8 ways to speed up network through Regedit in Windows 10
Here are some ways to speed up your network without having to pay for these applications.
Warning:
All the modifications below are related to the registry editing. Therefore, you must exercise caution and back up your registry before making any of the modifications mentioned below. Accidental deletion and modification can damage the functionality of a computer. It's best to back up the registry before you continue.
8 registry values to help speed up the network
- 1. IRPStackSize
- 2. SizReqBuf
- 3. DefaultTTL
- 4. Tcp1323Opts
- 5. MaxFreeTcbs
- 6. MaxUserPort
- 7. GlobalMaxTcpWindowSize
- 8. MTU
1. IRPStackSize
IRPStackSize (I / O Request Packet Stack Size) denotes the number of 36-byte receive buffer that the computer can use simultaneously. It allows the computer to receive more data at the same time. If you have a fast Internet connection (more than 10Mb / s), you will benefit from this. On a slow Internet connection, you may not notice even the slightest difference, so ignore this.
The system typically allocates 15 IRPs in its network stack. Usually you will benefit more with 32 IRPs, although you can configure up to 50 IRPs. Let's try the 32 IRP level first.
Here is the location of the key in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesLanmanServerParameters
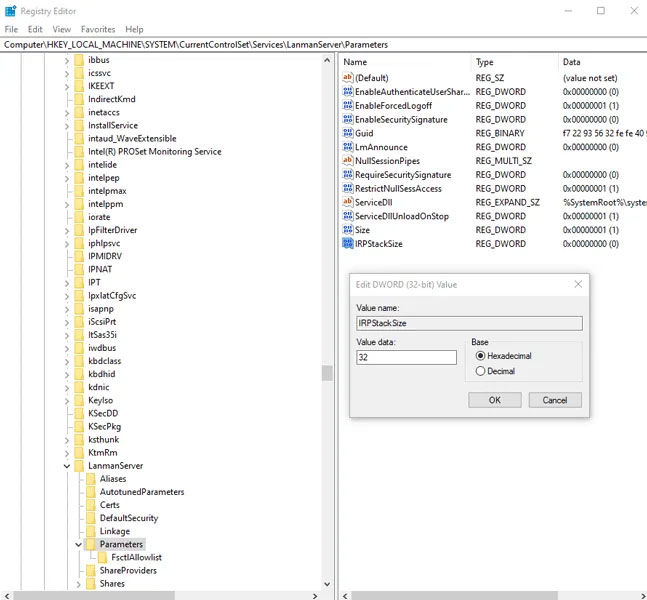
Add 'IRPStackSize' as the DWORD value on the right side of the regedit window and modify the value to 32.
2. SizReqBuf
SizReqBuf represents the size of the raw receive buffer in the host environment. This means that it affects your ability to host certain content in a high latency environment. Let's say you host a game server and a lot of people complain about latency. Modifying this value will help reduce the impact of latency. You will also benefit if you are hosting a website or any other service, including file sending via instant messenger or Neo Modus Direct Connect.
The system typically sets this buffer at 16384 bytes. For most servers this is effective enough, but sometimes you have a small amount of memory and cannot keep up with high volumes of requests.
Here is the location of the key in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesLanmanServerParameters
Add 'SizReqBuf' as the DWORD value on the right side of the regedit window. If you own a server with more than 512MB physical memory, modify the value to 17424. If you have less than 512MB of memory you should consider buying a new computer, but you can modify this value to 4356 in the meantime.
3. DefaultTTL
Time to Live (TTL) tells routers how long a packet will last for delivery, before giving up and discarding the packet. When this value is set to a high level, the computer spends more time waiting for a packet to not be delivered, effectively reducing productivity in the network.
If no value is set, Windows will wait 128 seconds before finishing. This makes your computer lag terribly, if you are working on something and your connection to the server suddenly crashes.
Here is the location of the key in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters
Add 'DefaultTTL' as the DWORD value in the 'Parameters' key. Set the value to any number between 1 and 255. The best value is 64, although you can set lower values if you want the package to be canceled faster.
4. Tcp1323Opts
Tcp1323Opts allows you to use RFC 1323, called 'TCP Extensions for High Performance' in 3 ways. This allows the TCP connection to negotiate a receive window size with the server, allowing the computer to specify the receive window up to 1GB.
Navigate to the following location in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters
Tcp1323Opts
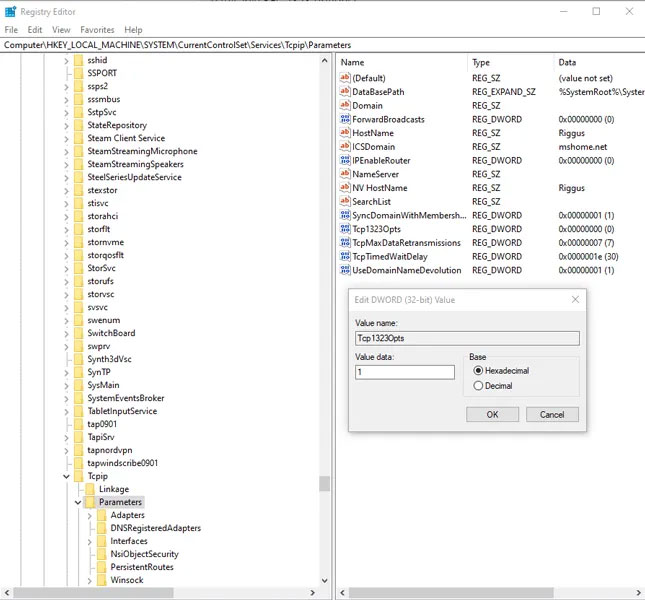
You should see TCP1323Opts as 'DWORD' value on the right side of Registry Editor. (Create it if you haven't already). Right click on it and modify this value to '1'.
5. MaxFreeTcbs
MaxFreeTcbs is a iffy value. It determines the number of active TCP connections the computer can handle at any given moment based on the amount of physical memory you have and the computer performance relative to bandwidth.
If the number is too high, the computer may not be able to properly process TCP transactions due to the high number of active connections communicating with the computer at the same time. However, if the number is too low, you cannot host or require as many connections as you want. Although the setting is determined arbitrarily, you may want to increase the number when upgrading your hardware or Internet connection.
To get to the location of this value, access the following path in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters
Create or edit 'MaxFreeTcbs' and set its value to 65536. If you are using an old computer with low performance hardware you can set this value to a lower number, such as 16000.
6. MaxUserPort
When an application requires an available port to open from Windows, the operating system chooses a port from 1024 to the specified maximum level called 'MaxUserPort'. A port on your computer allows you to establish a TCP / UDP connection over the Internet and in your local area network.
What happens when you open more options for programs looking for a port? The answer is they found a port much faster.
Windows sets this value to 5000 by default, but you can set it for any number between 5000 and 65534.
The location that 'MaxUserPort' must go to is in the following registry path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters
Create a value called 'MaxUserPort' and set it to 65534. That's it!
7. GlobalMaxTcpWindowSize
This value has a long name, but you won't regret modifying it if you have a fast Internet connection (10 Mb / s or more) and often have to upload content. This value represents the amount of data that can be sent from your computer without receiving confirmation packets (ACKs).
Every time you send a small amount of data on the Internet, your computer has to wait for this packet, which will notify the beginning of the network that 'Everything is fine! Send more! "Sometimes, due to latency, this might not be ideal. So you can edit this to allow more data to be sent without waiting for the packet to arrive.
Create a DWORD named 'GlobalMaxTcpWindowSize' in the following registry path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParameters
Set the value to 65535 and you're done! This will make it possible for the computer to send 64 kilobytes without waiting for confirmation. If you feel the speed decrease after modifying, delete the value or try to increase it slightly to 128 kilobytes (by setting the value to 131072).
8. MTU
The MTU affects the upstream speed more than the downstream speed, but equally important is the upstream speed, ensuring that larger chunks of data are sent at the same time. Although this number is usually set automatically by the network card, you can adjust it based on the speed of your Internet connection.
Setting this value is difficult. You must first find out your optimal MTU value, which does not require packet fragmentation because of Internet connection speed limitations.
You can do this by going to the Command Prompt and typing the following:
ping -f -l
Replace '' with a number between 88 and 4294967295. Replace '' with the port that the network adapter uses to connect to the Internet. If you don't know your port, enter ipconfig in the command line to find its value under 'Default Gateway', displayed under the network adapter you use for the Internet.
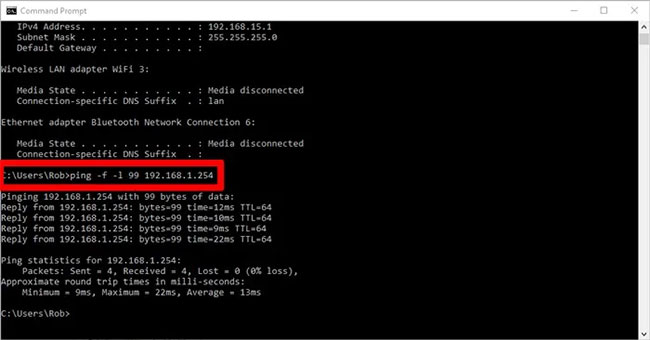
When you ping, you will know you have reached a too high number when the response has the following message: Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set (The package needs to be fragmented but DF has been set).
As long as you choose one that doesn't require package fragmentation, everything should be fine. Choose the highest number possible without package fragmentation, and you'll have the most optimal MTU.
Now, to set this number, go to the following path in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpipParametersInterfacesInterface ID
See the image above for an example of how to find your primary network interface. There may be other network interfaces installed on the computer, especially when you use it as a router.
Replace 'Interface ID' with the GUID for your network interface. Just browse through the different GUIDs displayed in 'Interfaces' and look at the information on the right side of the regedit window to see if it matches the details of the network interface you use to connect to the web.
When you get to that interface, add 'MTU' as the DWORD and set it to the number you got when you ping the gateway.