Configuring Hyper-V security with Authorization Manager
Network Administration - If you want to deploy Hyper-V and virtual machines, one of the key requirements is to ensure your environment is safe. This article will show you how to configure Hyper-V security using Authorization Manager. The article also introduces Hyper-V security best practices and provides some examples of how to enforce Hyper-V security with Authorization Manager.
Terms
Parent Partition: Windows Server 2008 running the Hyper-V role is called Parent Partition. Parent Partition is responsible for creating Child Partition and controlling communication between virtual machines.
Child Partition : A virtual machine running on Hyper-V Server is called Child Partition. Parent Partition creates Child Partition.
Authorization Manager : Authorization Manager ensures resource security. Hyper-V uses Authorization Manager to secure virtual machines.
The first task that IT administrators need to perform is to provide security for the server infrastructure before being executed in a production environment. Hyper-V is one of them. Many IT administrators don't know how to implement a secure Hyper-V environment. This is not the fault of the administrators but because Hyper-V is still very new in the virtualization world. In other words, Hyper-V, compared to VMware, is much younger. This new technology contains many differences compared to its competitors. For example, VMware uses Monolithic VMM architecture, while Hyper-V uses Microkernelized VMM architecture. The difference may also be in the security architecture.
Hyper-V has no built-in tools to use for protecting virtual machines; instead, it uses a Windows component called Authorization Manager to secure virtual machines and Hyper-V. Authorization Manager is a component included in Windows Server 2008 and is enabled by default. The security issue here is related to all aspects. For example, security of operating systems involves securing operating system files (such as DLL and OCX files). Similarly, with Hyper-V, you should also know what security is required when you want to secure Hyper-V and your virtual machines (such as if you want to secure virtual machines or the entire Hyper-V environment). ?).
However, security of virtual machines is not much related to administration. You only need to know how to use Authorization Manager and perform some security tasks. To secure the entire Hyper-V environment, you must know everything about Hyper-V, need to know where Hyper-V copies all its files, all ports are open for running services. on Hyper-V and the Hyper-V default configuration.
We will introduce you to the following topics in this series:
- Default Hyper-V configuration and file and folder protection
- Virtual machine and NTFS privileges
- Overview and security of Hyper-V services
- Hyper-V firewall rules and configuration
- Secure Hyper-V and virtual machines with Authorization Manager
- Example of Hyper-V security with Authorization Manager
- Some of the best security practices
The default configuration of Hyper-V and file and directory security
Administrators need to know the default configuration of Hyper-V. First, we will cover the security of the directories that contain virtual machines VHD and configuration files (XML).
When you activate the Hyper-V role on Windows Server 2008 for the first time, the program will create several folders and copy many files in it. Here we need to know the default location for saving virtual machines and configuration files before we start implementing security for Hyper-V.
% SystemRoot% ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsHyper-VVirtual Machines
% SystemRoot% ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsHyper-VVirtual Hard Disks
% SystemRoot% ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsHyper-VSnapshots
By default, Hyper-V uses the above directories to store virtual machine configuration files as well as VHDs and snapshots related to virtual machines. You must change the default location before moving Hyper-V to the production environment. It is best to change the default location for saving VHD, XML and Snapshot files to the SAN drive.
When you install Hyper-V Role, a special security group called "Virtual Machines" will be created. This security group includes the GUIDs of all virtual machines registered with Hyper-V Server, and it has access to the directory.
% SystemRoot% ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsHyper-VVirtual Machines
This is the directory that stores the configuration files (XML Files) of the virtual machines. If the Security Group is deleted or not in the Security tab of the virtual machine directory, you cannot access virtual machines running on Hyper-V. The VMMS.EXE process is responsible for managing access for all virtual machines, using the "Virtual Machines" security group to increase access to virtual machines on Hyper-V Server.
Default, security privileges on the directory
Hyper-VVirtual Machines
as shown below:
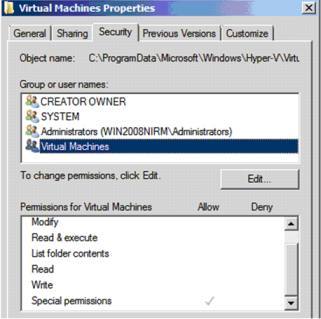
Default security privileges on the Virtual Machines folder
At the very least, keep the security groups mentioned below in the property of the directory
Hyper-VVirtual Machines:
SYSTEM Account-Full Control
Administrators-Full Control
Virtual Machines -Special Permissions
By default, Hyper-V does not allow anyone to access virtual machines except the SYSTEM Account and Local Administrators Account. This is completely clear in the picture above. The Local Administrators Security Group is added to Authorization Manager's policy repository and it is given full control over Hyper-V, including virtual machines running on it.
The same security settings, shown in the image above, are used for the Hyper-Vsnapshots folder.
Tip : If you want to prevent users or administrators from creating virtual machines on the Hyper-V Server, remove the special security group "Virtual Machines" from the directory:
Hyper-VVirtual Machines
The next directory that needs security on Hyper-V is
Hyper-VVirtual Hard Disks
Securing this directory is more important than the directory containing XML files because Hyper-V supports virtual machines in VHD format. These VHD formats can be used with previous versions of virtualization software. Users who do not authenticate access to VHD files can copy the VHD file and use it with Virtual Server or Virtual PC. The default settings on the folder
Hyper-VVirtual Hard Disks
shown as below:
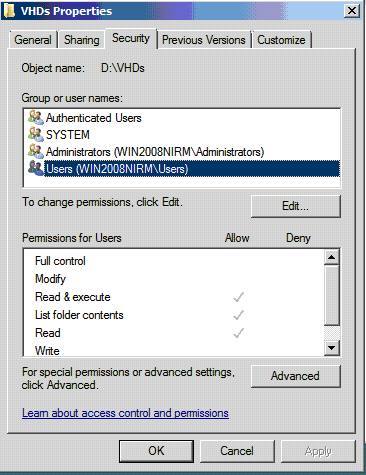
Default security privileges on the Virtual Hard Disks folder
To further tighten the security issue for a folder containing VHD, you can remove the Users security group that was added when the initial Hyper-V Role was activated. At a minimum, you should keep the security groups below in the Security tab:
SYSTEM - Full Control
Administrators - Full Control
Authentic Users - Read & Execute
How to secure virtual machine access with DACL
Authorization Manager, which will be covered later, is a key tool for securing virtual machine access. However, you can also configure DACL on virtual machine directory to secure virtual machines running on Hyper-V. This type of security is done using NTFS privileges.
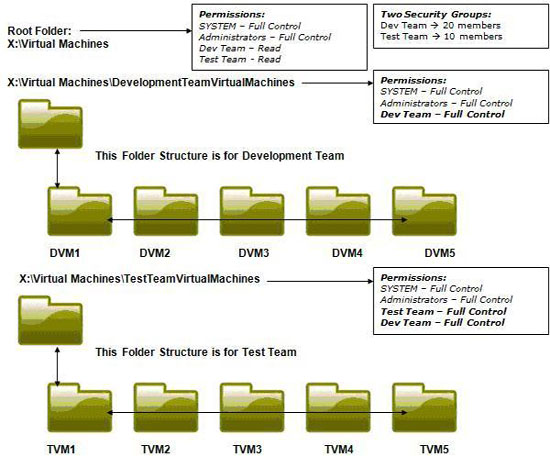
Secure access to virtual machines with DACL
As you can see in the image above, the organization shows two groups: the development team and the Test team. Two security groups have been created for each team - Dev Team and Test Team. The Development team is responsible for writing code, then handing them over to the Test team for testing. The development team must access all 10 virtual machines (for example). At the same time, make sure the Test team does not have access to their virtual machines, except TVM1 to TVM5. To do so, assign NTFS privileges on virtual machine folders.
In this example, there are three virtual machine directories:
- X: Virtual Machines
- X: Virtual MachinesDevelopmentTeamVirtualMachines
- X: Virtual MachinesTestTeamVirtualMachines
The development team is given full control privileges on folders 2 and 3, and the Test group is assigned full privileges only on directory 3. Sometimes the Test team does not even have read privileges on directory 3.
Overview of Hyper-V services and security services
Hyper-V is a client / server application. Hyper-V has three default services below:
service nameFunction
Security content
Configuration should be set
Virtual Machine Management Service
Manages overall Hyper-V environment
SYSTEM Account
Default
Hyper-V Image Management Service
Management of Virtual Hard Disks
Network Service
Default
Hyper-V Network Management Service
Management of Hyper-V Virtual Networking
SYSTEM Account
Default
The above services are configured to start automatically under the security contents of SYSTEM Account. The account under which these services run has the highest privileges on the system. You should not change the account below the content they run. If changed, hackers or malicious code can attack virtual machines or Parent Partition of Hyper-V. SYSTEM account password also needs to be kept secret. Running these services in a domain user account is not safe at all because hackers can now find passwords using software.
Conclude
In this article, I have explained how Hyper-V stores VHD files and XML files on the system drive. One point to emphasize in this article is that you should change the default location to save VHD and XML to SAN Drive, then perform security by assigning NTFS permissions. We also provided an example of how to secure virtual machine access using NTFS privileges.