math.h in C
math.h in C
Header files named math.h in Library C define diverse math functions and a macro. All functions available in this library receive double as a parameter and return the result in type double.
Macros are defined in math.h
There is only one Macro defined in this library:
HUGE_VAL: This macro is used when the result of a function cannot be represented as a floating-point number. If the size to correctly represent the result is too large, the errno set function to ERANGE to indicate a Range Error, and return a value large enough, specifically named by HUGE_VAL or its counter - HUGE_VAL .
If the size of the result is too small, a value of 0 is returned. In this case, errno may or may not be set to ERANGE.
Functions are defined in math.h
Here are some functions defined in math.h in Library C:
Description function double acos (double x)Returns arcos of x (radian value)
double asin (double x)Returns arcsin of x (radian value)
double atan (double x)Returns arctan of x (radian value)
double atan2 (doubly y, double x)Returns arctan of y / x (radian value)
double cos (double x)Returns cos of the angle x (radian value)
double cosh (double x)Returns cosh (hyperbolic cosine function) of x (radian value)
double sin (double x)Returns the sine of the angle x (radian value)
double birth (double x)Returns birth (hyperbolic sin function) of x (radian value)
double fish (double x)Returns tanh (tan hyperbolic function) of x (radian value)
double exp (double x)Returns e x
double frexp (double x, int * exponent)The value returned is the mantissa (the mantissa) and the integer pointed to by exponent (exponent). The result value is x = mantissa * 2 ^ exponent
double ldexp (double x, int exponent)Returns x * 2 exponent
double log (double x)Returns lnx
double log10 (double x)Returns log10 (x)
double modf (double x, double * integer)Returns the decimal part of x
double pow (double x, double y)Returns x y
double sqrt (double x)Returns the square root of x
double ceil (double x)Returns the smallest integer value greater than or equal to x
double fabs (double x)Returns the absolute value of x
double floor (double x)Returns the maximum integer value less than or equal to x
double fmod (double x, double y)Returns the remainder of the x / y division
1. The function acos () in C
The function double acos (double x) in Library C returns the arcos of x (radian value).
Declare acos () function in C
Below is the declaration for acos () function in C:
double acos ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the actual floating point number in the paragraph [-1, + 1].
Return value:
This function returns the arcos of x, in the segment [0, pi] radian.
For example:
The following program C illustrates how to use the acos () function in C:
#include #include #define PI 3.14159265 int main () { double x , ret , val ; x = 0.9 ; val = 180.0 / PI ; ret = acos ( x ) * val ; printf ( "Gia tri arccos cua %lf la bang %lf" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

2. The asin () function in C
The double asin (double x) function in Library C returns arcsin of x (radian value).
Declare the function asin () in C
Below is the declaration for the asin () function in C:
double asin ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the actual floating point number in the paragraph [-1, + 1].
Return value:
This function returns arcsin of x, in the [-pi / 2, + pi / 2] radian segment.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of the asin () function in C:
#include #include #define PI 3.14159265 int main () { double x , ret , val ; x = 0.9 ; val = 180.0 / PI ; ret = asin ( x ) * val ; printf ( "Gia tri arcsin cua %lf la bang %lf" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

3. The atan () function in C
Double atan (double x) function in C Library returns arctan of x (radian value).
Declaring the function atan () in C
Below is the declaration for the atan () function in C:
double atan ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns arctan of x, in the [-pi / 2, + pi / 2] radian.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the use of atan () function in C:
#include #include #define PI 3.14159265 int main () { double x , ret , val ; x = 1.0 ; val = 180.0 / PI ; ret = atan ( x ) * val ; printf ( "Gia tri arctan cua %lf la bang %lf" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

4. The function atan2 () in C
Double atan2 (doubly y, double x) in Library C returns arctan of y / x (radian value).
Declare the function atan2 () in C
Here is the declaration for the atan2 () function in C:
double atan2 ( doubly y , double x )
Parameters:
- x - This is a real floating point value representing the x coordinate.
- y - This is the actual numerical value of floating point representing y coordinate.
Return value:
This function returns arctan of y / x, in the [-pi, + pi] radian segment.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of atan2 () function in C:
#include #include #define PI 3.14159265 int main () { double x , y , ret , val ; x = - 7.0 ; y = 7.0 ; val = 180.0 / PI ; ret = atan2 ( y , x ) * val ; printf ( "Gia tri arctan2 cua x = %lf, y = %lf " , x , y ); printf ( "la bang %lfn" , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

5. Function cos () in C
The double cos function (double x) in Library C returns the cos of the angle x (measured in radians).
Declaring the function cos () in C
Below is the declaration for the function cos () in C:
double cos ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is a real floating point value representing an angle expressed in radian values.
Return value:
This function returns the cos of x.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of function cos () in C:
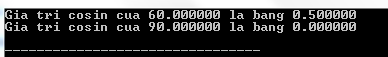
#include #include #define PI 3.14159265 int main () { double x , ret , val ; x = 60.0 ; val = PI / 180.0 ; ret = cos ( x * val ); printf ( "Gia tri cosin cua %lf la bang %lfn" , x , ret ); x = 90.0 ; val = PI / 180.0 ; ret = cos ( x * val ); printf ( "Gia tri cosin cua %lf la bang %lfn" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
6. Cosh () function in C
The double cosh (double x) function in Library C returns the hyperbolic cosine of x.
Declare the function cosh () in C
Below is the declaration for the cosh () function in C:
double cosh ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns the hyperbolic cosine of x.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of the cosh () function in C:
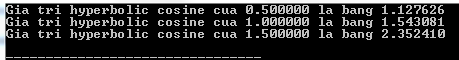
#include #include int main () { double x ; x = 0.5 ; printf ( "Gia tri hyperbolic cosine cua %lf la bang %lfn" , x , cosh ( x )); x = 1.0 ; printf ( "Gia tri hyperbolic cosine cua %lf la bang %lfn" , x , cosh ( x )); x = 1.5 ; printf ( "Gia tri hyperbolic cosine cua %lf la bang %lfn" , x , cosh ( x )); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
7. Function sin () in C
The double sin (double x) function in Library C returns the sine of the angle x (radian value).
Declaring the function sin () in C
Below is the declaration for function sin () in C:
double sin ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is a real floating point value representing an angle expressed in radian values.
Return value:
This function returns the sine of x.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of the function sin () in C:
#include #include #define PI 3.14159265 int main () { double x , ret , val ; x = 45.0 ; val = PI / 180 ; ret = sin ( x * val ); printf ( "Sin cua %lf bang %lf" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

8. The generating function () in C
The double function generates (double x) in Library C returns the hyperbolic sine of x.
Declare the generating function () in C
Below is the declaration for the generating function () in C:
double sinh ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns the hyperbolic sine of x.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of the generating function () in C:
#include #include int main () { double x , ret ; x = 0.5 ; ret = sinh ( x ); printf ( "Hyperbolic sine cua %lf bang %lf" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

9. Ham function () in C
The function double tanh (double x) in Library C returns the hyperbolic tangent of x.
Declaring fish function () in C
Below is the declaration for the fishy function () in C:
double tanh ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns the hyperbolic tangent of x.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of the fishy function () in C:
#include #include int main () { double x , ret ; x = 0.5 ; ret = tanh ( x ); printf ( "Hyperbolic tangent cua %lf bang %lf" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

10. Function exp () in C
The function double exp (double x) in Library C returns e hats x.
Declare the function exp () in C
Below is the declaration for exp () in C:
double exp ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns ex.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of exp () in C:
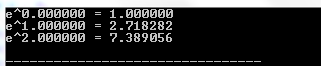
#include #include int main () { double x = 0 ; printf ( "e^%lf = %lfn" , x , exp ( x )); printf ( "e^%lf = %lfn" , x + 1 , exp ( x + 1 )); printf ( "e^%lf = %lfn" , x + 2 , exp ( x + 2 )); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
11. Function frexp () in C
The double frexp function (double x, int * exponent) in Library C returns the mantissa (the mantissa) and the integer pointed to by exponent (exponent). The result value is x = mantissa * 2 ^ exponent.
Declaring the function frexp () in C
Below is the declaration for frexp () function in C:
double frexp ( double x , int * exponent )
Parameters:
x - This is the actual floating point number value to be calculated.
exponent - This is the pointer to an int object where the exponent value is stored.
Return value:
This function returns the mantissa and the integer pointed to by exponent.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of frexp () function in C:
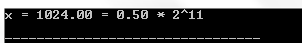
#include #include int main () { double x = 1024 , fraction ; int e ; fraction = frexp ( x , & e ); printf ( "x = %.2lf = %.2lf * 2^%dn" , x , fraction , e ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
12. The ldexp () function in C
The double ldexp (double x, int exponent) function in Library C returns x * 2exponent.
Declare the function ldexp () in C
Below is the declaration for ldexp () in C:
double ldexp ( double x , int exponent )
Parameters:
x - This is the actual floating point number, also representing the number of digits after the comma.
exponent - This is the value of exponent.
Return value:
This function returns x * 2 exp
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of ldexp () in C:
#include #include int main () { double x , ret ; int n ; x = 0.65 ; n = 3 ; ret = ldexp ( x , n ); printf ( "%f * 2^%d = %fn" , x , n , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
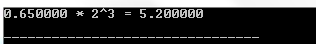
13. Log () function in C
The double log (double x) function in Library C returns lnx.
Declare the log () function in C
Below is the declaration for the log () function in C:
double log ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns lnx.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of the log () function in C:
#include #include int main () { double x , ret ; x = 2.7 ; /* tim gia tri cua log(2.7) */ ret = log ( x ); printf ( "log(%lf) = %lf" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:

14. Log10 () function in C
The double log10 function (double x) in Library C returns log10 (x).
Declare log10 () function in C
Below is the declaration for log10 () function in C:
double log10 ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns log10 (x), with x greater than 0.
For example:
The following C program illustrates how to use the log10 () function in C:
#include #include int main () { double x , ret ; x = 1000 ; /* tim gia tri cua log 10 1000 */ ret = log10 ( x ); printf ( "log10(%lf) = %lfn" , x , ret ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
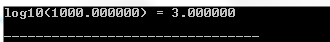
15. Modf () function in C
The function double modf (double x, double * integer) in Library C returns the decimal part of x.
Declare the modf () function in C
Below is the declaration for the modf () function in C:
double modf ( double x , double * integer )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
integer - This is a pointer to an object where the integer part is stored.
Return value:
This function returns the decimal part of x, with the same sign.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of the modf () function in C:
#include #include int main () { double x , fractpart , intpart ; x = 7.123456 ; fractpart = modf ( x , & intpart ); printf ( "Phan nguyen = %lfn" , intpart ); printf ( "Phan thap phan = %lf n" , fractpart ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
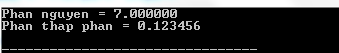
16. The pow () function in C
Double pow function (double x, double y) in Library C returns xy.
Declare the function pow () in C
Below is the declaration for pow () in C:
double pow ( double x , double y )
Parameters:
- x - This is the radix, which is a floating point real number value.
- y - This is an exponent, which is a floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns xy.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of the pow () function in C:
#include #include int main () { printf ( "9.0 ^ 3 = %lfn" , pow ( 9.0 , 3 )); printf ( "4.05 ^ 2.98 = %lf" , pow ( 4.05 , 2.98 )); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
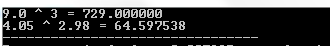
17. The sqrt () function in C
The function double sqrt (double x) in Library C returns the square root of x.
Declare the function sqrt () in C
Below is the declaration for the sqrt () function in C:
double sqrt ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns the square root of x.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of the sqrt () function in C:
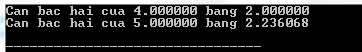
#include #include int main () { printf ( "Can bac hai cua %lf bang %lfn" , 4.0 , sqrt ( 4.0 ) ); printf ( "Can bac hai cua %lf bang %lfn" , 5.0 , sqrt ( 5.0 ) ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
18. Function ceil () in C
The double ceil (double x) function in Library C returns the smallest integer value greater than or equal to x.
Declare the function ceil () in C
Below is the declaration for the function ceil () in C:
double ceil ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
Returns the smallest integer value not less than x.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of the function ceil () in C:
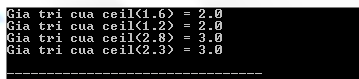
#include #include int main () { float val1 , val2 , val3 , val4 ; val1 = 1.6 ; val2 = 1.2 ; val3 = 2.8 ; val4 = 2.3 ; printf ( "Gia tri cua ceil(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val1 , ceil ( val1 )); printf ( "Gia tri cua ceil(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val2 , ceil ( val2 )); printf ( "Gia tri cua ceil(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val3 , ceil ( val3 )); printf ( "Gia tri cua ceil(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val4 , ceil ( val4 )); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
19. The fabs () function in C
The function double fabs (double x) in Library C returns the absolute value of x.
Declare fabs () in C
Below is the declaration for fabs () in C:
double fabs ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns the absolute value of x.
For example:
The following C program illustrates the usage of the fabs () function in C:
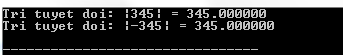
#include #include int main () { int a , b ; a = 345 ; b = - 345 ; printf ( "Tri tuyet doi: |%d| = %lfn" , a , fabs ( a )); printf ( "Tri tuyet doi: |%d| = %lfn" , b , fabs ( b )); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
20. Floor () function in C
The double floor (double x) function in Library C returns the largest integer value less than or equal to x.
Declare the floor () function in C
Below is the declaration for the floor () function in C:
double floor ( double x )
Parameters:
x - This is the floating point real number value.
Return value:
This function returns the largest integer not greater than x.
For example:
The following program C illustrates the usage of the floor () function in C:
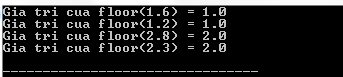
#include #include int main () { float val1 , val2 , val3 , val4 ; val1 = 1.6 ; val2 = 1.2 ; val3 = 2.8 ; val4 = 2.3 ; printf ( "Gia tri cua floor(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val1 , floor ( val1 )); printf ( "Gia tri cua floor(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val2 , floor ( val2 )); printf ( "Gia tri cua floor(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val3 , floor ( val3 )); printf ( "Gia tri cua floor(%.1f) = %.1lfn" , val4 , floor ( val4 )); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
21. Function fmod () in C
Double fmod (double x, double y) in Library C returns the remainder of the division x / y.
Declaring the function fmod () in C
Here is the declaration for fmod () function in C:
double fmod ( double x , double y )
Parameters:
x - This is a floating point numerical value that serves as a numerator.
y - This is a floating point numerical value that serves as a denominator.
Return value:
This function returns the remainder of the x / y division.
For example:
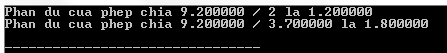
The following program C illustrates the usage of the fmod () function in C:
#include #include int main () { float a , b ; int c ; a = 9.2 ; b = 3.7 ; c = 2 ; printf ( "Phan du cua phep chia %f / %d la %lfn" , a , c , fmod ( a , c )); printf ( "Phan du cua phep chia %f / %f la %lfn" , a , b , fmod ( a , b )); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous lesson: locale.h in C
Next lesson: Library C: