Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - Part 4
 Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - 1
Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - 1
 Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - 2
Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - 2
 Deploy IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - 3
Deploy IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - 3
In this article we will show you how to test clients and how security certificates are assigned, removed automatically as well as how clients are connected or disconnected from the network. how. In Part 3 of the 4-part series on configuring NAP by IPsec policy enforcement, we configured the NAP IPsec policy and then configured the clients for testing. In this final section, we will test the clients and study how the security certificates are assigned or removed automatically as well as how the client is connected and disconnected from the network. how.
We will focus on the following two main tasks:
- Test Health Certificate and configuration Auto-remediation
- Verify NAP policy enforcement on VISTASP1
Test Health Certificate and Auto-remediation Configuration
In this section we will perform the following tasks:
- Confirm that both VISTASP1 and VISTASP1-2 have health certificates (Health Certificate)
- Enter VISTASP1-2 into the Domain
- Evaluate Auto-remediation on VISTASP1
Confirming both VISTASP1 and VISTASP1-2 has a Health Certificate
Use the following procedure to verify the enrollment of health certificates of VISTASP1 in an authenticated domain environment and VISTASP1-2 in the workgroup (workgroup) environment.
Follow the steps below on both VISTASP1 and VISTASP1-2:
- Open the Run dialog box and enter mmc , then press ENTER.
- On the File menu, click Add / Remove Snap-in .
- Click Certificates , click Add and select Computer account , and then click Next .
- Verify that Local computer: (the computer this console is running on) is selected, click Finish , and then click OK .
- In the left pane of the console, double-click Certificates (Local Computer) , double-click Personal , and then click Certificates.
- In the details pane, under Issued By , verify the subordinate CA, msfirewall-WIN2008SRV1-CA , is displayed. Verify that Intended Purposes displays System Health Authentication . Because VISTASP1-2 has not been authenticated against the msfirewall.org domain, the client name will not be displayed under Issued To , and the certificate meaning of Client Authentication does not appear. Verify that the certificate on VISTASP1-2 has Intended Purposes of System Health Authentication . This is a valid NAP health certificate for clients in a workgroup environment. An authenticated domain health certificate is similar to a certificate that achieves the name VISTASP1 .
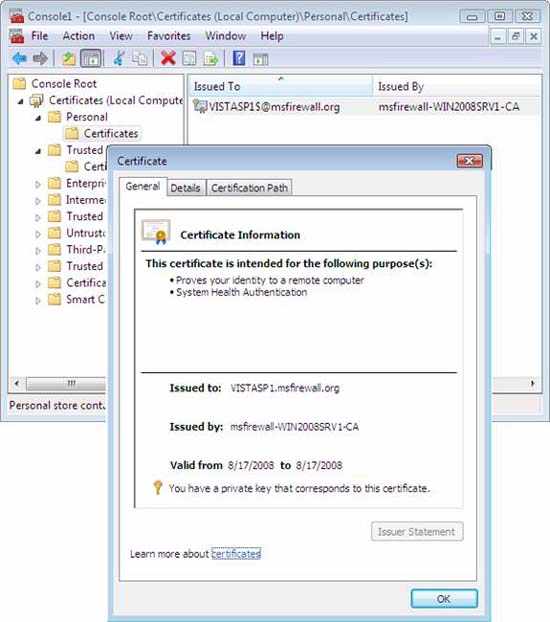
Figure 1
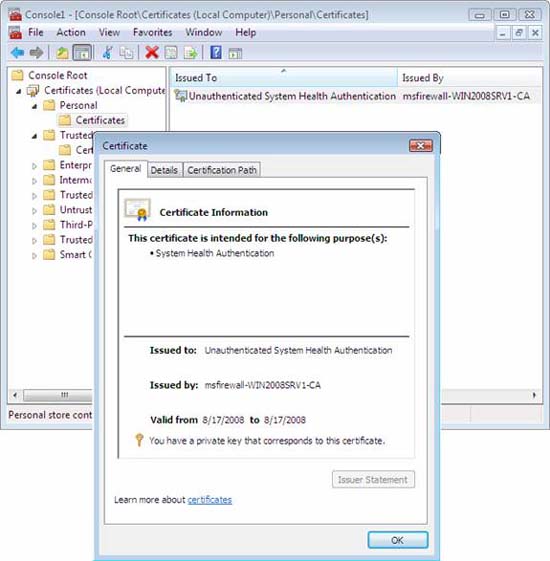
Figure 2
- Close Certificates interface
Enter VISTASP1-2 into the domain
Using the same procedure you used above to enter VISTASP1 and the msfirewall.org domain, enter VISTASP1-2 into the msfirewall.org domain. Login with domain administrator privileges after the computer restarts.
Evaluate Auto-remediation on VISTASP1
NAP IPsec with HRA Noncompliant network policy specifies that noncompliant computers will be automatically negotiated. The following procedure will verify that VISTASP1 is automatically negotiated when Windows Firewall is turned off.
- On VISTASP1 , open the Run dialog box and enter firewall.cpl , then press ENTER.
- In the Windows Firewall control panel, click hange settings , click Off (not recommended) , and then click OK .
- You may see a message in the notification area indicating that the computer does not have enough health requirements. This message is displayed because Windows Firewall is turned off. Click on this message to see more details about the health status of VISTASP1 . See the example below.
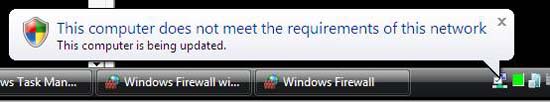
Figure 3
- The NAP client will automatically turn on Windows Firewall to become compliant with the network health requirements. The following message will appear in the notification area: This computer meets the requirements of this network .
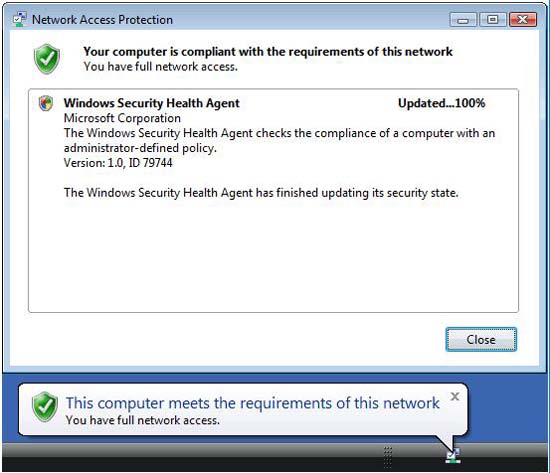
Figure 4
- Because auto-remediation occurs quite quickly, you may not see these messages. To review the NAP notification icon, type napstat at the command prompt, and then press ENTER.
Verify NAP policy enforcement on VISTASP1
Let's see how to verify the NAP policy enforcement is being used on the client system. Start by testing with VISTASP1 . To perform the test, we perform the following procedures:
- Configure Windows SHV to be more restrictive by requiring computers to install antivirus software. When we have not installed any antivirus software on the clients, the clients will not have this requirement.
- Refresh SoH (health statement) on VISTAP1 . This will cause the client to send a new Statement of Health to the Health Registration Authority and will report that the client does not have consent.
- Confirm that the client's health certificate is removed. The Health Certificate is removed because the client does not have sufficient consent.
- Restore health policy to a less restrictive state so that the client can agree. We will remove the required anti-virus software so that the client becomes consensus again.
- Refreshing SoH on VISTASP1 will display the computer that is currently in agreement with the new policy.
- Confirm that the client health certificate is restored.
Configure WSHV to request an antivirus application
First, configure the NAP policy to request an antivirus application, causing CLIENT1 to become non-compliant.
Follow the steps below on WIN2008SRV1:
- On WIN2008SRV1 , click Start , click Run , type nps.msc and press ENTER.
- In the left pane of the console, open Network Access Protection , and then click System Health Validators .
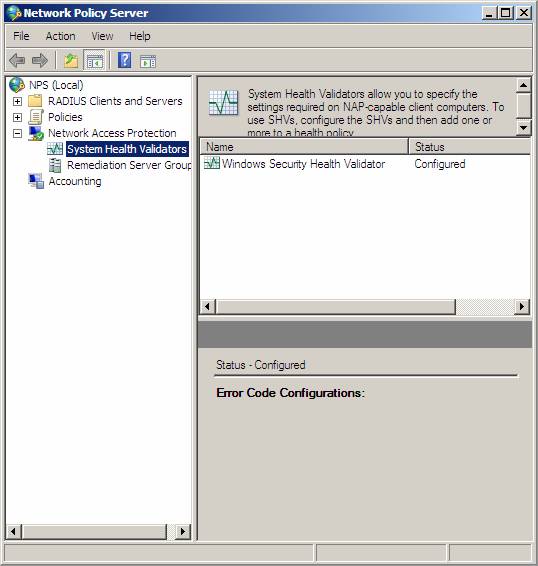
Figure 5
- In the details pane, double-click Windows Security Health Validator , and then click Configure .
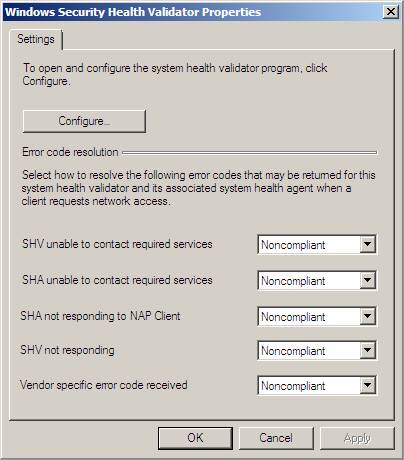
Figure 6
- In the Windows Security Health Validator dialog box, under Virus Protection , select the check box next to An antivirus application is on .
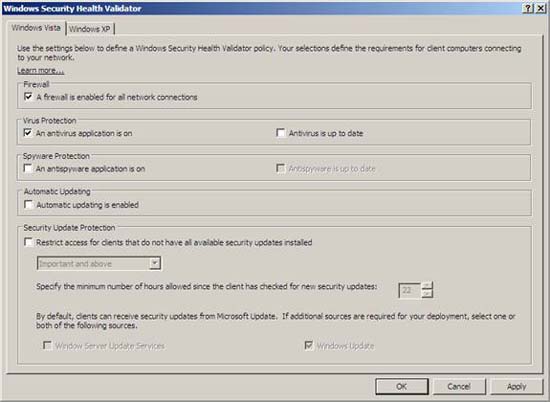
Figure 7
- Click OK and then click OK again to close the Windows Security Health Validator Properties window .
- To open the NPS interface for the following procedures.
Refresh SoH on VISTASP1
Since health policies have been changed after VISTASP1 received a health certificate, we need to enable the sending of a new health statement (SoH) from VISTASP1 to evaluate with the term health policies. more prepared. This issue will appear when the health certificate on VISTASP1 expires, or when a change in the health status of the client is deleted. We can make a change in health status by turning off Windows Firewall.
Follow the steps below on VISTASP1:
- On VISTASP1 , click Start , and then click Control Panel .
- Click Security , click Windows Firewall , and then click Change settings .
- In the Windows Firewall Settings dialog box, click Off (not recommended) , and then click OK.
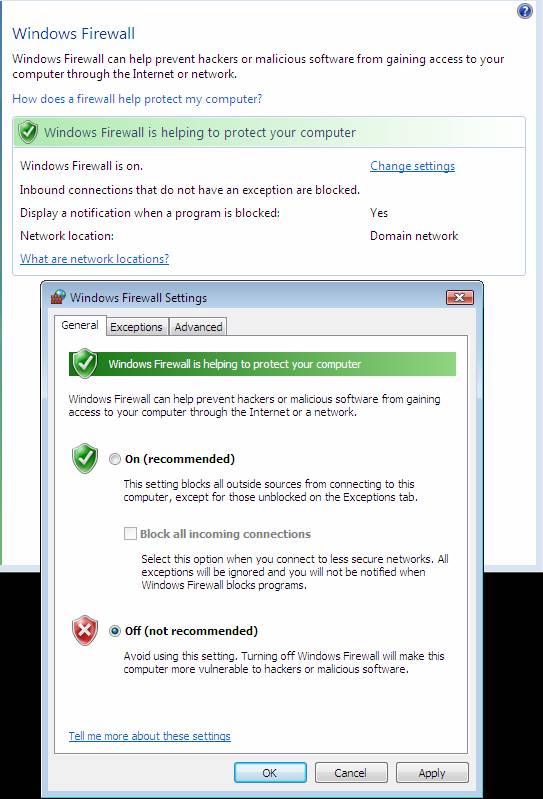
Figure 8
- Windows Firewall is turned back on automatically because auto-remediation is enabled. However, because NAP policies currently require an antivirus application, VISTASP1 will appear in a non- compliant state and will not be able to obtain a health certificate.
Confirm the health certificate has been removed
Next, see the computer certificates on CLIENT1 to verify that the health certificate has been removed.
- On VISTASP1 , open the Run dialog box and type mmc , then press ENTER.
- On the File menu, click Add / Remote Snap-in
- Click Certificates , click Add , select Computer account , and then click Next
- Verify that Local computer: (the computer this console is running on) is selected, click Finish , and then click OK .
- In the console tree, open Certificates (Local Computer) Personal .
- Verify that no health certificate is present.
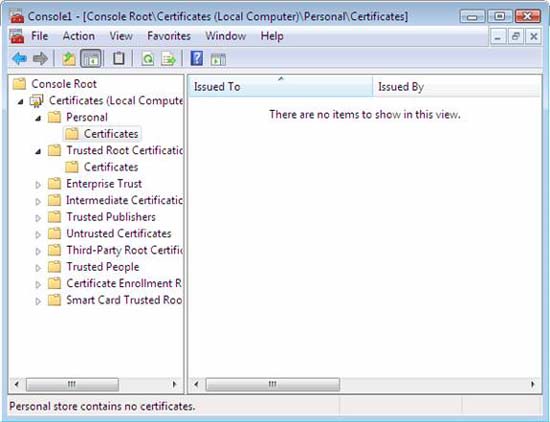
Figure 9
- Leave the Certificates interface open to perform the following procedures.
Remove the antivirus health requirement so that VISTASP1 becomes consensus
Change NAP policies so that VISTASP1 becomes consensus.
- On WIN2008SRV1 , in the left pane of the NAP interface, open Network Access Protection , and then click System Health Validators .
- Double-click Windows Security Health Validator and click Configure.
- In the Windows Security Health Validator dialog box, under Virus Protection , clear the check box next to An antivirus application is on .
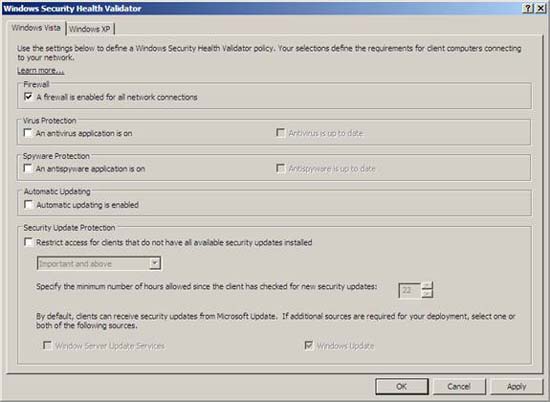
Figure 10
- Click OK and then click OK again to close the Windows Security Health Validator Properties window.
- Close the NPS interface.
Refresh SoH on VISTASP1
Perform the previous procedure to refresh SoH on VISTASP1 by turning off Windows Firewall. A new SoH will be activated and Windows Firewall will be enabled. Because VISTASP1 now agrees with NAP policies, it will have a health certificate available.
See the computer certificates on VISTASP1 to verify that the health certificate has been restored.
- On VISTASP1 , in the console, the interface tree, click Personal .
- Right-click on the details panel and then click Refresh . Verify that the health certificate is present.
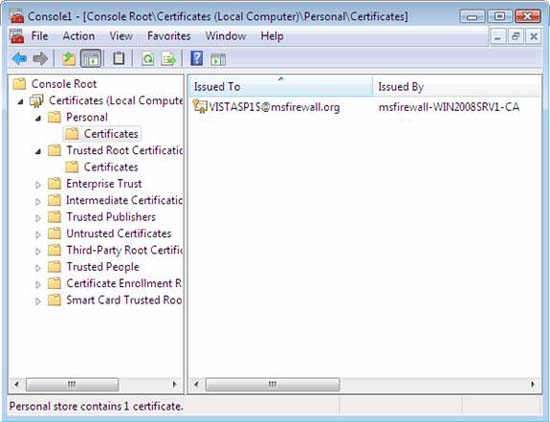
Figure 11
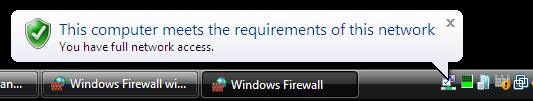
Figure 12
Conclude
In this series we have provided you with many parts related to NAP IPsec enforcement solutions. As you can see in this article, there are many components in the solution and each of those components must be properly configured to work. Many Windows administrators are concerned about the complexity of NAP with IPsec policy enforcement and therefore have not adopted this powerful and effective security technology. Before performing the test, create a copy of your proof in the testing room before performing this implementation of the production network name.
You should read it
- ★ Deploying IPsec Server and Domain Isolation with Windows Server 2008 Group Policy - Part 1
- ★ Overview of Windows Server 2008 Firewall with advanced security features (continued part 3)
- ★ Overview of Windows Server 2008 Firewall with advanced security features - Part 3
- ★ Remote workstation security in Windows Server 2008 R2
- ★ Top 5 security settings in Group Policy of Windows Server 2008