Check your machine configuration with CPU-Z in the most detailed way
The following article is a guide for 1.86.0 version, 64bit version. In this version, the tapes are arranged in order of CPU, Caches, Mainboard, Memory, SPD, Graphics, Bench and About. When selecting any tab, there will be information in that tab.
 Specific tapes in CPU-Z
Specific tapes in CPU-Z Download CPU - Z here:
https://download.com.vn/cpu-z-32-bit/download
CPU tab
Tap CPU has information on name, multiplier, socket number, thread number, power consumption, technology, clock speed, .

Inside:
Name: CPU name, in my computer screenshot is Intel Core i3 4005U.
Code Name: The code name of the CPU microarchitecture.
Max TDP: Maximum CPU power consumption.
Package: CPU socket type, with different socket types will have different pins. This parameter is very important when you want to upgrade the CPU, you can not bring a CPU socket 478 socket attached to socket 1155 and vice versa. TipsMake.com has an article on the CPU socket list quite detailed, you can refer to more.
Technology: Technology of transistors. As in my example of 22nm, this number is as small as possible, because it helps the chip can contain more transistors, run faster, more efficiently. This technology is increasingly being improved, in the latest CPU has been able to reach 14nm (Intel's Coffee Lake line). On phones Apple has begun producing 7nm A12 processors for its devices.
Core Voltage: Voltage for the core of the chip, this parameter is usually not fixed because modern chips often adjust the consumption voltage to save power.
Specification: The full CPU name of the computer.
Family: The main architecture of the chip. For example, on an Intel CPU with Family 6, the P6 generation (Pentium Pro, Pentium II, Pentium III and Pentium M - all with the same execution unit design). You can refer to Wikipedia for a list of processors for Intel chips.
Model: The type of CPU in Family that a computer is. For example, with Family 15 (NetBrust generation), model 0 is the Willamette core, model 1 is the improved Willamette core. Model 2 is Northwood built on newer technology. Model 3 is the Prescott core above with 90nm technology, model 4 is still Prescott but with additional enhancements such as No-eXecute support. This model number is basically a way to identify the CPU core type. You can look up your model in the link of the Family section above for more information about your CPU.
Stepping: This is the number that determines what kind of improvement has been made to the core, and how much is the new level. Can be interpreted as software patches, the larger the number, the more it has been fixed and improved from previous versions.
Revision: Combining Family, Model and Stepping can give you the Revision name (must be checked in the datasheet provided by Intel). By knowing Revision, you can find improvements made between the same Family and Model chips but with different Stepping. And with the Revision parameter that CPU-Z, you can easily know the Revision name without having to search the datasheet anymore. In the example of this article Revision is C0.
Instructions: This is a list of instructions that the chip processes.
Core Speed: CPU clock, this parameter with the core voltage often changes to save power.
Multiplier: The clock multiplier (also called the bus ratio) sets the ratio of the internal clock rate to the supplied external clock. For example, if this number is x10 then 10 internal cycles will be found for each external clock cycle.
Bus Speed: Bus speed.
Level 3: The cache specification, the higher the better, because the CPU will be less congested when processing data. The bigger the number, the faster the CPU runs.
Cores and Threads: The number of cores (or cores) and the number of threads in the CPU. This number is usually an even number, as shown in my photo with 2 cores and 4 threads.
Caches tab
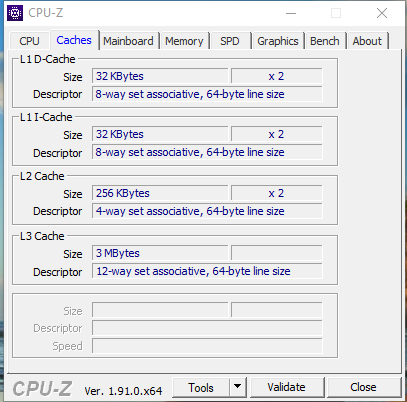
For Tap Caches will help you get more information about cache. Early CPUs had only one cache level, and that level was not divided into L1 D-Cache (for data) and L1 I-Cache (for instructions). Most modern CPUs have divided L1 Cache. All modern CPUs have multiple levels of cache and most of them have L2 Cache, and more recently L3 Cache. L2 usually does not divide and acts as a common repository for L1. Each core in the multi-core chip has a dedicated L2 cache and is usually not shared among the cores. L3 Cache is a higher-level cache, shared between the cores and undivided. There is L4 Cache, but this cache is not common on CPU, it appears on DRAM more.
Mainboard tab
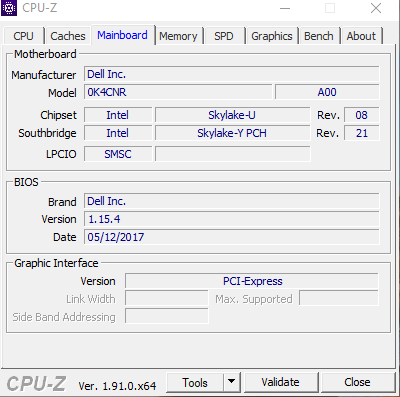
In this Tap, you will know the manufacturer of the motherboard, chipset, BIOS and graphics interface.
Specifically in this tab you will have:
- Manufacturer: Motherboard manufacturer name, e.g. Acer, Asus, Foxconn, .
- Model: Model of the motherboard, next to the version name.
- Chipset: Manufacturer, chip type and Revision.
- Southbridge: Manufacturer, southbridge and Revision type.
- BIOS: Displays information about brand, version and date of BIOS production.
- Graphic Interface: Information about the graphics card slot on the mainboard. Version is the supported version, usually only PCI-Express and AGP. Link Width is the width of the bandwidth, but not all motherboards support this slot.
Memory tab
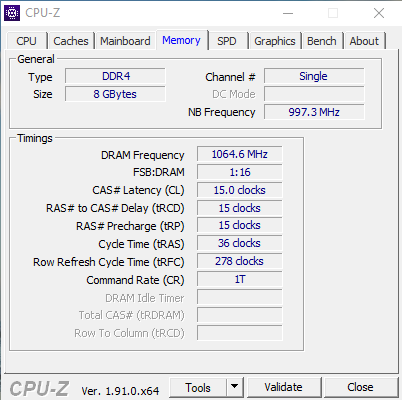
The Memory tab gives information about RAM and most of the information in this tab is for advanced users.
- Type: RAM type of the computer, here is DDR3.
- Size: RAM capacity, here is 4GB
- Chanel #: Indicates how many RAM slots you are using, Single is 1, Dual is 2. Parameters are Single also sometimes the machine has only 1 RAM slot. You can check your computer's RAM slot in the SPD tab as shown below.
- DRAM Frequency: Real bus speed of RAM
- NB Frequency: The speed of NorthBridge.
Note: When you have free RAM slots and want to upgrade RAM, you need to pay attention to the parameters of RAM type and speed of RAM to choose to buy properly.
SPD tab
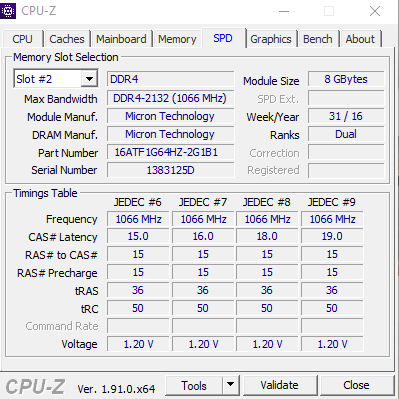
In this tab, you'll see information about each memory stick in each slot on the motherboard. It is possible to see the size of the chip, the type of RAM and the frequency it operates. In addition, there is also a scheduler that displays detailed information based on the configuration.
- Slot # 1: Click the arrow next to Slot # 1, how many slots are available for RAM slots. Usually a computer will have 2 or 4 RAM slots, which is equivalent to the maximum of Slot # 2 or 4.
- DDR3: RAM type
- Module Size: The size of the RAM plugged in the current slot, calculated in MB units, 4096MB equivalent to 4GB.
- Max Bandwidth: Maximum bandwidth speed. Thanks to this parameter you can calculate the RAM RAM, by taking the clock rate in parentheses multiplied by 2. In my picture is 800Mhz x 2 = 1600Mhz.
- Manufacturer: Name of RAM manufacturer.
- The other sections of this tab, you can find more on Google offline, for normal users I think stop here is okay.
Graphics tab

The graphics tab provides information about the GPU, such as the name, manufacturer, and GPU technology. If you want to take a closer look at the graphics card, you can use a dedicated tool, GPU-Z.
- Display Device Selection: This part is blurred because I only have one video card. If the computer has multiple video cards, this section will light up and you can select the card to view.
- Name: The name of the graphics chip manufacturer.
- Code name: The code name of the graphics chip is running on the machine.
- Core: GPU clock speed.
- Size: Size of the graphics card.
- Technology: Technology of graphics card, like CPU chip technology, the smaller the number the better.
- Type: Processing type, eg: 64bit, 128bit, 256bit The higher this parameter, the higher is your card and the better the graphics processing.
Bench tab
For Tab Ben, you will know the benchmark score of the CPU running on the computer by running a small test. After running, you can compare your CPU with other CPUs, by selecting in the blue Reference box. Checking the box next to the black Reference will convert the result to% for easy comparison.
Tab About

This tab will give you detailed information about the software and some details about the system. For example, you can see the version of Windows, the service pack installed, and the version of DirectX. From this tab, you can dump data into an HTML file.