalnum (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is non-numeric
Int isalpha function (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is a letter
Function int iscntrl (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is a control character
Function int isdigit (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is a decimal number
Function int isgraph (int c)This function checks to see if the transmitted character must be graphical with Locale given
Int islower (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is a lowercase letter
Int isprint function (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character can print
Function int ispunct (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is a char punctuation
Function int isspace (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is white-space
Function int isupper (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is a capital letter
Function int isxdigit (int c)This function checks whether the transmitted character is a hexadecimal character
1. Function int isalnum (int c)
The function isalnum () in C
Void isalnum function (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a character - number.
Declare isalnum () function in C
Below is the declaration for the isalnum () function in C.
int isalnum (int c);
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked
Returns the value
This function returns a non-zero value if c is a number or a letter, otherwise it returns 0.
For example
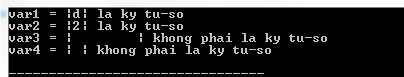
The following program C illustrates the usage of isalnum () in C.
#include
#include
int main ()
{
int var1 = 'd';
int var2 = '2';
int var3 = 't';
int var4 = '';
if (isalnum (var1))
{
printf ("var1 = |% c | la ky tu-son", var1);
}
else
{
printf ("var1 = |% c | is not sure", var1);
}
if (isalnum (var2))
{
printf ("var2 = |% c | la ky tu-son", var2);
}
else
{
printf ("var2 = |% c | is not sure", var2);
}
if (isalnum (var3))
{
printf ("var3 = |% c | la ky tu-son", var3);
}
else
{
printf ("var3 = |% c | is not sure", var3);
}
if (isalnum (var4))
{
printf ("var4 = |% c | la ky tu-son", var4);
}
else
{
printf ("var4 = |% c | is not sure", var4);
}
return (0);
}
Compiling and running the above C program will result:
2. The isalpha () function in C
Isalpha () function in C
Void function isalpha (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a letter.
Declare isalpha () function in C
Below is the declaration for the isalpha () function in C:
int isalpha ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a non-zero value if c is a letter, otherwise the function returns 0.
For example
The following program C illustrates the usage of isalpha () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = 'd' ; int var2 = '2' ; int var3 = 't' ; int var4 = ' ' ; if ( isalpha ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la mot chu cain" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| khong phai la mot chu cain" , var1 ); } if ( isalpha ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la mot chu cain" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| khong phai la mot chu cain" , var2 ); } if ( isalpha ( var3 ) ) { printf ( "var3 = |%c| la mot chu cain" , var3 ); } else { printf ( "var3 = |%c| khong phai la mot chu cain" , var3 ); } if ( isalpha ( var4 ) ) { printf ( "var4 = |%c| la mot chu cain" , var4 ); } else { printf ( "var4 = |%c| khong phai la mot chu cain" , var4 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

3. The function iscntrl () in C
The function iscntrl () in C
Function void iscntrl (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a control character
According to the standard ASCII character set, ASCII encoded control characters are 0x00 (NUL), 0x1f (US), and 0x7f (DEL). Some private implementations of specific platforms may define some additional control characters in the extended character set (on 0x7f).
Declare the function iscntrl () in C
Below is the declaration for the iscntrl () function in C:
int iscntrl ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a non-zero value if c is a control character. If not, the function returns 0.
For example
The following C program illustrates the usage of iscntrl () in C:
#include #include int main () { int i = 0 , j = 0 ; char str1 [] = "Hoc a lap trinh t hay nhat" ; char str2 [] = "tai n QTM" ; /* in chuoi cho toi khi gap ky tu a */ while ( ! iscntrl ( str1 [ i ]) ) { putchar ( str1 [ i ]); i ++; } /* in chuoi cho toi khi gap ky tu n */ while ( ! iscntrl ( str2 [ j ]) ) { putchar ( str2 [ j ]); j ++; } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

4. The isdigit () function in C
The isdigit () function in C
Void isdigit function (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a decimal number.
Decimal digits include - 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9.
Declare isdigit () function in C
Below is the declaration for the isdigit () function in C:
int isdigit ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a non-zero value if c is a digit. If not, the function returns 0.
For example
The following C program illustrates the usage of isdigit () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = 'h' ; int var2 = '2' ; if ( isdigit ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la mot ky son" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky son" , var1 ); } if ( isdigit ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la mot ky son" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky son" , var2 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

5. Ham isgraph () in C
Function isgraph () in C
The function void isgraph (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character must be graphical with Locale given.
Graphic characters are a set of alphanumeric characters and punctuation characters
Declare the function isgraph () in C
Here is the declaration for the function isgraph () in C:
int isgraph ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a non-zero value if c is a graphical character. If not, the function returns 0.
For example
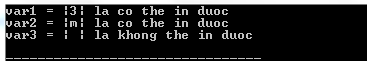
The following program C illustrates the usage of the isgraph () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = '3' ; int var2 = 'm' ; int var3 = ' ' ; if ( isgraph ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la co the in duocn" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la khong the in duocn" , var1 ); } if ( isgraph ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la co the in duocn" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la khong the in duocn" , var2 ); } if ( isgraph ( var3 ) ) { printf ( "var3 = |%c| la co the in duocn" , var3 ); } else { printf ( "var3 = |%c| la khong the in duocn" , var3 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
6. Islower () function in C
The islower () function in C
The int islower (int c) function in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a lowercase letter.
Declare islower () function in C
Below is the declaration for the islower () function in C:
int islower ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a value other than 0 (true) if c is a lowercase letter. Otherwise the function returns 0 (false).
For example
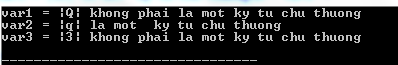
The following program C illustrates the usage of islower () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = 'Q' ; int var2 = 'q' ; int var3 = '3' ; if ( islower ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la mot ky tu chu thuongn" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu chu thuongn" , var1 ); } if ( islower ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la mot ky tu chu thuongn" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu chu thuongn" , var2 ); } if ( islower ( var3 ) ) { printf ( "var3 = |%c| la mot ky tu chu thuongn" , var3 ); } else { printf ( "var3 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu chu thuongn" , var3 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
7. The isprint () function in C
The isprint () function in C
The int isprint (int c) function in Library C checks whether the transmitted character can print. A printable character is a character that is not a control character.
Declare the isprint () function in C
Below is the declaration for the isprint () function in C:
int isprint ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a value other than 0 (true) if c is a printable character. Otherwise the function returns 0 (false).
For example
The following program C illustrates the usage of the isprint () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = 'k' ; int var2 = '8' ; int var3 = 't' ; int var4 = ' ' ; if ( isprint ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| co the in duocn" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| khong the in duocn" , var1 ); } if ( isprint ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| co the in duocn" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| khong the in duocn" , var2 ); } if ( isprint ( var3 ) ) { printf ( "var3 = |%c| co the in duocn" , var3 ); } else { printf ( "var3 = |%c| khong the in duocn" , var3 ); } if ( isprint ( var4 ) ) { printf ( "var4 = |%c| co the in duocn" , var4 ); } else { printf ( "var4 = |%c| khong the in duocn" , var4 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

8. The ispunct () function in C
The function ispunct () in C
The int ispunct (int c) function in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a char punctuation. Character punctuation is a collection of! "# $% & '() * +, -. /:; <=>? @ [] ^ _` {|} ~
Declare the ispunct () function in C
Here is the declaration for the ispunct () function in C:
int ispunct ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a value other than 0 (true) if c is a punctuation character. Otherwise the function returns 0 (false).
For example
The following program C illustrates the use of the ispunct () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = 't' ; int var2 = '1' ; int var3 = '/' ; int var4 = ' ' ; if ( ispunct ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var1 ); } if ( ispunct ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var2 ); } if ( ispunct ( var3 ) ) { printf ( "var3 = |%c| la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var3 ); } else { printf ( "var3 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var3 ); } if ( ispunct ( var4 ) ) { printf ( "var4 = |%c| la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var4 ); } else { printf ( "var4 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu punctuationn" , var4 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

9. The isspace () function in C
The isspace () function in C
The function int isspace (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is white-space.
Here are the whitespace characters in Library C:
' ' ( 0x20 ) kho ả ng tr ố ng ( SPC ) 't' ( 0x09 ) tab ngang ( TAB ) 'n' ( 0x0a ) newline ( d ò ng m ớ i ) - d ò ng m ớ i ( LF ) 'v' ( 0x0b ) tab doc ( VT ) 'f' ( 0x0c ) feed ( FF ) 'r' ( 0x0d ) carriage return ( CR )
Declare the isspace () function in C
Below is the declaration for the isspace () function in C:
int isspace ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a value other than 0 (true) if c is the whitespace character. Otherwise the function returns 0 (false).
For example
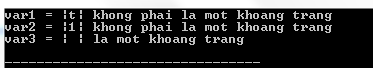
The following program C illustrates the usage of the isspace () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = 't' ; int var2 = '1' ; int var3 = ' ' ; if ( isspace ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la mot khoang trangn" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| khong phai la mot khoang trangn" , var1 ); } if ( isspace ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la mot khoang trangn" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| khong phai la mot khoang trangn" , var2 ); } if ( isspace ( var3 ) ) { printf ( "var3 = |%c| la mot khoang trangn" , var3 ); } else { printf ( "var3 = |%c| khong phai la mot khoang trangn" , var3 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
10. The isupper () function in C
The isupper () function in C
The function int isupper (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a capital letter.
Declare isupper () function in C
Below is the declaration for the isupper () function in C:
int isupper ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a value other than 0 (true) if c is uppercase. Otherwise the function returns 0 (false).
For example
The following program C illustrates the usage of the isupper () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int var1 = 'M' ; int var2 = 'm' ; int var3 = '3' ; if ( isupper ( var1 ) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%c| la mot ky tu chu hoan" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu chu hoan" , var1 ); } if ( isupper ( var2 ) ) { printf ( "var2 = |%c| la mot ky tu chu hoan" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu chu hoan" , var2 ); } if ( isupper ( var3 ) ) { printf ( "var3 = |%c| la mot ky tu chu hoan" , var3 ); } else { printf ( "var3 = |%c| khong phai la mot ky tu chu hoan" , var3 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
11. Isxdigit () function in C
Isxdigit () function in C
The function int isxdigit (int c) in Library C checks whether the transmitted character is a hexadecimal character (hexa character).
Declare isxdigit () function in C
Below is the declaration for the isxdigit () function in C:
int isxdigit ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is the character to be checked.
Returns the value
This function returns a value other than 0 (true) if c is a hexadecimal character. Otherwise the function returns 0 (false).
For example
The following C program illustrates the usage of isxdigit () function in C:
#include #include int main () { char var1 [] = "tuts" ; char var2 [] = "0xE" ; if ( isxdigit ( var1 [ 0 ]) ) { printf ( "var1 = |%s| la mot ky tu hexan" , var1 ); } else { printf ( "var1 = |%s| khong phai la mot ky tu hexan" , var1 ); } if ( isxdigit ( var2 [ 0 ] )) { printf ( "var2 = |%s| la mot ky tu hexan" , var2 ); } else { printf ( "var2 = |%s| khong phai la mot ky tu hexan" , var2 ); } return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

The library nge.h also contains two conversion functions that receive and return an int:
Int tolower (int c) - This function converts uppercase letters to lowercase
Int toupper (int c) - This function converts lowercase letters to uppercase
12. Function tolower () in C
Function tolower () in C
The int tolower function (int c) in Library C converts the given character to lowercase.
Declare tolower () function in C
Here is the declaration for tolower () function in C:
int tolower ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is a character to be converted to lowercase.
Returns the value
This function returns a letter that is normally equivalent to c if that value exists, otherwise c will not change. The value is returned as an int value that can be implicitly cast to char.
For example
The following C program illustrates the use of tolower () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int i = 0 ; char c ; char str [] = "TUTORIALS POINT" ; while ( str [ i ] ) { putchar ( tolower ( str [ i ])); i ++; } return ( 0 ); } Compile and run the above C program to see the results:
13. Toupper () function in C
The toupper () function in C
The int toupper function (int c) in Library C converts lowercase letters to uppercase.
Declare the toupper () function in C
Below is the declaration for the toupper () function in C:
int toupper ( int c );
Parameters
c - This is a character to be converted to uppercase.
Returns the value
This function returns a capital letter equivalent to c if that value exists, otherwise c will not change. The value is returned as an int value that can be implicitly cast to char.
For example
The following program C illustrates the usage of the toupper () function in C:
#include #include int main () { int i = 0 ; char c ; char str [] = "Tutorials Point" ; while ( str [ i ]) { putchar ( toupper ( str [ i ])); i ++; } return ( 0 ); } Compile and run C program to see results:
Explain some character classes
Character class Description DigitThis is a collection of all numbers {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
Hexadecimal digitsThis is a set of {0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ABCDEF abcdef}
Lowercase lettersIs a collection of all lowercase {abcdefghijklmnopqrstu vwxyz}
Flower lettersIs a collection of all uppercase letters {ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTU VWXYZ}
AlphabetIs a collection of all upper and lower case letters
Alphanumeric charactersIs a set of numbers, upper and lower case letters
Punctuation charactersIs a collection! "# $% & '() * +, -. /:; <=>? @ [] ^ _` {|} ~
Graphical charactersIs a set of alphanumeric characters and punctuation characters
Whitespace charactersA set of tabs, newline (new line), vertical tab, form feed, carriage return, and space
Printable charactersA set of alphanumeric characters, punctuation characters and whitespace characters
Control charactersIn ASCII, these characters have octal encoding from 000 to 037, and 177 (DEL)
Blank charactersThese characters include space and tab characters
Alphabetical charactersIs a collection of upper and lower case letters
According to Tutorialspoint
Last lesson: assert.h in C
Next article: errno.h in C
 errno.h in C
errno.h in C float.h in C
float.h in C limits.h in C
limits.h in C locale.h in C
locale.h in C math.h in C
math.h in C Installation instructions C
Installation instructions C