limits.h in C
limits.h in C
The file header named limits.h in Library C defines the various attributes of different variable types. Macros, defined in this header, limit the value of various variable types such as char, int, and long.
These limits determine that a variable cannot contain any value that exceeds those limits, for example, an unsigned char can hold a maximum value of 255.
The macros are defined in limits.h
The following values are separate implementers and are defined with #define directives, but these values cannot be lowercase.
Macro Value Description CHAR_BIT 8 Defines the number of bits in a byte SCHAR_MIN -128 Definition of the minimum value for a signed char SCHAR_MAX 127 Maximum value definition for a signed char UCHAR_MAX 255 Defines the maximum value for an unsigned char CHAR_MIN 0 Define the smallest value for a char type and its value is equal to SCHAR_MIN if char represents negative values, otherwise 0 CHAR_MAX 127 Defines the minimum value for a char type and its value is equals SCHAR_MAX if char represents negative values, otherwise UCHAR_MAX MB_LEN_MAX 1 Defines the maximum number of bytes in a multi-byte char (character represented by multiple bytes) SHRT_MIN -32768 Defines the minimum value for a short int SHRT_MAX +32767 Maximum value definition for a USHRT_MAX 65535 short int Definition maximum value for an unsigned short int INT_MIN -32768 Define the minimum value for an INT_MAX int +32767 Define the maximum value for an int UINT_MAX 65535 Define the maximum value for an unsigned int LONG_MIN -2147483648 Definition minimum value for a long int LONG_MAX +2147483647 Defining the maximum value for a long int ULONG_MAX 4294967295 Defining the maximum value for an unsigned long intFor example
The following C program illustrates the usage of some constants defined in limits.h.
#include #include int main () { printf ( "So bit de bieu dien mot byte la %dn" , CHAR_BIT ); printf ( "Gia tri nho nhat cua SIGNED CHAR = %dn" , SCHAR_MIN ); printf ( "Gia tri lon nhat cua SIGNED CHAR = %dn" , SCHAR_MAX ); printf ( "Gia tri lon nhat cua UNSIGNED CHAR = %dn" , UCHAR_MAX ); printf ( "Gia tri nho nhat cua SHORT INT = %dn" , SHRT_MIN ); printf ( "Gia tri lon nhat cua SHORT INT = %dn" , SHRT_MAX ); printf ( "Gia tri nho nhat cua INT = %dn" , INT_MIN ); printf ( "Gia tri lon nhat cua INT = %dn" , INT_MAX ); printf ( "Gia tri nho nhat cua CHAR = %dn" , CHAR_MIN ); printf ( "Gia tri lon nhat cua CHAR = %dn" , CHAR_MAX ); printf ( "Gia tri nho nhat cua LONG = %ldn" , LONG_MIN ); printf ( "Gia tri lon nhat cua LONG = %ldn" , LONG_MAX ); return ( 0 ); } Compiling and running the above C program will result:
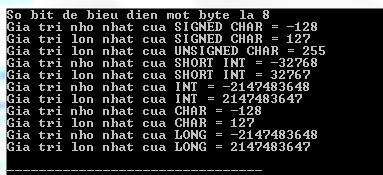
According to Tutorialspoint
Last lesson: float.h in C
Next article: locale.h in C
Share by
Kareem Winters
Update 25 May 2019